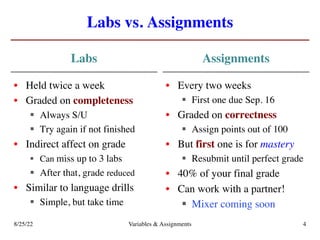
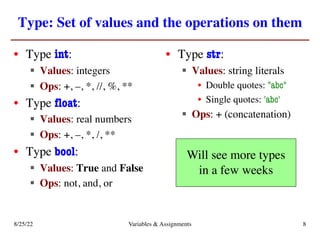
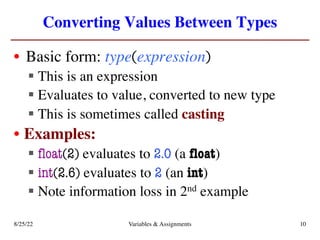
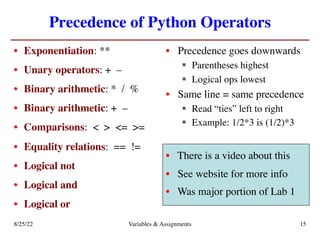
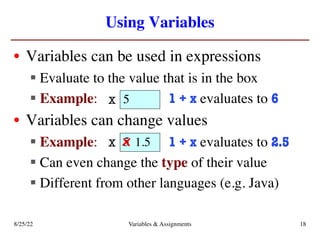
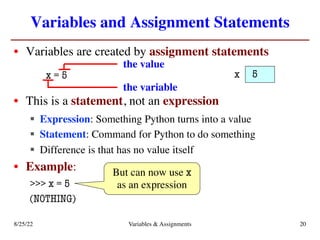
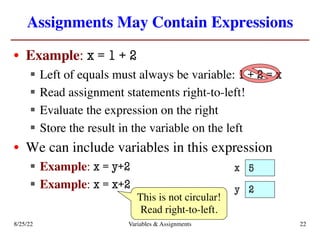
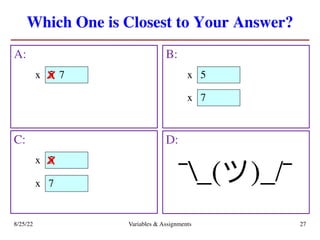
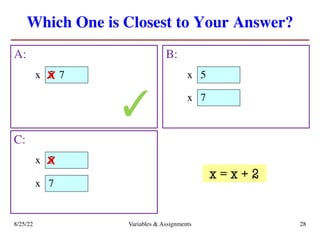
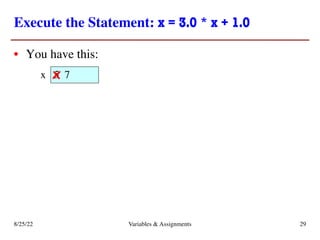
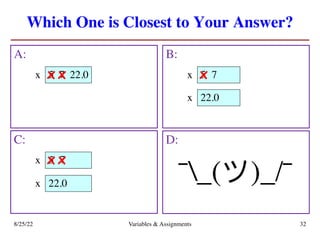
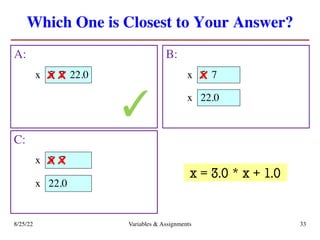
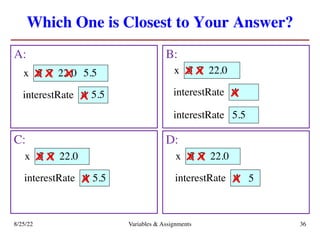
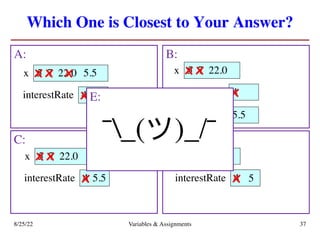
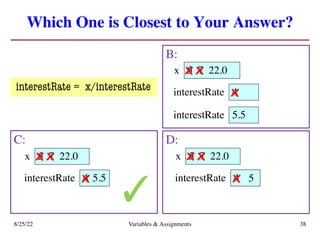
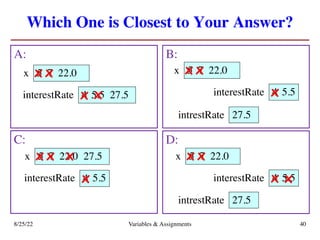
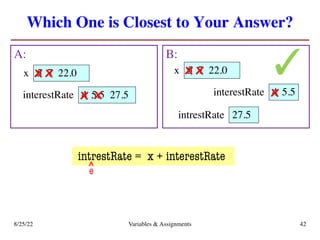
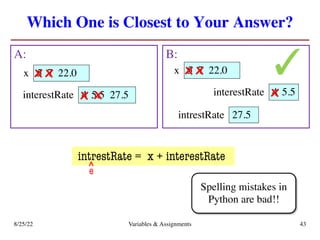
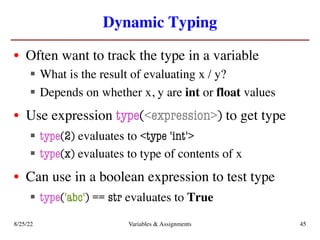
The lecture covers essential topics including the installation of Python and Kivy, registration of clickers, and completion of lab assignments and surveys. It emphasizes the importance of academic integrity, provides resources for assistance, and explains the differences between labs and assignments in terms of grading and completion expectations. Additionally, it introduces Python concepts such as variable assignment, type conversion, and operator precedence.