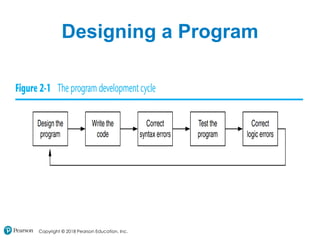
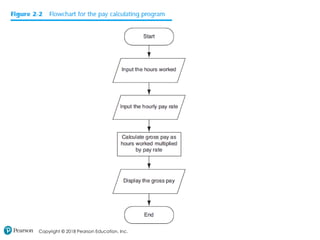
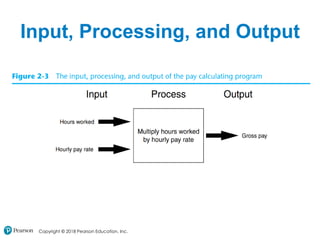
This chapter discusses program design and the input/output process. It covers designing programs through pseudocode, flowcharts and algorithms. The chapter then explains how programs take in input, perform processing, and output results. It discusses printing output, using variables, reading keyboard input, performing calculations, and formatting output display. The chapter emphasizes designing programs before writing code.