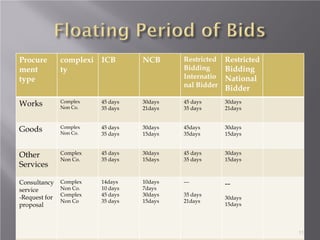
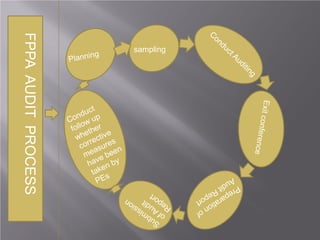
The document discusses the significance of public procurement, which constitutes a significant portion of the annual government budget and plays a critical role in economic development. It outlines the legal framework for procurement, including regulations and approved methods, as well as emphasizes the importance of local businesses and good governance. Additionally, it addresses challenges in procurement processes and suggests improvements like introducing e-procurement and enhancing transparency and efficiency.