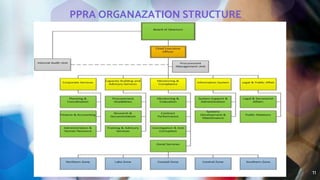
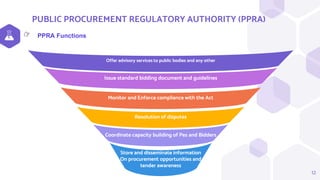
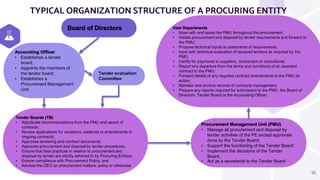
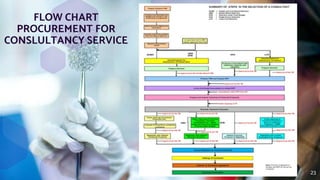
The document outlines the national legal framework for public procurement in Tanzania, detailing the roles and responsibilities of the Public Procurement Regulatory Authority (PPRA) and the regulations governing consultancy services. It emphasizes the importance of efficiency, transparency, and accountability in procurement processes, which are crucial for successful economic development. The framework includes various components such as constitutional laws, procurement regulations, and standard bidding documents to guide the acquisition of services and ensure value for money.