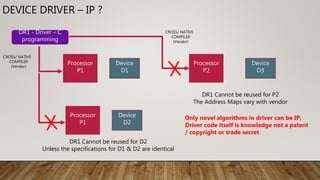
This document discusses intellectual property options for embedded software components. It outlines different types of intellectual property like patents, copyrights, and trade secrets. It provides examples of what parts of embedded software projects might be protected under each type of IP, such as novel algorithms under patents or source code under copyright. It also discusses popular myths around intellectual property and methods that can be used to protect source code.