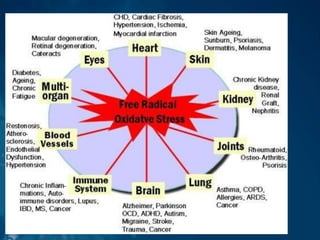
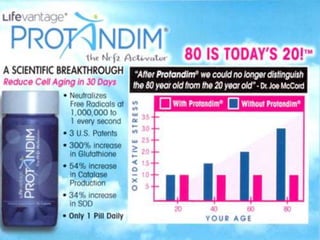
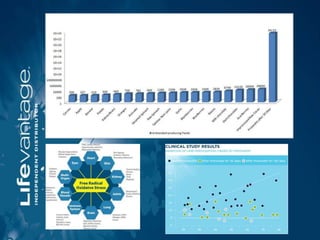
Chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, diabetes, and lung disease are linked by their common root of oxidative stress and free radical damage. Oxidative stress occurs when the body produces too many free radicals and fails to neutralize them, resulting in cellular damage that can contribute to disease development over time if left unchecked. Factors that can increase oxidative stress include environmental toxins, radiation, smoking, chronic inflammation, processed foods, stress, and pesticides/herbicides.