Java has had a tremendous success and, in the last few years, has evolved quite significantly. However, it was still difficult to interface with libraries written in other programming language because of some complexity with JNI and some syntactic and semantic barriers. New projects to improve Java could help alleviate, even nullify, these barriers. Projects Panama, Valhalla, and Babylon exist to make it easier to use different programming and memory models in Java and to interface with foreign programming languages. This presentation describes the problem with the Java “isthmus” and the three projects in details, with real code examples. It shows how, combined, these three projects could make of Java the new Python.
















![18/172
2. Naming
Java
No nesting
Impact on visibility
C++
Nesting
No impact on visibility
package a.b;
public class X {
}
package b;
public class X {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(a.b.X.class);
System.out.println(b.X.class);
}
namespace a {
namespace b {
int x = 0;
}
}
namespace b {
string x;
}
using namespace a;
void foo() {
b::x = 42;
}
error: reference to 'b' is ambiguous](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-18-320.jpg)
![19/172
2. Naming
Java
Modules
C++
No equivalent
– Maybe linker libs?
module isthmus.java {
requires java.logging;
}
package net.ptidej.isthmus;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class Main {
private static Logger java. Logging =
Logger.getLogger("net.ptidej.isthmus");
public static void main(final String[] args) {
Main.logger.fine("Hello, World!");
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-19-320.jpg)
![20/172
3. Data types
Java
Booleans are their own
Strings are immutable
C/C++
Booleans are shorts
Strings are mutable
bool a[5];
bool result;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << a[i] << " ";
result += a[i];
}
cout << endl << result << endl;
boolean a[] = new boolean[5];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
string string1 = "Hello";
string string2 = ", World!";
string string3 = string1 + string2;
cout << string3 << endl;
string3[0] = 'Y';
cout << string3 << endl;
final String string1 = "Hello";
final String string2 = ", World!";
final String string3 = string1 + string2;
System.out.println(string3);
final StringBuilder string4 =
new StringBuilder(string3);
string4.setCharAt(0, 'Y');
System.out.println(string4);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-20-320.jpg)
 {
return (abs(a) < abs(b)); });
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-21-320.jpg)













![39/172
Java Native Interface
package net.ptidej.panama.jni;
public class Main {
static {
System.loadLibrary("net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main");
}
public static native int stringLength(final String s);
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final String s = "Hello, world!";
System.out.println(Main.stringLength(s));
}
}
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include <jni.h>
/* Header for class net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main */
#ifndef _Included_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
#define _Included_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Class: net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
* Method: stringLength
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)I
*/
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main_stringLength
(JNIEnv *, jclass, jstring);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
#include <cstring>
#include "net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main.h"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main_stringLength
(JNIEnv *env, jclass jc, jstring js) {
const char* s = env->GetStringUTFChars(js, NULL);
return strlen(s);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-39-320.jpg)
![40/172
Java Native Interface
package net.ptidej.panama.jni;
public class Main {
static {
System.loadLibrary("net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main");
}
public static native int stringLength(final String s);
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final String s = "Hello, world!";
System.out.println(Main.stringLength(s));
}
}
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include <jni.h>
/* Header for class net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main */
#ifndef _Included_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
#define _Included_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Class: net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
* Method: stringLength
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)I
*/
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main_stringLength
(JNIEnv *, jclass, jstring);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
#include <cstring>
#include "net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main.h"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main_stringLength
(JNIEnv *env, jclass jc, jstring js) {
const char* s = env->GetStringUTFChars(js, NULL);
return strlen(s);
}
Opens a door in the JVM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-40-320.jpg)
![41/172
Java Native Interface
package net.ptidej.panama.jni;
public class Main {
static {
System.loadLibrary("net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main");
}
public static native int stringLength(final String s);
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final String s = "Hello, world!";
System.out.println(Main.stringLength(s));
}
}
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include <jni.h>
/* Header for class net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main */
#ifndef _Included_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
#define _Included_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Class: net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
* Method: stringLength
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)I
*/
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main_stringLength
(JNIEnv *, jclass, jstring);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
#include <cstring>
#include "net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main.h"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main_stringLength
(JNIEnv *env, jclass jc, jstring js) {
const char* s = env->GetStringUTFChars(js, NULL);
return strlen(s);
}
Opens a door in the JVM
JVM jargon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-41-320.jpg)
![42/172
Java Native Interface
package net.ptidej.panama.jni;
public class Main {
static {
System.loadLibrary("net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main");
}
public static native int stringLength(final String s);
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final String s = "Hello, world!";
System.out.println(Main.stringLength(s));
}
}
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include <jni.h>
/* Header for class net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main */
#ifndef _Included_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
#define _Included_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Class: net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main
* Method: stringLength
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)I
*/
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main_stringLength
(JNIEnv *, jclass, jstring);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
#include <cstring>
#include "net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main.h"
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_net_ptidej_panama_jni_Main_stringLength
(JNIEnv *env, jclass jc, jstring js) {
const char* s = env->GetStringUTFChars(js, NULL);
return strlen(s);
}
Opens a door in the JVM
JVM jargon
JVM C API](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-42-320.jpg)



![47/172
java.lang.foreign.Linker
public class Main {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Throwable {
final Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker();
final SymbolLookup dll = SymbolLookup.libraryLookup(
"net_ptidej_panama_version2_Main.dll", Arena.global());
final MethodHandle strlen = linker.downcallHandle(
dll.find("stringLength").orElseThrow(),
FunctionDescriptor.of(
ValueLayout.JAVA_LONG, ValueLayout.ADDRESS));
try (final Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
final MemorySegment cString = arena.allocateFrom("Hello, World!");
final long length = (long) strlen.invoke(cString);
System.out.println(length);
}
}
}
#include <cstring>
#include "net_ptidej_panama_version2_Main.h"
long stringLength(const char *s) {
return strlen(s);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-47-320.jpg)
![48/172
java.lang.foreign.Linker
public class Main {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Throwable {
final Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker();
final SymbolLookup dll = SymbolLookup.libraryLookup(
"net_ptidej_panama_version2_Main.dll", Arena.global());
final MethodHandle strlen = linker.downcallHandle(
dll.find("stringLength").orElseThrow(),
FunctionDescriptor.of(
ValueLayout.JAVA_LONG, ValueLayout.ADDRESS));
try (final Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
final MemorySegment cString = arena.allocateFrom("Hello, World!");
final long length = (long) strlen.invoke(cString);
System.out.println(length);
}
}
}
#include <cstring>
#include "net_ptidej_panama_version2_Main.h"
long stringLength(const char *s) {
return strlen(s);
}
Much simpler and
“natural” C code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-48-320.jpg)


![51/172
java.lang.foreign.Linker
public class Main {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Throwable {
final Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker();
final SymbolLookup stringh = linker.defaultLookup();
final MethodHandle strlen = linker.downcallHandle(
stringh.find("strlen").orElseThrow(),
FunctionDescriptor.of(ValueLayout.JAVA_LONG,
ValueLayout.ADDRESS));
try (final Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
final MemorySegment cString = arena.allocateFrom("Hello, World!");
final long length = (long) strlen.invokeExact(cString);
System.out.println(length);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-51-320.jpg)
![52/172
java.lang.foreign.Linker
public class Main {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Throwable {
final Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker();
final SymbolLookup stringh = linker.defaultLookup();
final MethodHandle strlen = linker.downcallHandle(
stringh.find("strlen").orElseThrow(),
FunctionDescriptor.of(ValueLayout.JAVA_LONG,
ValueLayout.ADDRESS));
try (final Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
final MemorySegment cString = arena.allocateFrom("Hello, World!");
final long length = (long) strlen.invokeExact(cString);
System.out.println(length);
}
}
}
Default lookup](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-52-320.jpg)
![53/172
java.lang.foreign.Linker
public class Main {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Throwable {
final Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker();
final SymbolLookup stringh = linker.defaultLookup();
final MethodHandle strlen = linker.downcallHandle(
stringh.find("strlen").orElseThrow(),
FunctionDescriptor.of(ValueLayout.JAVA_LONG,
ValueLayout.ADDRESS));
try (final Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
final MemorySegment cString = arena.allocateFrom("Hello, World!");
final long length = (long) strlen.invokeExact(cString);
System.out.println(length);
}
}
}
Default lookup
For a known C function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-53-320.jpg)






![60/172
Java Split Personalities
Everything is an Object
Except for primitive types
– Eight of them: boolean, byte, char, short, int,
long, float, double
Except for arrays
– Class of Object[] is [Ljava.lang.Object;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-60-320.jpg)
![61/172
Java Split Personalities
Everything is an Object
Except for primitive types
– Eight of them: boolean, byte, char, short, int,
long, float, double
Except for arrays
– Class of Object[] is [Ljava.lang.Object;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-61-320.jpg)






















![85/172
Value Classes
Cannot compile with Eclipse
– Or any other current IDEs?
$ javac --enable-preview -source 23 -Xlint:preview -d ../bin/ net/ptidej/valhalla/valueclass/Substring.java
netptidejvalhallavalueclassSubstring.java:3: warning:
[preview] value classes are a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public value class Substring implements CharSequence {
^
netptidejvalhallavalueclassSubstring.java:3: warning:
[preview] value classes are a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public value class Substring implements CharSequence {
^
netptidejvalhallavalueclassSubstring.java:8: warning:
[preview] statements before super() is a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public Substring(final String str, final int start, final int end) {
^
3 warnings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-85-320.jpg)
![86/172
Value Classes
The class is implicitly final […]
All instance fields are implicitly final […]
The class does not extend an identity class
or an identity interface
All constructors are implicitly regulated, […],
limiting use of this […]
No instance methods are […] synchronised
(Possibly) The class does not declare a
finalize() method](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-86-320.jpg)
![87/172
Value Classes
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final Substring subs1 = new Substring("Hello, World!", 7, 13);
System.out.println(subs1);
final Substring subs2 = new Substring("Hello, World!", 7, 13);
System.out.println(subs1);
System.out.println(Modifier.isIdentity(Substring.class.getModifiers()));
System.out.println(subs1 == subs2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-87-320.jpg)
![88/172
Value Classes
World!
World!
false
true
public static void main(final String[] args) {
final Substring subs1 = new Substring("Hello, World!", 7, 13);
System.out.println(subs1);
final Substring subs2 = new Substring("Hello, World!", 7, 13);
System.out.println(subs1);
System.out.println(Modifier.isIdentity(Substring.class.getModifiers()));
System.out.println(subs1 == subs2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-88-320.jpg)

![90/172
Value and Identity
public identity interface ICounter {
int getValue();
void increment();
}
public value interface IJSONValue {
String toJsonString();
}
$ javac --enable-preview -source 23 -Xlint:preview -d ../bin/ net/ptidej/valhalla/valueclass/ICounter.java
netptidejvalhallavalueclassICounter.java:3: error: class, interface, enum, or record expected
public identity interface ICounter {
^
1 error
$ javac --enable-preview -source 23 -Xlint:preview -d ../bin/ net/ptidej/valhalla/valueclass/IJSONValue.java
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: warning:
[preview] value classes are a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: warning:
[preview] value classes are a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: error: illegal combination of modifiers: value and interface
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
1 error
2 warnings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-90-320.jpg)
![91/172
Value and Identity
public identity interface ICounter {
int getValue();
void increment();
}
public value interface IJSONValue {
String toJsonString();
}
$ javac --enable-preview -source 23 -Xlint:preview -d ../bin/ net/ptidej/valhalla/valueclass/ICounter.java
netptidejvalhallavalueclassICounter.java:3: error: class, interface, enum, or record expected
public identity interface ICounter {
^
1 error
$ javac --enable-preview -source 23 -Xlint:preview -d ../bin/ net/ptidej/valhalla/valueclass/IJSONValue.java
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: warning:
[preview] value classes are a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: warning:
[preview] value classes are a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: error: illegal combination of modifiers: value and interface
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
1 error
2 warnings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-91-320.jpg)
![92/172
Value and Identity
public identity interface ICounter {
int getValue();
void increment();
}
public value interface IJSONValue {
String toJsonString();
}
$ javac --enable-preview -source 23 -Xlint:preview -d ../bin/ net/ptidej/valhalla/valueclass/ICounter.java
netptidejvalhallavalueclassICounter.java:3: error: class, interface, enum, or record expected
public identity interface ICounter {
^
1 error
$ javac --enable-preview -source 23 -Xlint:preview -d ../bin/ net/ptidej/valhalla/valueclass/IJSONValue.java
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: warning:
[preview] value classes are a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: warning:
[preview] value classes are a preview feature and may be removed in a future release.
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
netptidejvalhallavalueclassIJSONValue.java:3: error: illegal combination of modifiers: value and interface
public value interface IJSONValue {
^
1 error
2 warnings
Not yet implemented](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-92-320.jpg)
![93/172
Value and Identity
By default, an interface may be implemented
by both value classes and identity classes
[If an] interface is only meant for one kind of
class or the other
“It is an error for a value class or interface to
extend an identity class or interface […]”
public identity interface ICounter {
int getValue();
void increment();
}
public value interface IJSONValue {
String toJsonString();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-93-320.jpg)
![94/172
Value and Identity
By default, an interface may be implemented
by both value classes and identity classes
[If an] interface is only meant for one kind of
class or the other
“It is an error for a value class or interface to
extend an identity class or interface […]”
public identity interface ICounter {
int getValue();
void increment();
}
public value interface IJSONValue {
String toJsonString();
}
New keywords](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-94-320.jpg)



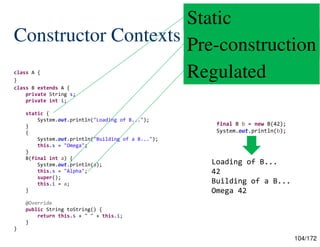
![98/172
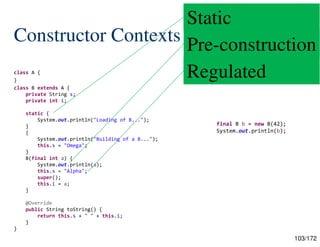
Constructor Contexts
Static
– “The purpose of a static context is to demarcate code that must not
refer explicitly or implicitly to the current instance of the class whose
declaration lexically encloses the static context. for which there is no
current instance defined of the class whose declaration lexically
encloses the static context.”
Pre-construction
– “Unlike in a static context, an expression in a pre-construction
context is free, for example, to refer to the type of the instance under
construction.”
Regulated
– “[A] constructor must not make any use of this in its body, except to
write to an instance field.”
https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/22/docs/specs/statements-before-super-jls.html
https://openjdk.org/jeps/8277163](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-98-320.jpg)




















![128/172
API for Code Models
With @CodeReflection
Size: 3,437 bytes
public static jdk.incubator.code.op.CoreOp$FuncOp
op$net$ptidej$babylon$a$traversal$Main::sub(double, double)double();
descriptor: ()Ljdk/incubator/code/op/CoreOp$FuncOp;
flags: (0x1009) ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC, ACC_SYNTHETIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=0, args_size=0
0: ldc #1
// String func @"sub" @loc="33:2:[...]/Main.java" (%0 : double, %1 : double)double ->
{n %2 : Var<double> = var %0 @"a" @loc="33:2";n %3 : Var<double> = var %1
@"b" @loc="33:2";n %4 : double = var.load %2 @loc="35:10";n %5 : double =
var.load %3 @loc="35:14";n %6 : double = sub %4 %5 @loc="35:10";n return %6
@loc="35:3";n};
2: invokestatic #3
// Method jdk/incubator/code/parser/OpParser.fromStringOfFuncOp:
(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljdk/incubator/code/Op;
5: checkcast #9
// class jdk/incubator/code/op/CoreOp$FuncOp
8: areturn
LineNumberTable:
line 1: 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-128-320.jpg)
![129/172
API for Code Models
With @CodeReflection
Size: 3,437 bytes
public static jdk.incubator.code.op.CoreOp$FuncOp
op$net$ptidej$babylon$a$traversal$Main::sub(double, double)double();
descriptor: ()Ljdk/incubator/code/op/CoreOp$FuncOp;
flags: (0x1009) ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC, ACC_SYNTHETIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=0, args_size=0
0: ldc #1
// String func @"sub" @loc="33:2:[...]/Main.java" (%0 : double, %1 : double)double ->
{n %2 : Var<double> = var %0 @"a" @loc="33:2";n %3 : Var<double> = var %1
@"b" @loc="33:2";n %4 : double = var.load %2 @loc="35:10";n %5 : double =
var.load %3 @loc="35:14";n %6 : double = sub %4 %5 @loc="35:10";n return %6
@loc="35:3";n};
2: invokestatic #3
// Method jdk/incubator/code/parser/OpParser.fromStringOfFuncOp:
(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljdk/incubator/code/Op;
5: checkcast #9
// class jdk/incubator/code/op/CoreOp$FuncOp
8: areturn
LineNumberTable:
line 1: 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-129-320.jpg)
![130/172
API for Code Models
With @CodeReflection
Size: 3,437 bytes
public static jdk.incubator.code.op.CoreOp$FuncOp
op$net$ptidej$babylon$a$traversal$Main::sub(double, double)double();
descriptor: ()Ljdk/incubator/code/op/CoreOp$FuncOp;
flags: (0x1009) ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC, ACC_SYNTHETIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=0, args_size=0
0: ldc #1
// String func @"sub" @loc="33:2:[...]/Main.java" (%0 : double, %1 : double)double ->
{n %2 : Var<double> = var %0 @"a" @loc="33:2";n %3 : Var<double> = var %1
@"b" @loc="33:2";n %4 : double = var.load %2 @loc="35:10";n %5 : double =
var.load %3 @loc="35:14";n %6 : double = sub %4 %5 @loc="35:10";n return %6
@loc="35:3";n};
2: invokestatic #3
// Method jdk/incubator/code/parser/OpParser.fromStringOfFuncOp:
(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljdk/incubator/code/Op;
5: checkcast #9
// class jdk/incubator/code/op/CoreOp$FuncOp
8: areturn
LineNumberTable:
line 1: 0
Parser of textually-
serialised code models](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-130-320.jpg)

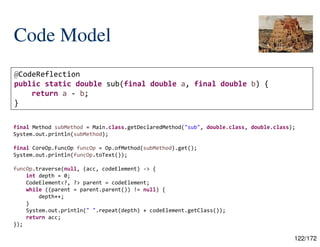
![132/172
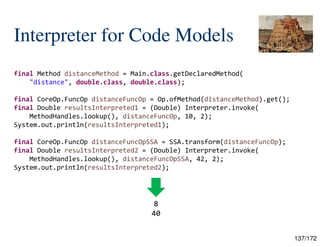
final Method subMethod = Main.class.getDeclaredMethod("sub", double.class, double.class);
System.out.println(subMethod);
final CoreOp.FuncOp funcOp = Op.ofMethod(subMethod).get();
System.out.println(funcOp.toText());
funcOp.traverse(null, (acc, codeElement) -> {
int depth = 0;
CodeElement<?, ?> parent = codeElement;
while ((parent = parent.parent()) != null) {
depth++;
}
System.out.println(" ".repeat(depth) + codeElement.getClass());
return acc;
});
@CodeReflection
public static double sub(final double a, final double b) {
return a - b;
}
public static double net.ptidej.babylon.a.traversal.Main.sub(double,double)
func @"sub" @loc="33:2:[...]/Main.java" (%0 : double, %1 : double)double -> {
%2 : Var<double> = var %0 @"a" @loc="33:2";
%3 : Var<double> = var %1 @"b" @loc="33:2";
%4 : double = var.load %2 @loc="35:10";
%5 : double = var.load %3 @loc="35:14";
%6 : double = sub %4 %5 @loc="35:10";
return %6 @loc="35:3";
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-132-320.jpg)

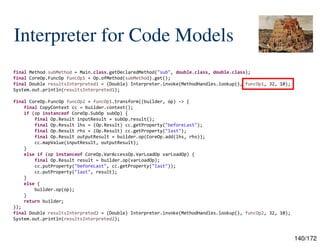
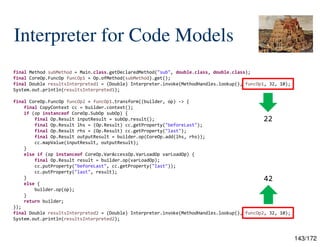
![134/172
Interpreter for Code Models
package jdk.incubator.code.interpreter;
public final class Interpreter {
private Interpreter() {
}
/**
* Invokes an invokable operation by interpreting the code elements within the
* operations body.
* <p>
* The sequence of arguments must [consist] of objects corresponding, in order,
* to the invokable operation's {@link Op.Invokable#parameters() parameters}. If
* the invokable operation {@link Op.Invokable#capturedValues() captures values}
* then the sequence of arguments must be appended with objects corresponding,
* in order, to the captured values.
*
* @param l the lookup to use for interpreting reflective operations.
* @param op the invokeable operation to interpret.
* @param args the invokeable's arguments appended with captured arguments, if any.
* @return the interpreter result of invokable operation.
* @param <T> the type of Invokable.
* @throws InterpreterException if there is a failure to interpret
* @throws Throwable if interpretation results in the throwing of an uncaught exception
*/
public static <T extends Op & Op.Invokable> Object invoke(MethodHandles.Lookup l, T op, Object... args) {
// ...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-134-320.jpg)




















![167/172
With Such An Approach
final OpenAiChatModel model = OpenAiChatModel.builder().apiKey(Main.API_KEY)
.modelName(OpenAiChatModelName.GPT_4_O_MINI).build();
final String answer = model.chat("Give me the advantages and disadvantages of Java");
System.out.println(answer);
Java is a widely-used programming language known for its versatility, portability, and robust nature. Here are some
advantages and disadvantages of using Java:
### Advantages of Java
1. **Platform Independence**: Java is designed to be platform-independent at both the source and binary levels, thanks
to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). This allows developers to write code once and run it anywhere (Write Once, Run
Anywhere - WORA).
[...]
8. **Mature Ecosystem**: Java has a mature ecosystem with enterprise-level solutions, making it a preferred choice for
large-scale applications, including web and mobile development.
### Disadvantages of Java
1. **Performance**: Java can be slower than some compiled languages (such as C or C++) due to the overhead of the JVM
and garbage collection, making it less suitable for performance-critical applications.
[...]
8. **Dependence on JVM**: Java applications require the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) to run, which may not be
available in all environments.
In conclusion, Java is a powerful and versatile language with many advantages, particularly in enterprise and cross-
platform applications. However, developers should consider its disadvantages when selecting a programming language for
specific projects.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaisthenewpythonv0-250306233126-21776970/85/Projects-Panama-Valhalla-and-Babylon-Java-is-the-New-Python-v0-9-167-320.jpg)




