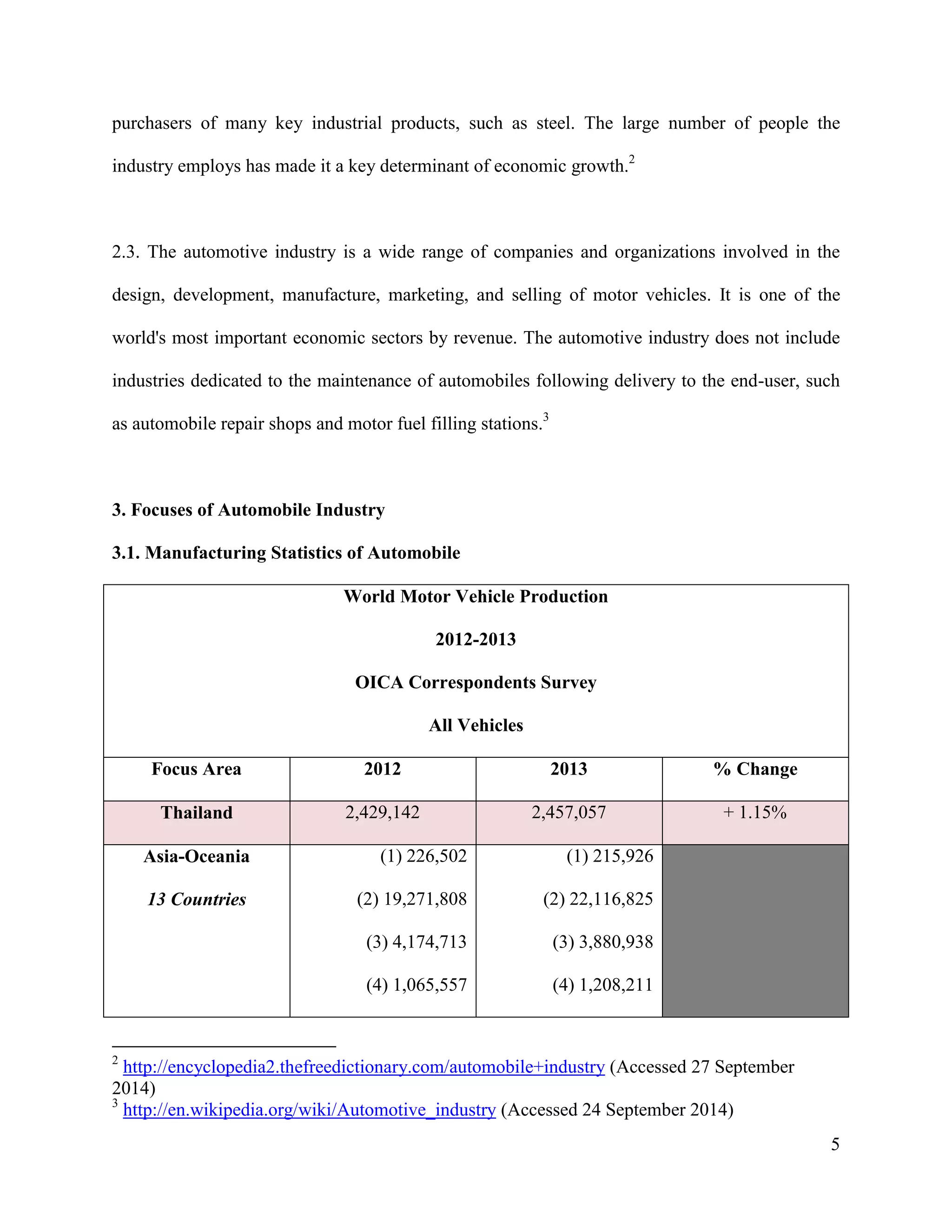
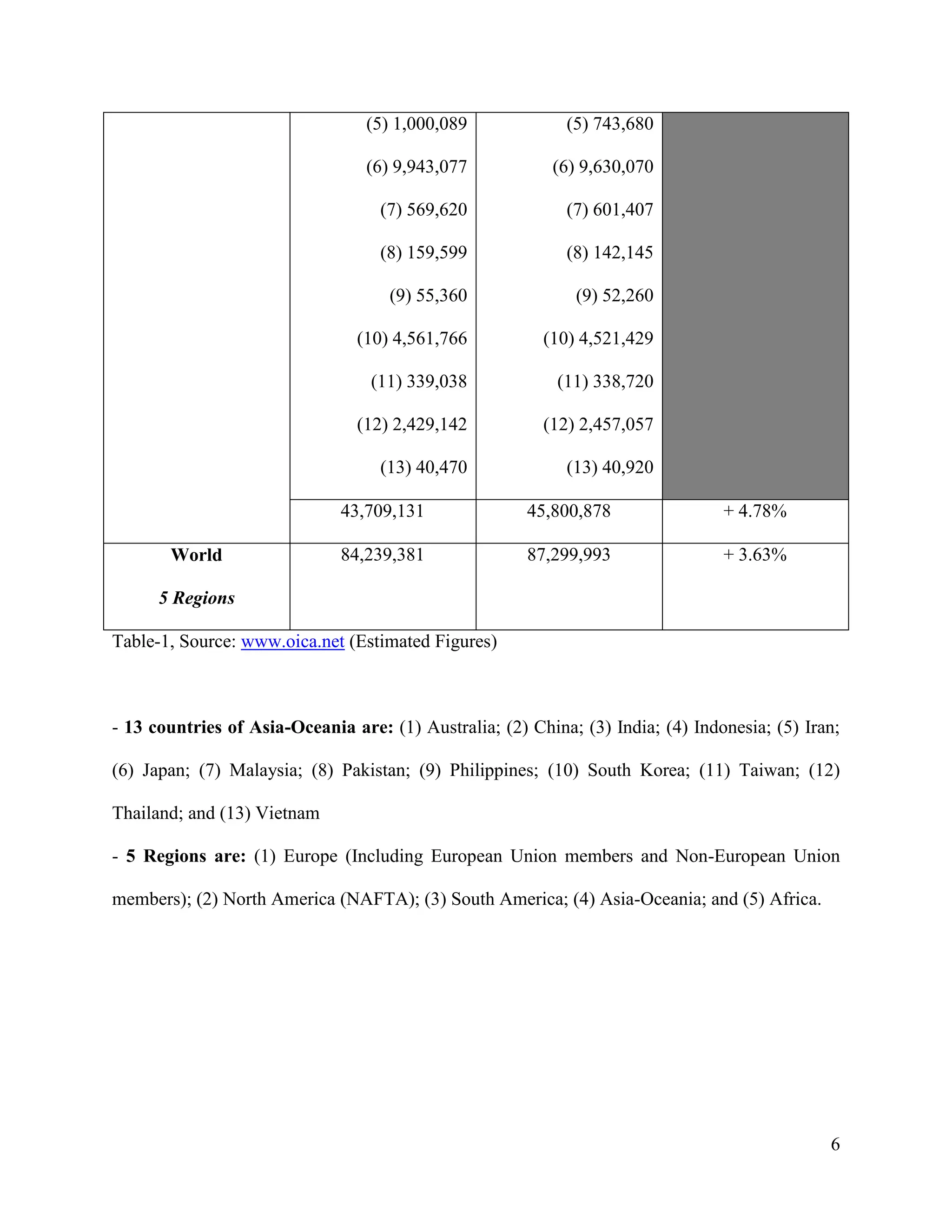
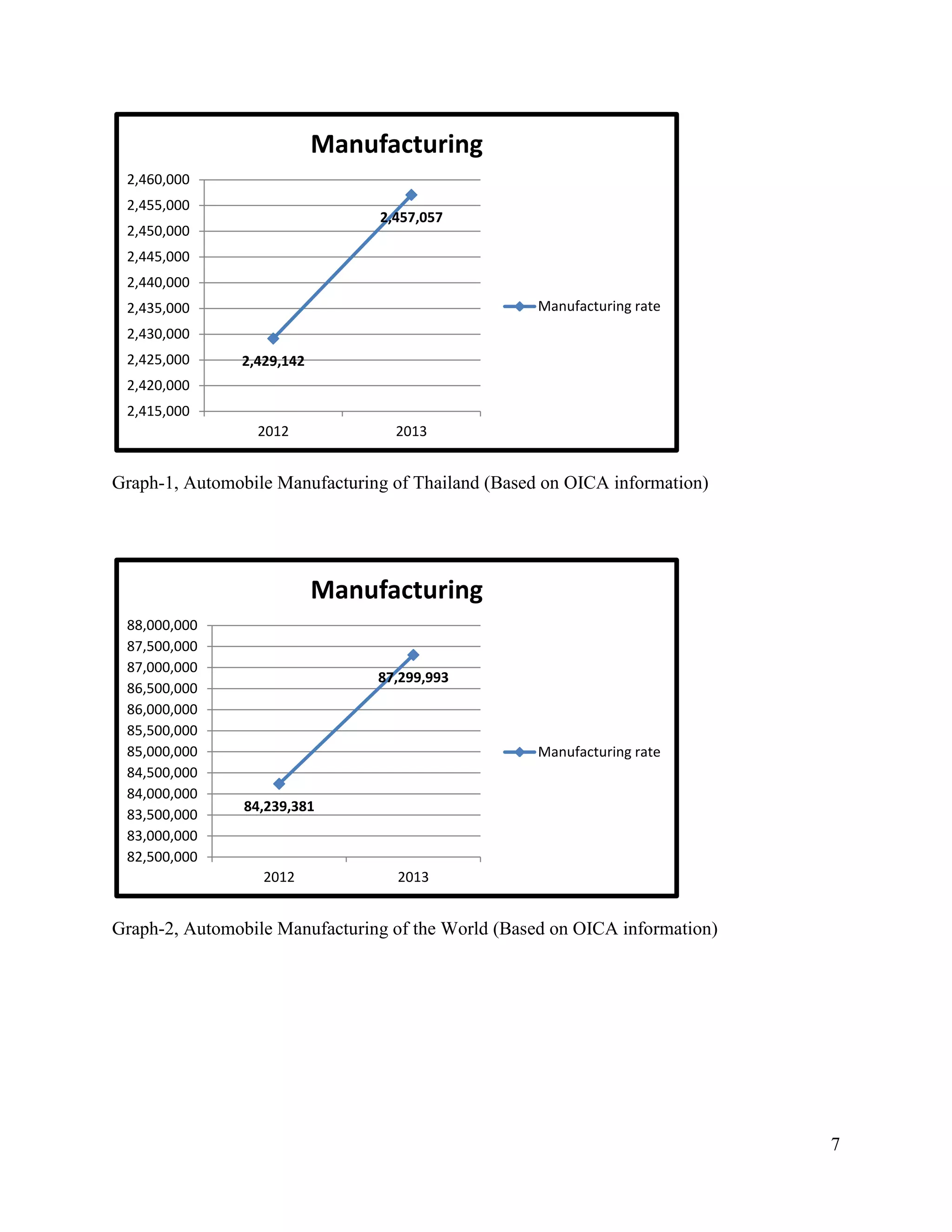
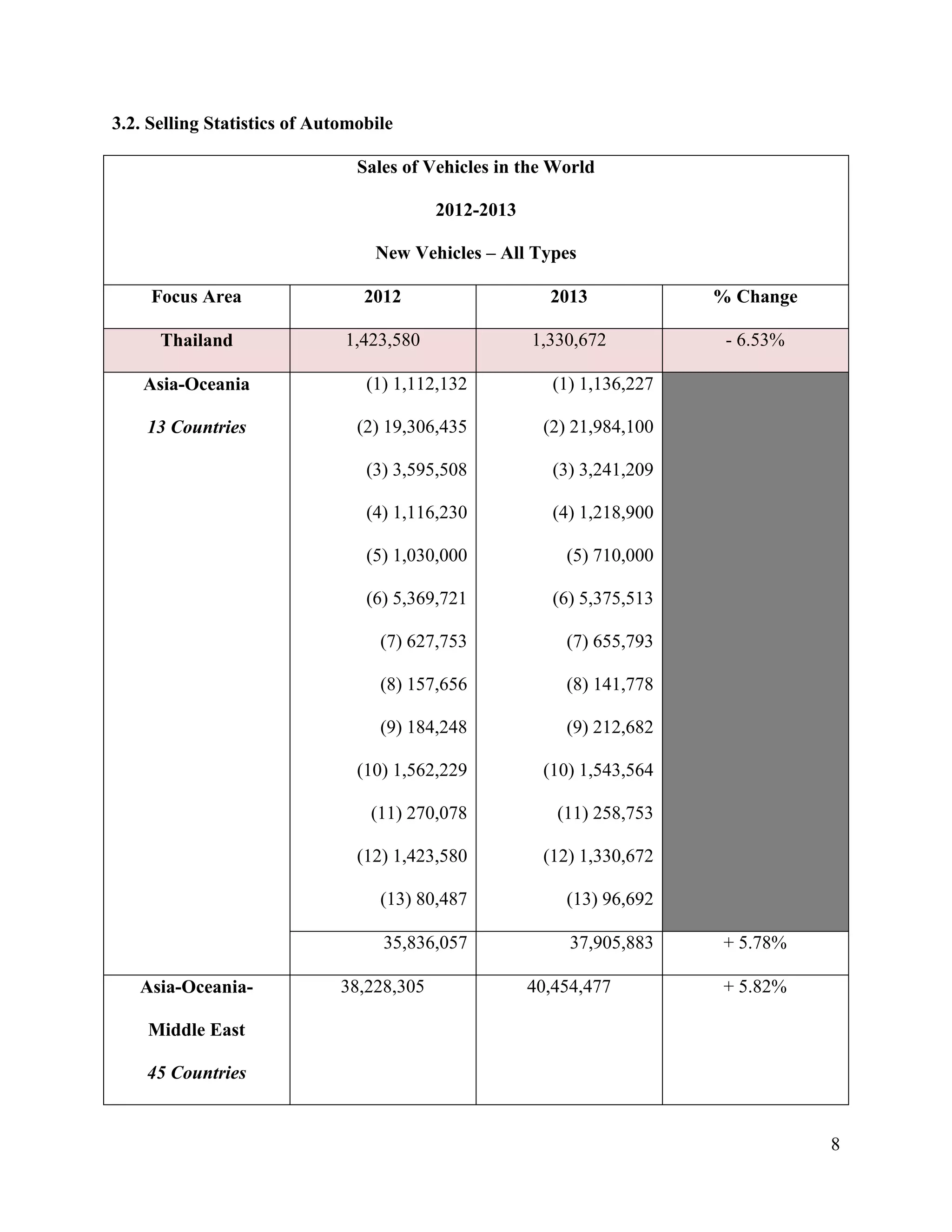
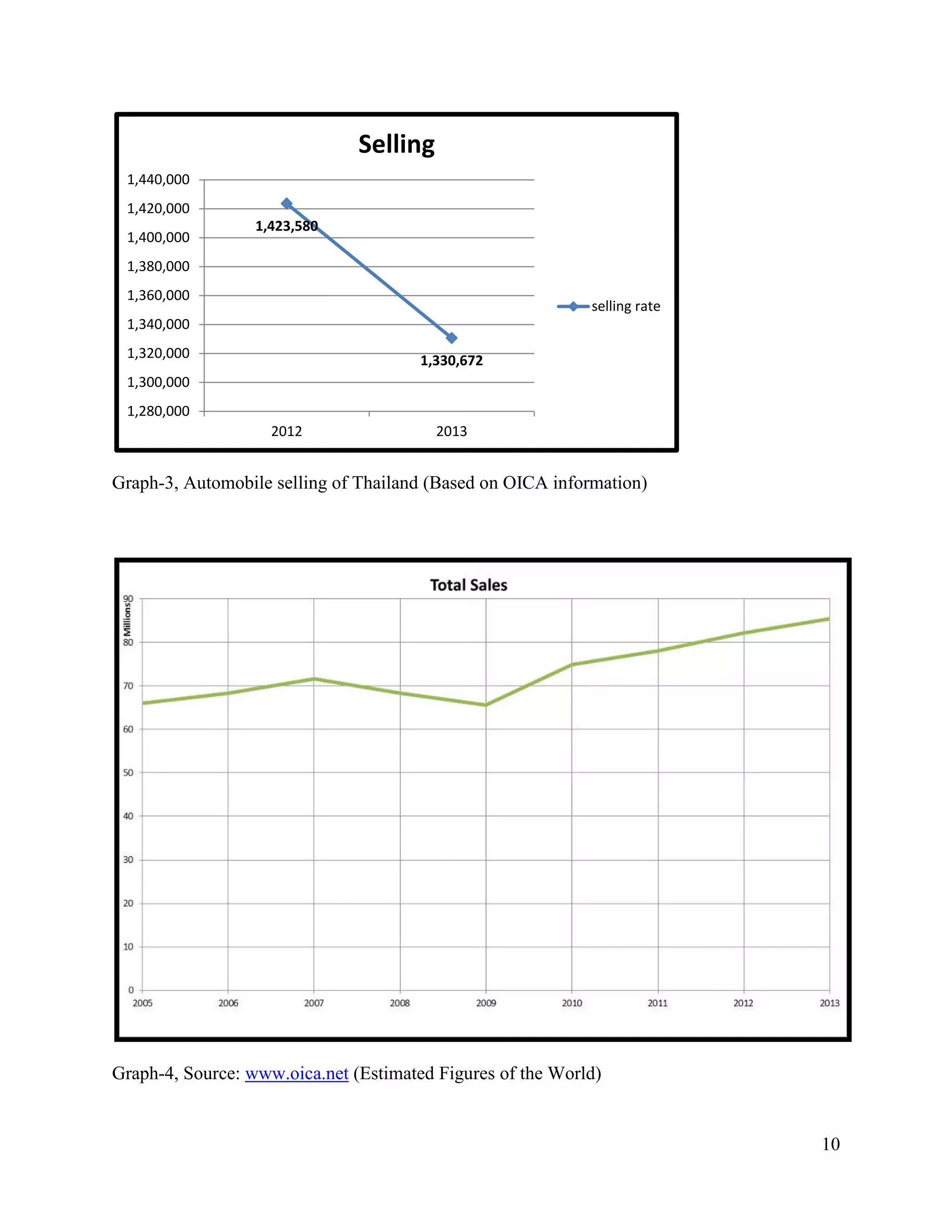
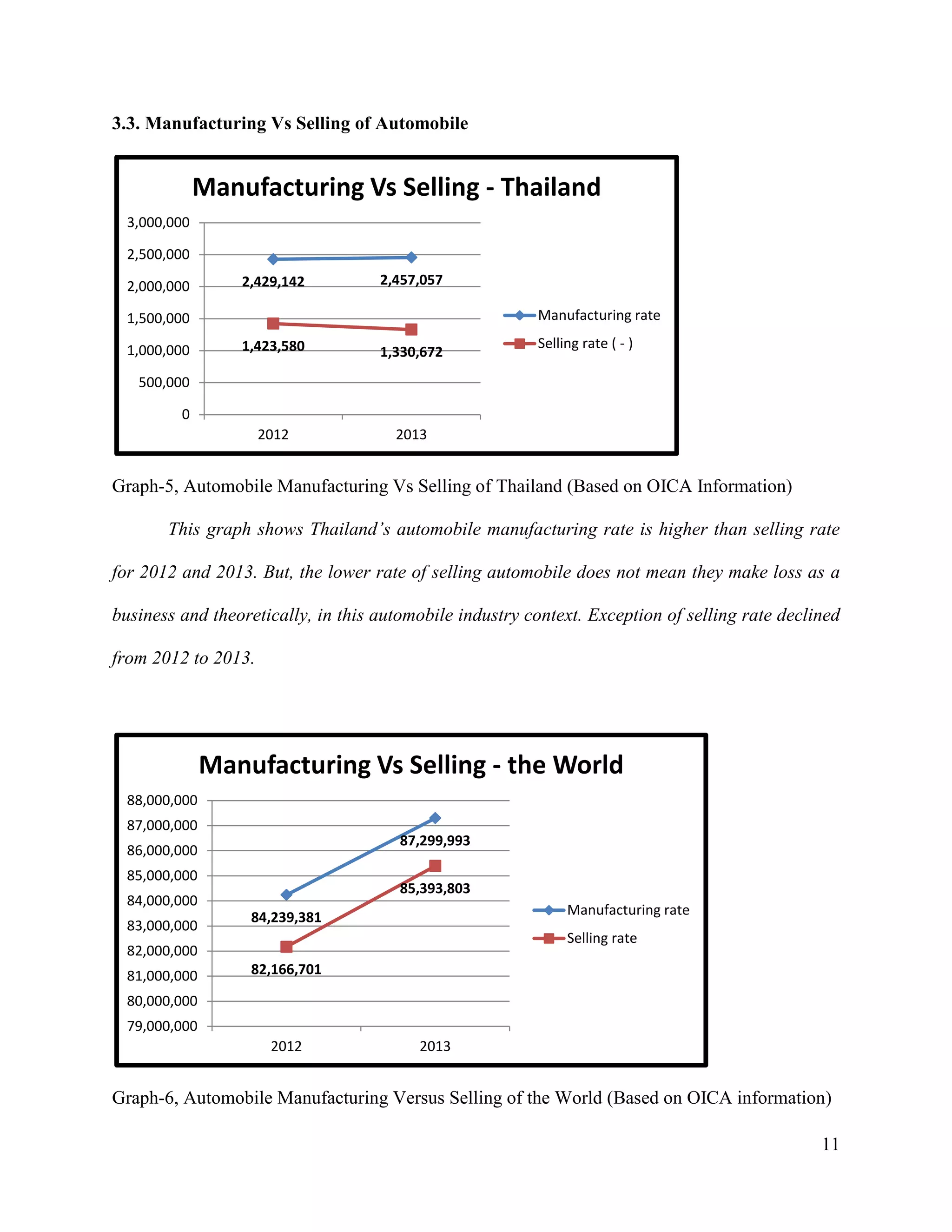
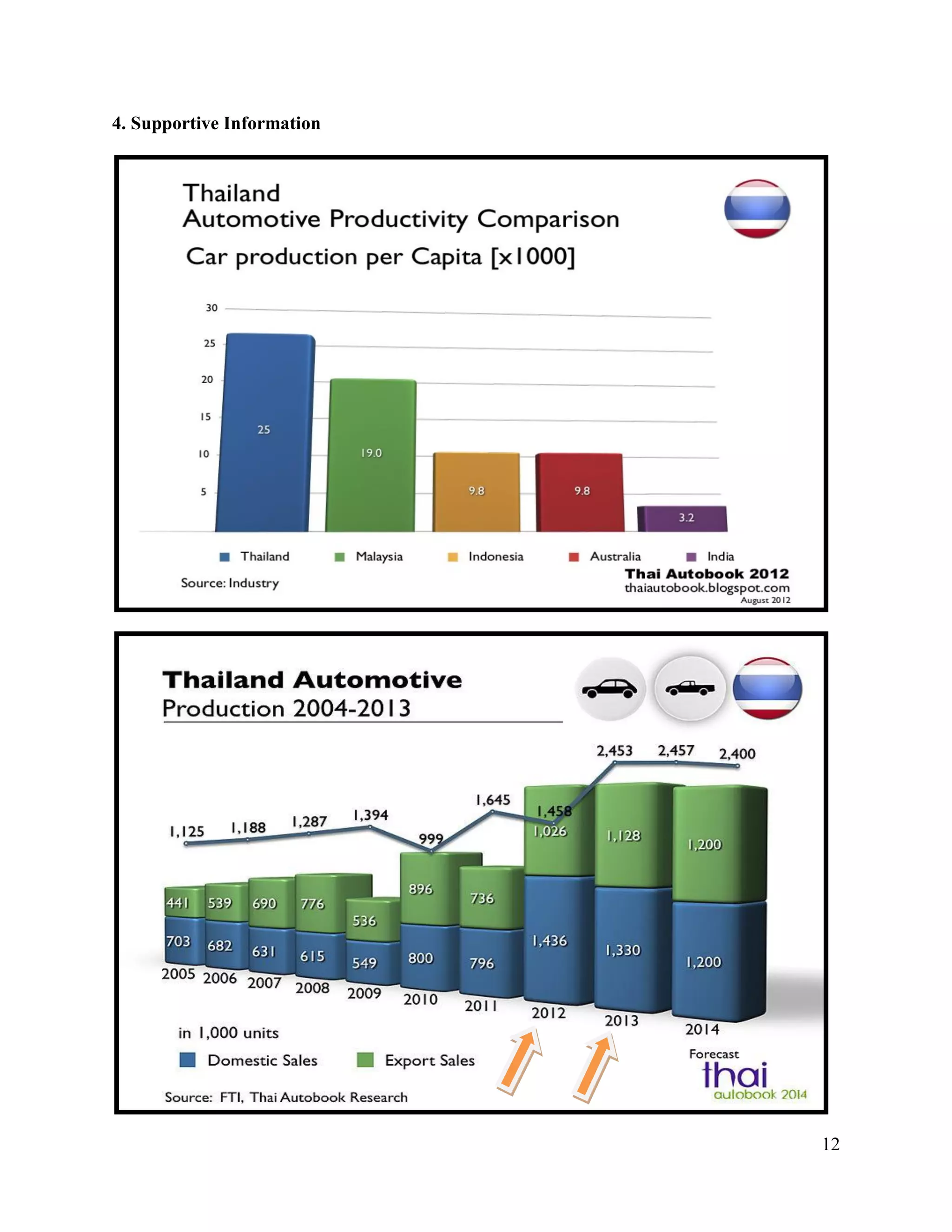
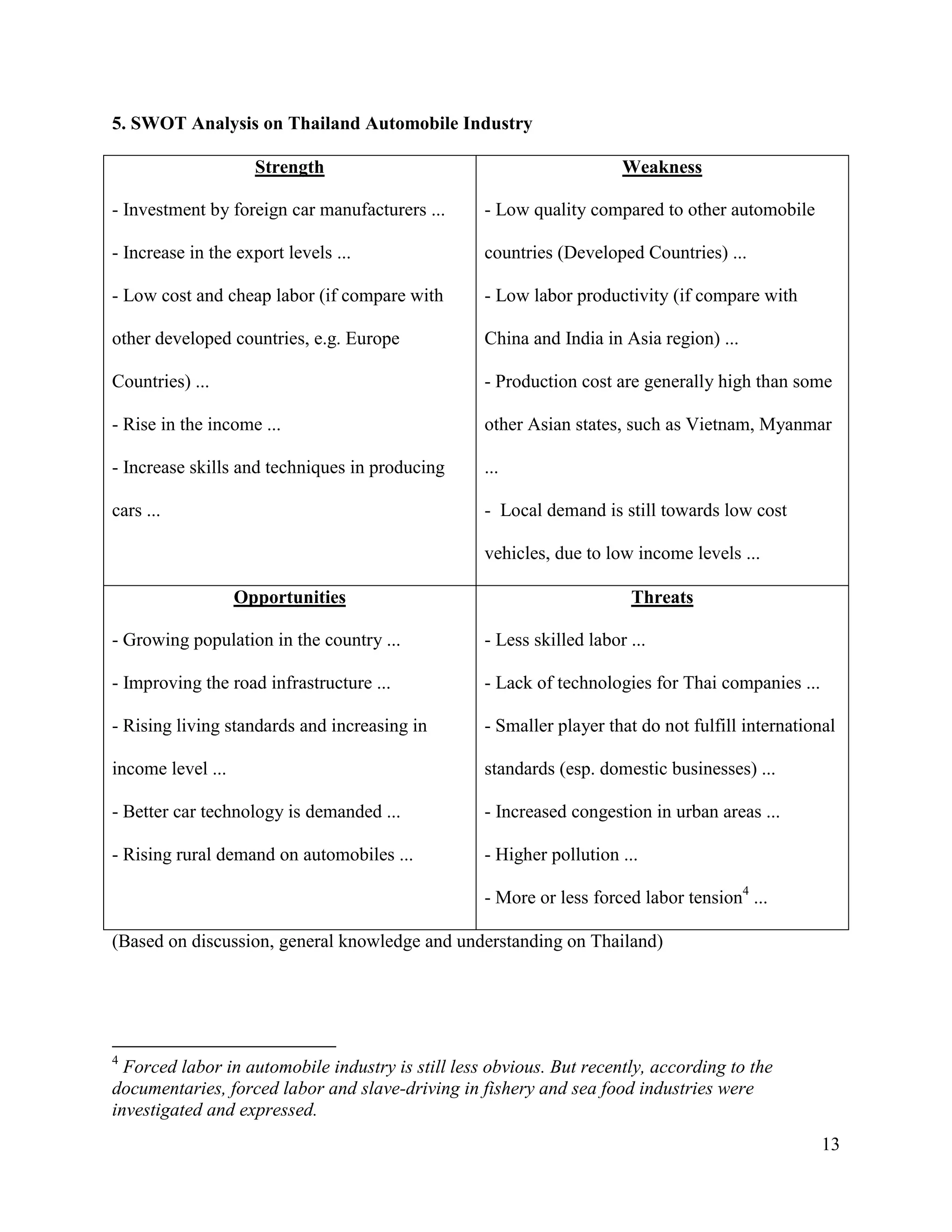
The document is a project paper by Saw Franklin D. Aye for a course in Managerial Economics, focusing on the manufacturing and selling of automobiles in Thailand and globally. It provides definitions, statistics on production and sales from 2012 to 2013, and a SWOT analysis of the Thai automobile industry, discussing strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of data in making strategic decisions, while acknowledging gaps in addressing social and environmental impacts related to the industry.