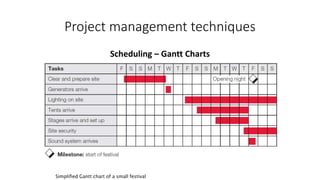
The document outlines the principles of project management as applied to events and festivals, detailing its phases, knowledge areas, and the role of a project manager. It emphasizes the importance of a systematic approach to ensure effective communication, accountability, and flexibility in managing events. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and limitations of project management in the context of the evolving event industry.