Embed presentation
Downloaded 15 times


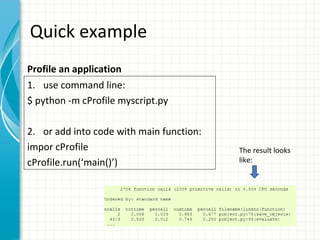





This document provides an introduction to profiling in Python. It discusses three main profilers in the Python standard library: cProfile, profile, and hotshot. It also provides a quick example of how to profile an application using cProfile from the command line or by adding code to the application. The document concludes with a brief discussion of profiling in Cython and reviewing profile results using the pstats module.






