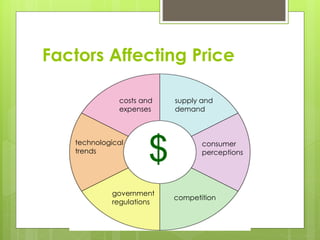
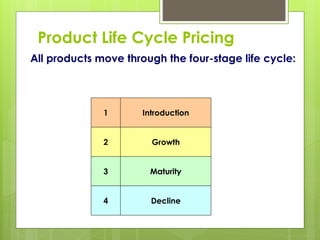
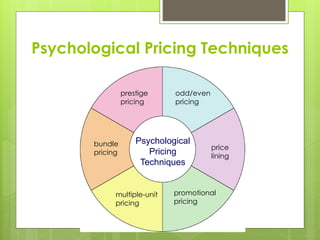
The document discusses factors that affect price strategy, including costs, supply and demand, competition, and technological trends. It describes different pricing approaches like cost-based pricing, demand-based pricing, and competition-based pricing. It also covers pricing techniques across a product's life cycle from introduction to decline, as well as psychological pricing techniques.