This document discusses requirements and procedures for line tightness and leak detector testing of underground storage tank systems in Tennessee. Key points include:
- Line tightness tests must detect a 0.1 GPH release and are required annually for pressurized piping unless monthly monitoring is used.
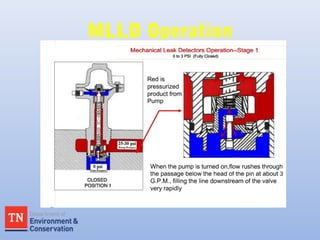
- Proper procedures are outlined for conducting line tightness tests using equipment such as the Petro-Tite line tightness tester and interpreting potential issues indicated by pressure and volume changes.
- Mechanical and electronic line leak detectors must be tested to simulate a 3.0 GPH leak to verify operability. The Petro-Tite system can be used to conduct this test on mechanical line leak detectors.