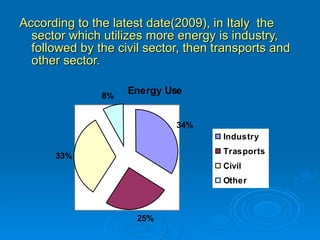
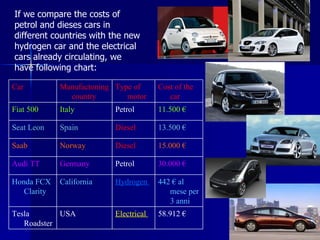
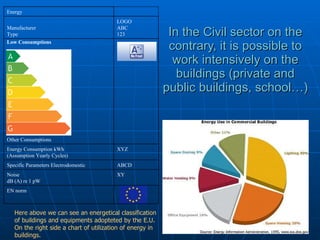
This document discusses various ways to save energy in different sectors such as transportation, buildings, and industry. It provides 20 simple rules for saving energy at home, such as setting thermostats no higher than 20°C, using fluorescent light bulbs, and installing double glazing and thermal insulation. Alternative energy sources like photovoltaic plants, solar panels, wind turbines, hydroelectric plants, geothermal and biomass are also mentioned as ways to save energy and reduce costs.