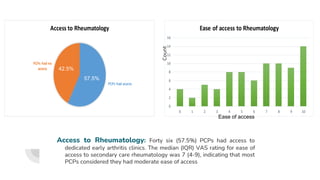
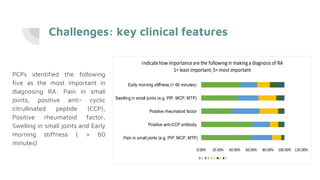
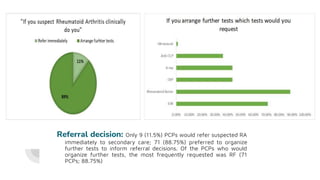
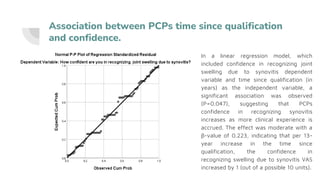
This document summarizes a research project examining barriers to diagnosing and referring patients with suspected rheumatoid arthritis (RA) among primary care physicians (PCPs) in Port Said, Egypt. The study found that most PCPs prefer to order additional tests before referring patients to rule out RA, rather than referring based on clinical symptoms alone. This can delay proper diagnosis and treatment. The study also found limited access to rheumatology clinics for referrals. It concludes with recommendations to establish clear diagnostic guidelines, increase access to early arthritis clinics, and educate PCPs on the importance of clinical assessment over diagnostic tests for suspected RA cases.







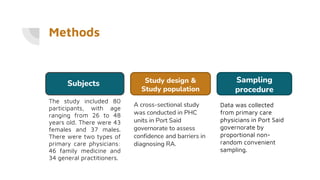
![Methods
Data was collected by a structured self-
administered questionnaire. The
questionnaire was filled out privately by
each primary care physician.
Questions evaluated
1. PCPs confidence in diagnosing RA and
recognizing synovitis
2. what PCPs felt were the most
important symptoms in diagnosing RA
3. what they felt were the most
important features in making a
decision to refer a patient with
suspected RA
4. whether they referred patients with
suspected RA immediately or
requested further tests first
5. their access to secondary care
rheumatology
6. what they felt were the challenges in
making an RA diagnosis
Data collection Questionnaire
Statistical analysis
Data was coded then SPSS software
version 26 was used for data processing.
All data were summarized descriptively,
using mean (S.D.), median [(IQR)] and
number (percentage) where appropriate
based on data type, and distributions. The
associations was evaluated using linear
regression models.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation-230529113518-701dd6dd/85/presentation-pptx-9-320.jpg)