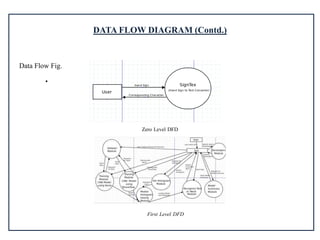
The project report outlines a system for converting sign language to text and speech using image processing and convolutional neural networks (CNN), aiming to improve communication for the deaf and mute community. It details the objectives, system architecture, model training, and results, highlighting high accuracy in translation with 99.97% precision. Future enhancements include expanding gesture vocabulary and adding multilingual support to further bridge communication gaps.