This document describes the microcontroller-based digital control of a DC motor. It includes:
1) Modeling of the separately excited DC motor and determining its electrical and mechanical specifications.
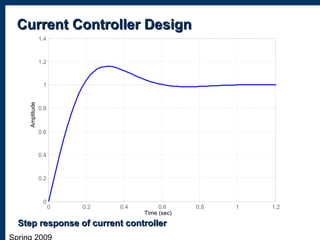
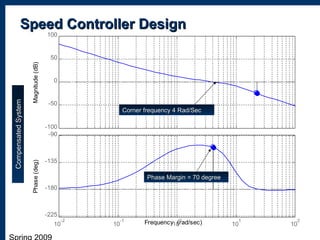
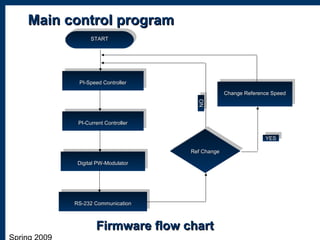
2) Designing a current controller and speed controller in the frequency domain and simulating their performance.
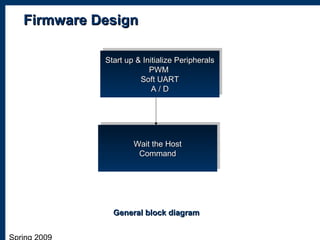
3) The physical implementation of the hardware including a general block diagram and descriptions of the hardware design, firmware design, and software design.
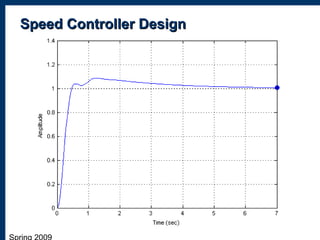
4) An overall design of the system operation and a graph showing the motor speed tracking the set point speed over time.