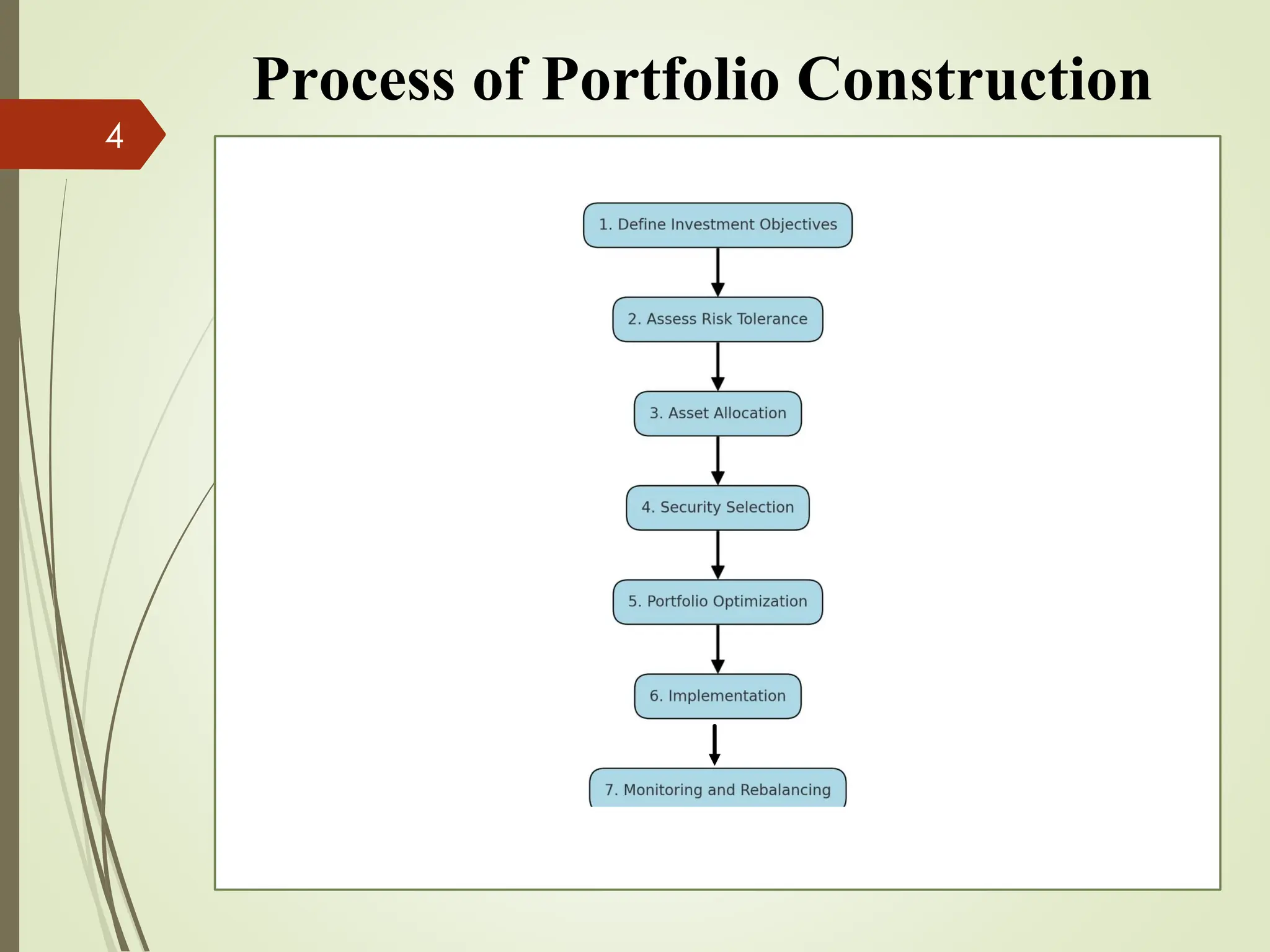
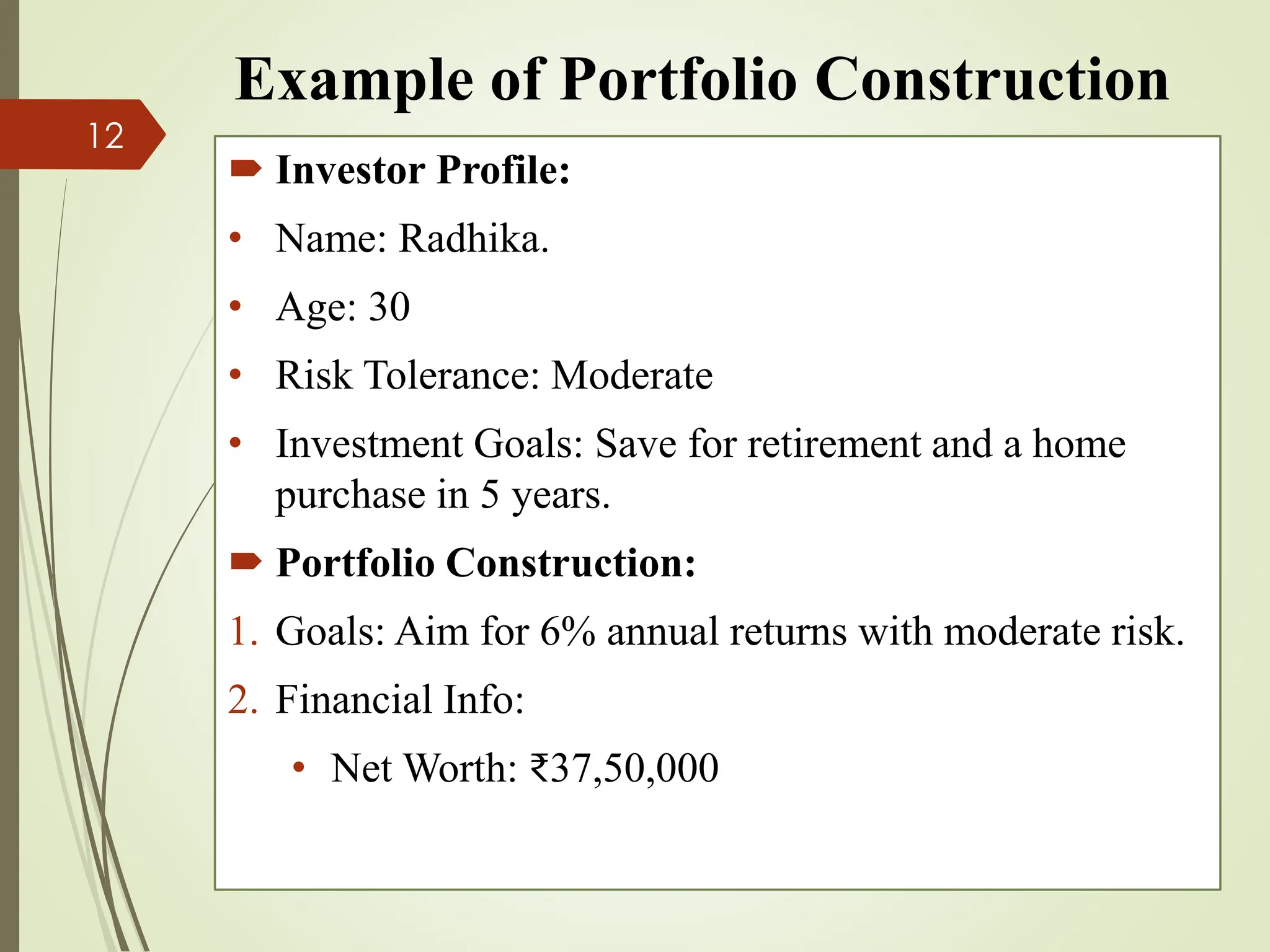
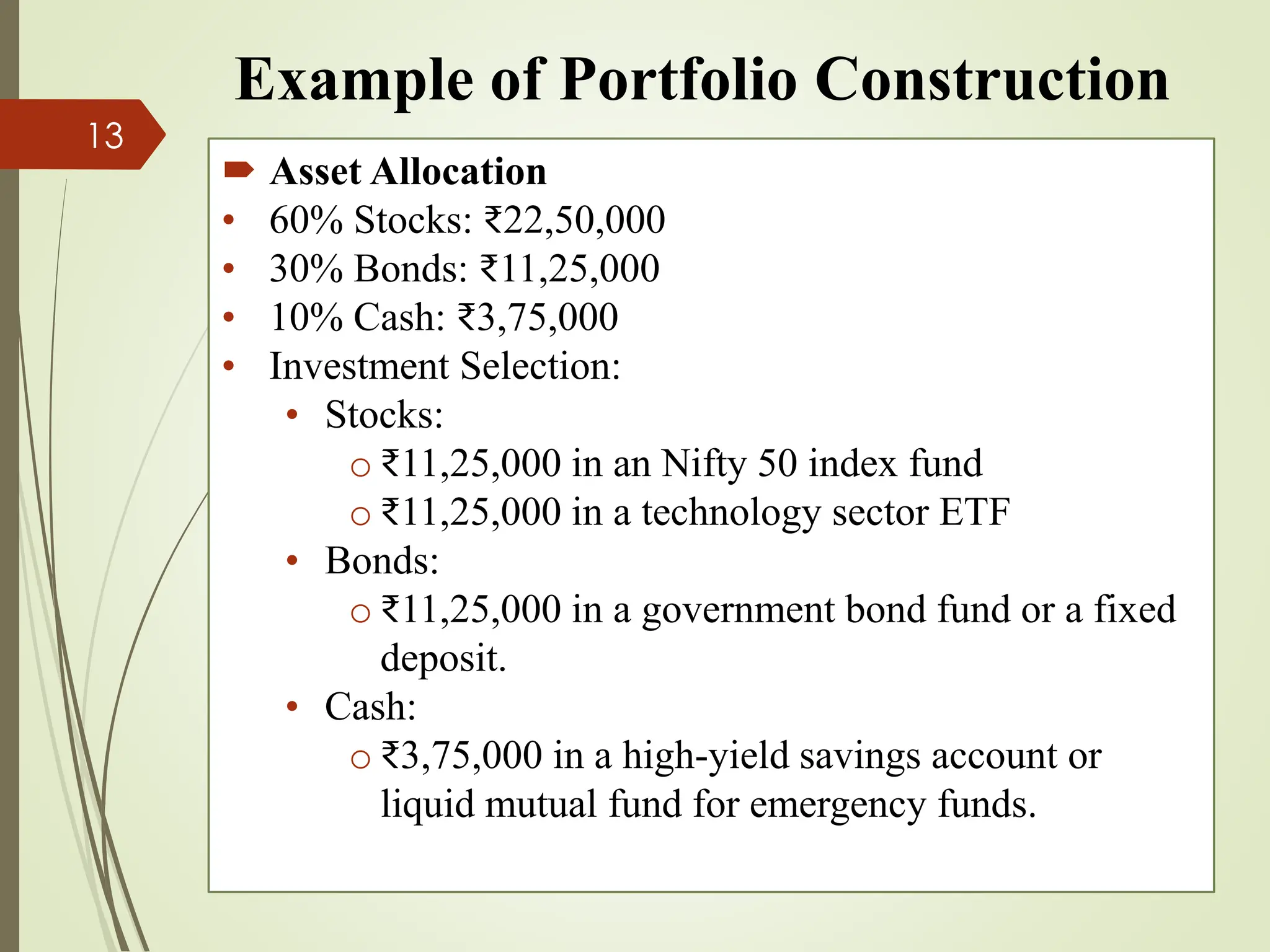
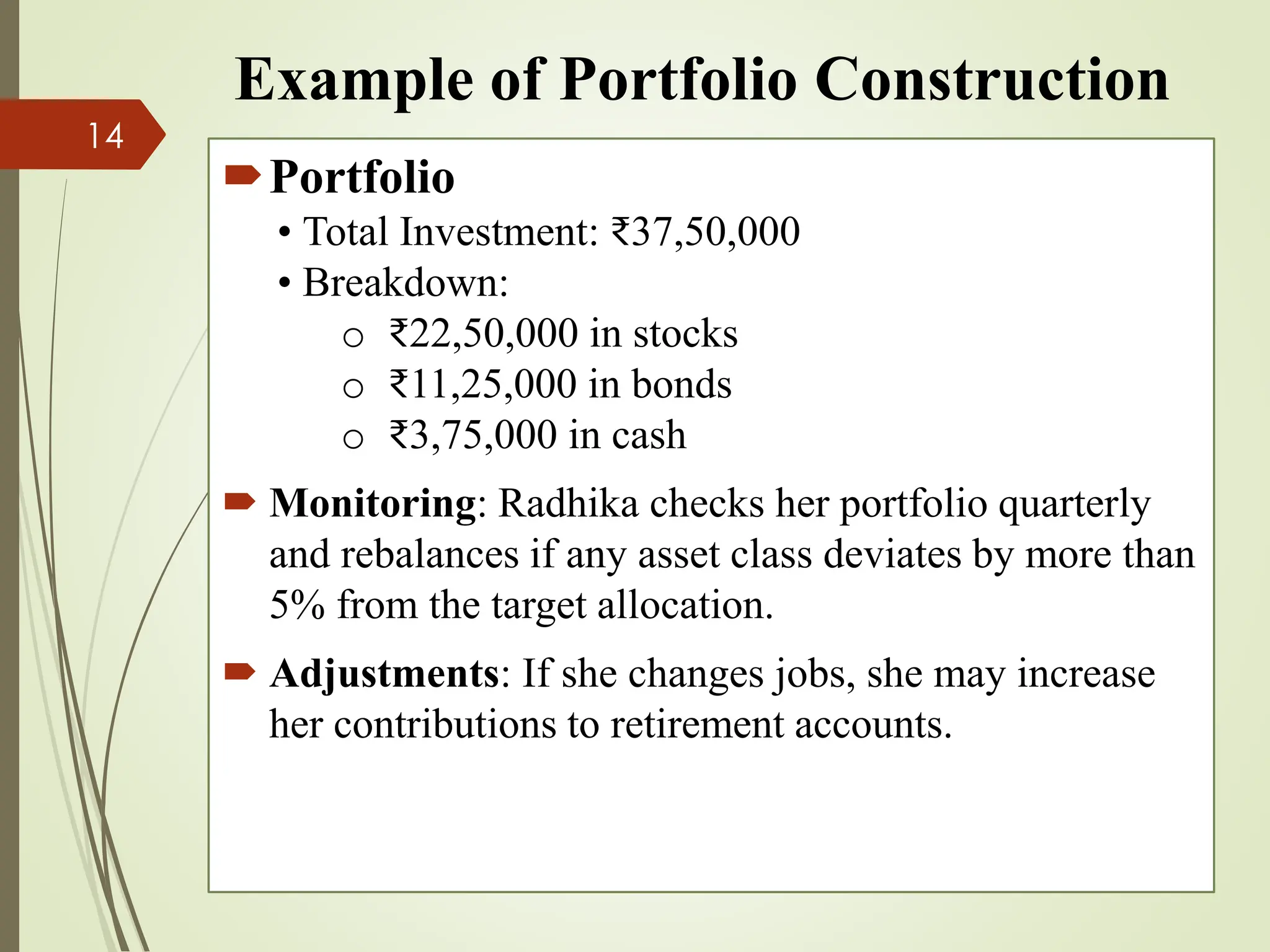
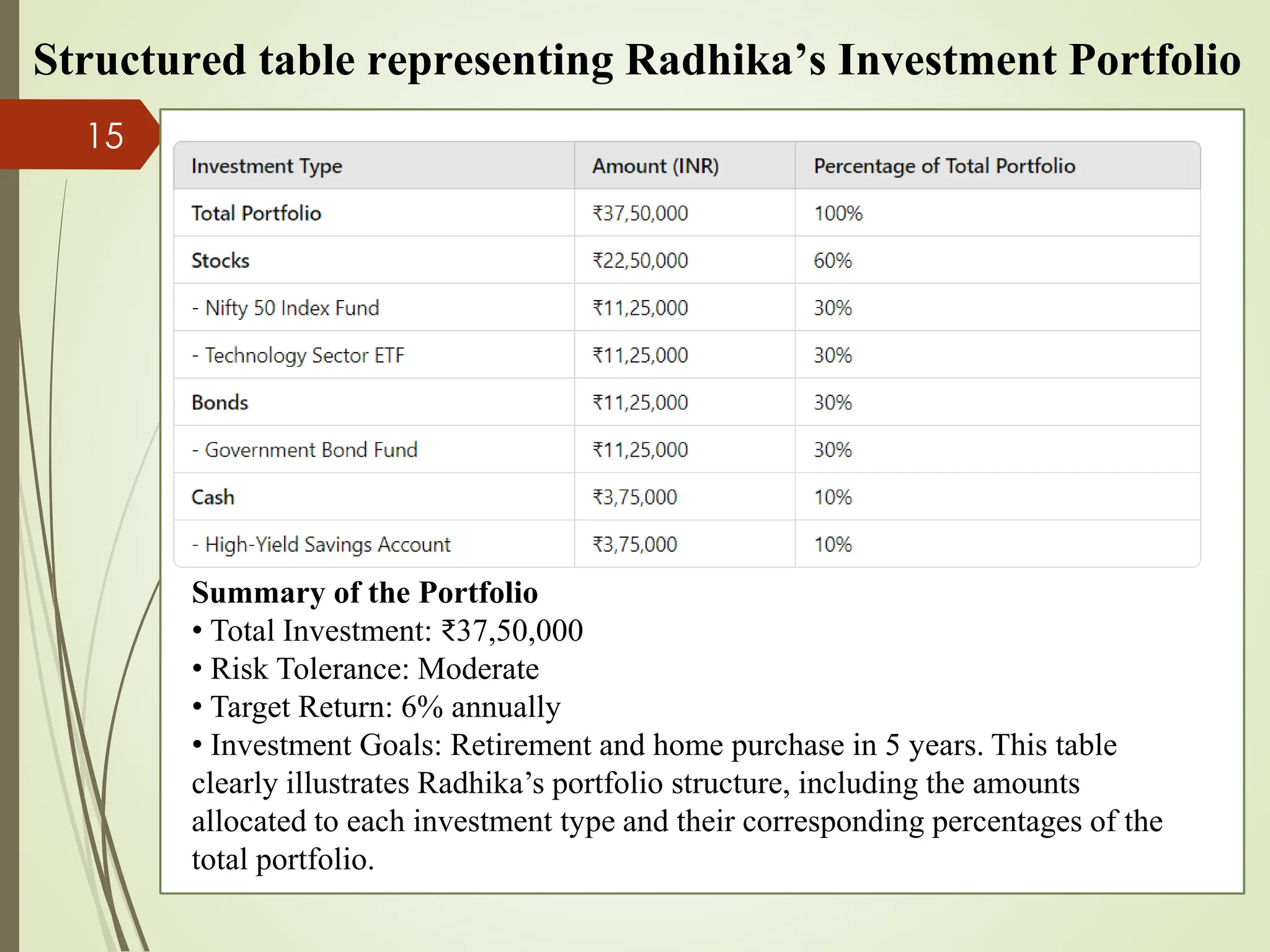
The document outlines the portfolio construction process, defined as combining securities to achieve desired returns with minimal risk, emphasizing diversification to reduce unsystematic risk. It details seven steps for effective portfolio construction, including defining investment objectives, assessing risk tolerance, asset allocation, security selection, portfolio optimization, implementation, and ongoing monitoring. An example portfolio is provided for an investor named Radhika, highlighting her investment strategy, asset breakdown, and management practices.