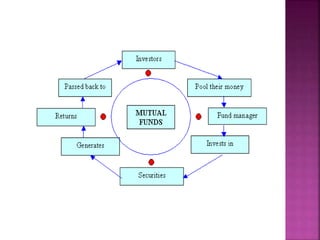
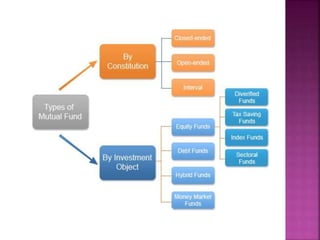
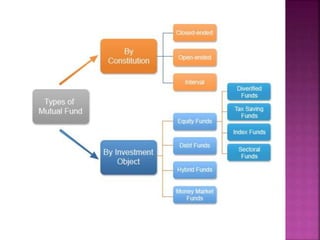
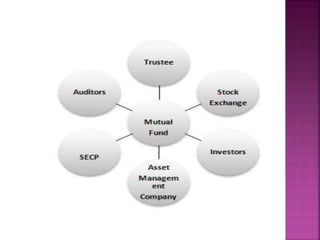
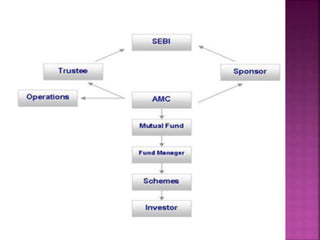
A mutual fund is a financial institution that pools money from shareholders and invests it in a portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other securities. The document defines mutual funds and describes their key features, benefits, types of schemes, roles of various parties involved like sponsors, trustees, asset management companies, and custodians. It also discusses the process of fund management including portfolio selection, revision, and calculation of returns.