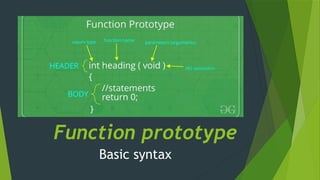
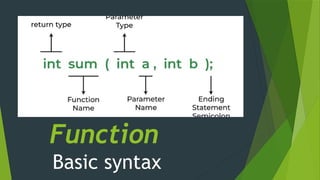
The document presents an overview of programming fundamentals, specifically focusing on functions, which are named blocks of code that perform actions when called. It discusses function components, types (built-in and user-defined), advantages, calling methods, and the basic syntax related to function definitions and prototypes. Additionally, it distinguishes between local and global functions in terms of their scope and usage.