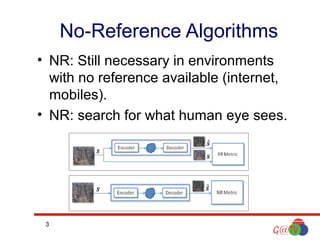
The document discusses no-reference algorithms for video quality assessment focused on artifact evaluation in MPEG-2 and H.264 encoding standards. It highlights advancements in encoding techniques and tools, including the impact of blocking and blurring artifacts on video quality. The conclusions emphasize the need for improved artifact detection methods informed by human visual perception.