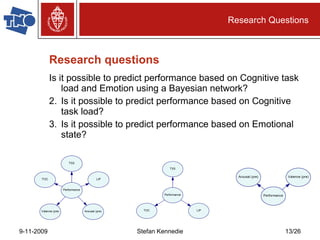
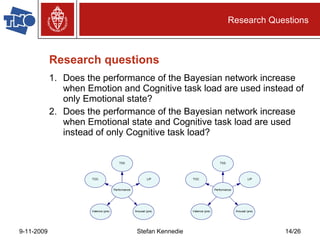
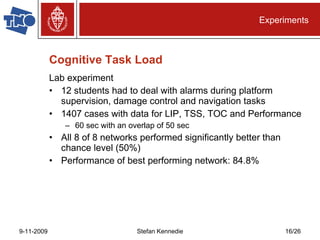
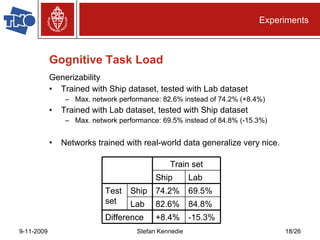
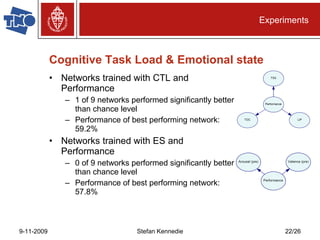
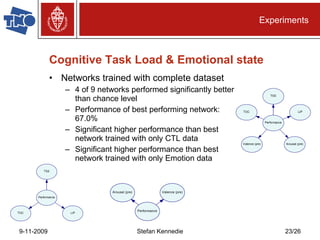
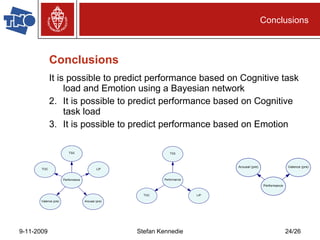
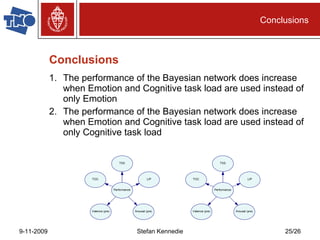
The document presents preliminary research on predicting performance for manned missions to Mars, focusing on cognitive task load and emotional state using Bayesian networks. Experiments indicated that performance predictions improved when both cognitive factors and emotions were considered together, outperforming predictions based on either factor alone. The research concludes that while Bayesian networks show promise for performance prediction in space missions, further study is necessary for effective application.
![Performance prediction: preliminary research for manned missions to Mars Stefan kennedie [kennedie[at]gmail.com]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentatiemasterscriptiestefankennedieonline-091130141542-phpapp01/75/Master-Thesis-1-2048.jpg)