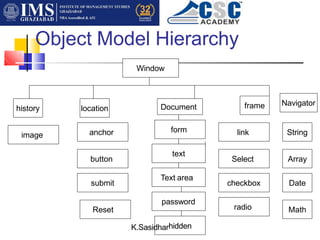
JavaScript is a scripting language that adds interactivity to HTML pages. It was originally developed by Netscape as a means to add dynamic elements to webpages. JavaScript can be embedded directly into HTML code using <script> tags and is interpreted by browsers rather than pre-compiled. As an object-based language, JavaScript can manipulate various HTML elements and properties through its Document Object Model. Common JavaScript objects include Window, Location, History, Form, and Date which allow for user interaction, navigation, and other functionality.



















![Example:
K.Sasidhar
■ var myArray= new Array(“rama”, “ravana”);
■ var elementIndex;
■ for(elementIndex in myArray)
■ {
■ document. Write(myArray[elementIndex]);
■}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-20-320.jpg)












![Document continue…..
<BODY
[BACKGROUND = “backgroundImage”]
[BGCOLOR = “backgroundColor”]
[TEXT = “foregroundColor”]
[LINK = “unfollowedLinkColor”]
[ALINK = “activatedLinkColor”]
[VLINK = “followedLinkColor”]
[onload = “methodName”]
[onUnload = “meK
.
tS
ha
os
i
dd
h
Na
rame”]>
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-34-320.jpg)
![K.Sasidhar
Form Object
■ This allows users interactions.
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
Gives life to static web pages.
Properties:
<FORM
[NAME=“formName”]
[ACTION=“ServerURL”]
[ENCTYPE=“encodingType”]
[METHOD = “GET|POST”]
[TARGET = “windowName”]
[onSubmit = “methodName”]
</FORM>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-35-320.jpg)
![Text Object
■ Common element to gather data entered by user.
<INPUT type=“text”
[Name = “objectname”]
[Value=“value”]
[Size=size]
[MAX.LENGTH = size]
[onBlur = “methodname”]
[onChange = “methodname”]
[onFocus = “methodname”]
[onSelect = “methodnK
a.S
mas
eid
”h
]ar
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-36-320.jpg)
![Text Area Object
K.Sasidhar
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
< TEXTAREA
[Name = “objectName”]
[ROWS=“numRows”]
[COLS=“numCols”
[WRAP=“off | virtual | physical”]
[onBlur = “methodname”]
[onChange = “methodname”]
[onFocus = “methodname”]
[onSelect = “methodname”]
</TEXTAREA>
■](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-37-320.jpg)
![Password object
K.Sasidhar
■
■
■
■
<INPUT type=“password”
[Name = “objectname”]
[Value=“defaultpassword”]
[Size=integer]
■ Anchor Object:
■ <A [HREF = URL ]
■ Name = “objectname”
■ [TARGET = “windowName”]>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-38-320.jpg)

![Button properties
K.Sasidhar
<INPUT
TYPE=“button | submit | reset”
[NAME = “objectName”]
[VALUE=“labelText”]
[onClick = “methodName”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-40-320.jpg)
![Select Object
K.Sasidhar
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
<SELECT>
[Name = “objectname”]
[Size=“numberVisible”]
[MULTIPLE]
[onBlur = “methodname”]
[onChange = “methodname”]
[onFocus = “methodname”]
<OPTION VALUE = “optionValue”
<[SELECTED]>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-41-320.jpg)
![Radio Object
K.Sasidhar
■ <input>
■ TYPE = “radio”
■ [NAME = “groupName”]
■ [VALUE = “value”][CHECKED]
■ [onClick=“methodName”]> [displayText]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-42-320.jpg)

![K.Sasidhar
Methods…..
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
Length
CharAt(pos)
IndexOf (search text[startPos],[endpos])
Substring(startPos,endPos)
Big
Blink
Fixed
Fontcolor
Fontsize
Small
Strike
Sub
Sup
toLowerCase
toUPperCase](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-44-320.jpg)








![K.Sasidhar
Arrays
■
■
<html>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
var i;
var mycars = new Array();
mycars[0] = "Saab";
mycars[1] = "Volvo";
mycars[2] = "BMW";
for (i=0;i<mycars.length;i++)
{
document.write(mycars[i] + "<br />");
}
</script>
</body>
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-53-320.jpg)
![Join two arrays
K.Sasidhar
</html>
■
<html>
■
■ <body>
<p id="demo">Click the button to join three arrays.</p>
<button onclick="myFunction()">Try it</button>
<script type="text/javascript">
function myFunction()
{
var hege = ["Cecilie", "Lone"];
var stale = ["Emil", "Tobias", "Linus"];
var kai = ["Robin"];
var children = hege.concat(stale,kai);
var x=document.getElementById("demo");
x.innerHTML=children;
}
</script>
</body>
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-54-320.jpg)
![Remove the last element
K.Sasidhar
</html>
■
<!DOCTYPE html>
■
■
■
<html>
<body>
<p id="demo">Click the button to remove the last array element.</p>
<button onclick="myFunction()">Try it</button>
<script type="text/javascript">
var fruits = ["Banana", "Orange", "Apple", "Mango"];
function myFunction()
{
fruits.pop();
var x=document.getElementById("demo");
x.innerHTML=fruits;
}
</script>
</body>
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■
■](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt1718-220914021717-b3ac8cfa/85/ppt-17-18-pptx-55-320.jpg)






