The document explains structures in C programming, defining them as user-defined data types that group various variables for better organization of complex data. It details the syntax for defining structures, accessing and modifying their members, and presents examples, including nested structures. Advantages of using structures include improved code readability and easier data handling.

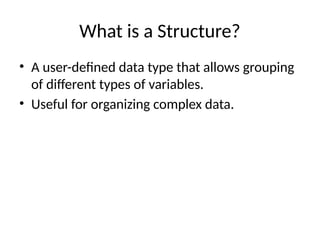

![Syntax of a Structure
• Defining a Structure:
struct StructureName {
dataType member1;
dataType member2;
};
• Example:
struct Student {
char name[50];
int age;
float grade;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structincprogramming1-241107063408-67467b95/85/Powerpoint-presentation-on-structures-in-C-programing-4-320.jpg)

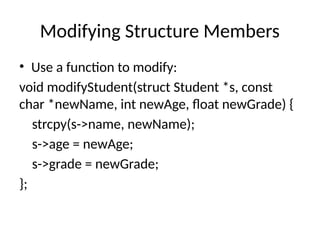

![Nested Structures
• Define Address structure:
struct Address {
char city[50];
char state[50];
};
• Define Student structure:
struct Student {
char name[50];
int age;
struct Address addr;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structincprogramming1-241107063408-67467b95/85/Powerpoint-presentation-on-structures-in-C-programing-8-320.jpg)