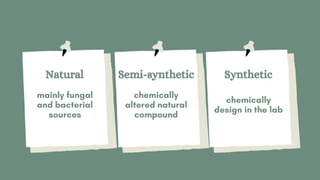
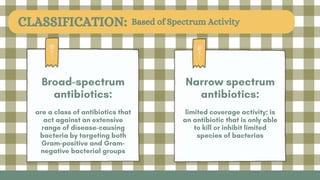
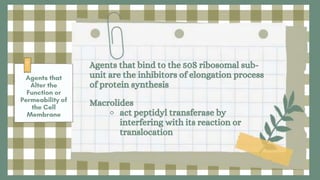
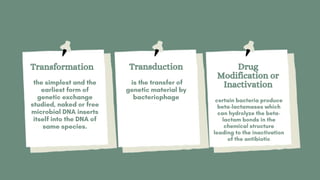
This document discusses antimicrobial agents and their classification and mechanisms of action. It describes how antibiotics can be classified based on their spectrum of activity, source, or mechanism. The main mechanisms discussed are inhibition of cell wall synthesis, disruption of cell membranes, inhibition of protein synthesis through effects on ribosomes, inhibition of DNA, RNA or folic acid synthesis. Factors leading to drug resistance and mechanisms of acquired resistance such as efflux pumps, target site mutations and enzymatic inactivation are also summarized.