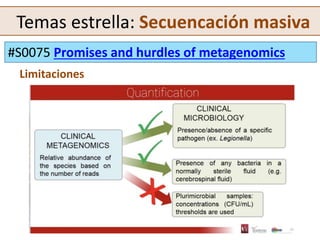
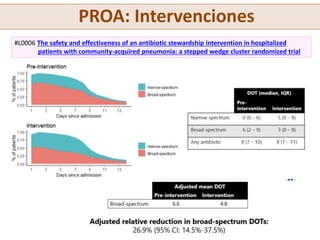
This document summarizes key topics and presentations from the ECCMID 2019 conference. It discusses the structure and attendance numbers of the conference, with Spain having the most accepted abstracts. It also provides guidance on how to effectively participate in such a large conference. Several emerging topics are highlighted, including immunotherapies and their impact on infection management, the use of artificial intelligence and new technologies in areas like automated infection surveillance and mobile microbiology labs, and the promises and challenges of clinical metagenomics using widespread DNA sequencing. Changes in bacterial taxonomy are also briefly noted.