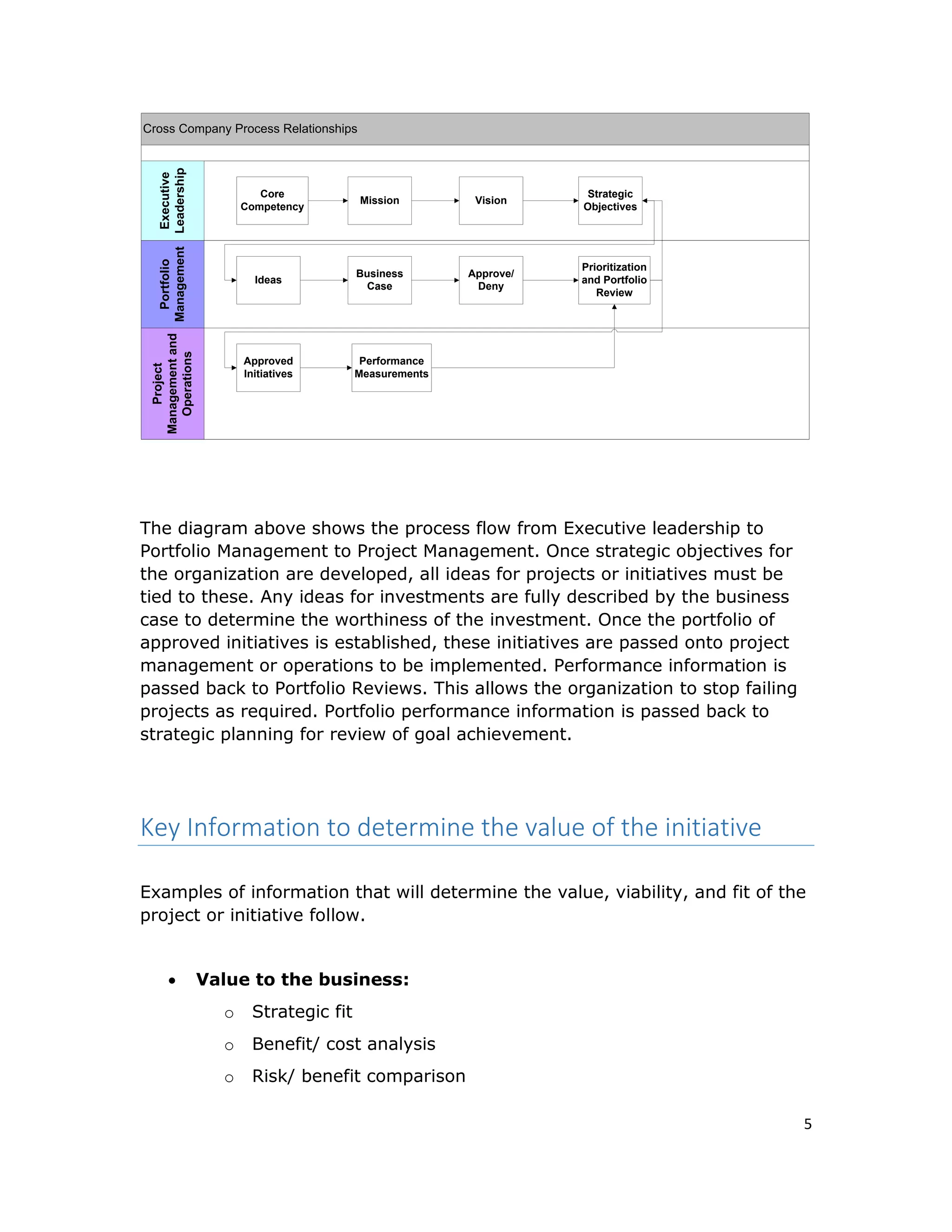
The document discusses the importance of portfolio management in improving business investments by ensuring strategic alignment, resource management, and maximizing returns. It highlights the need for a structured portfolio management system to facilitate decision-making and prioritize initiatives effectively, thus enabling organizations to respond to market changes and avoid funding failing projects. Overall, the implementation of portfolio management offers businesses the ability to maintain competitiveness by aligning all activities with corporate goals and enhancing investment value.