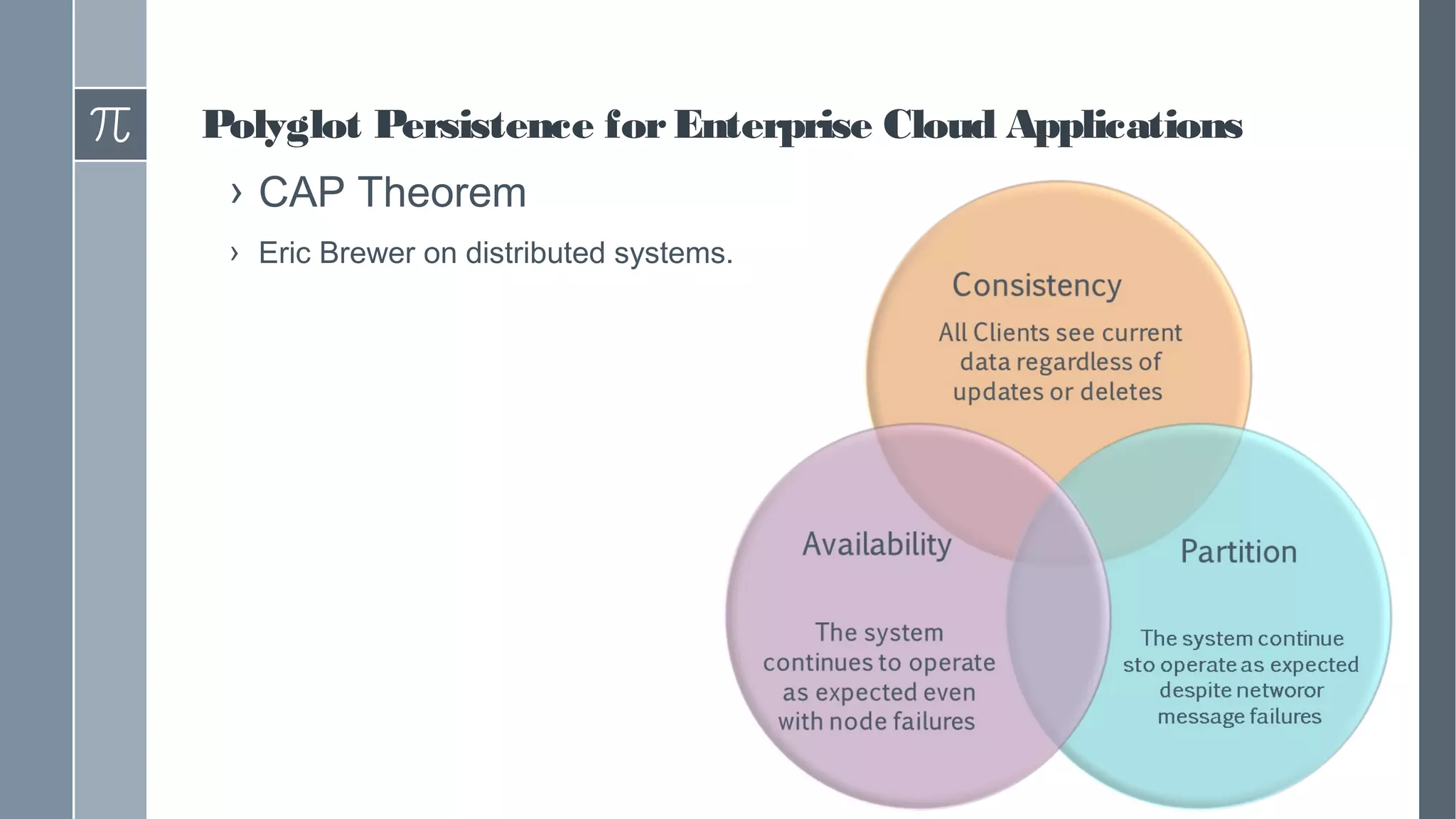
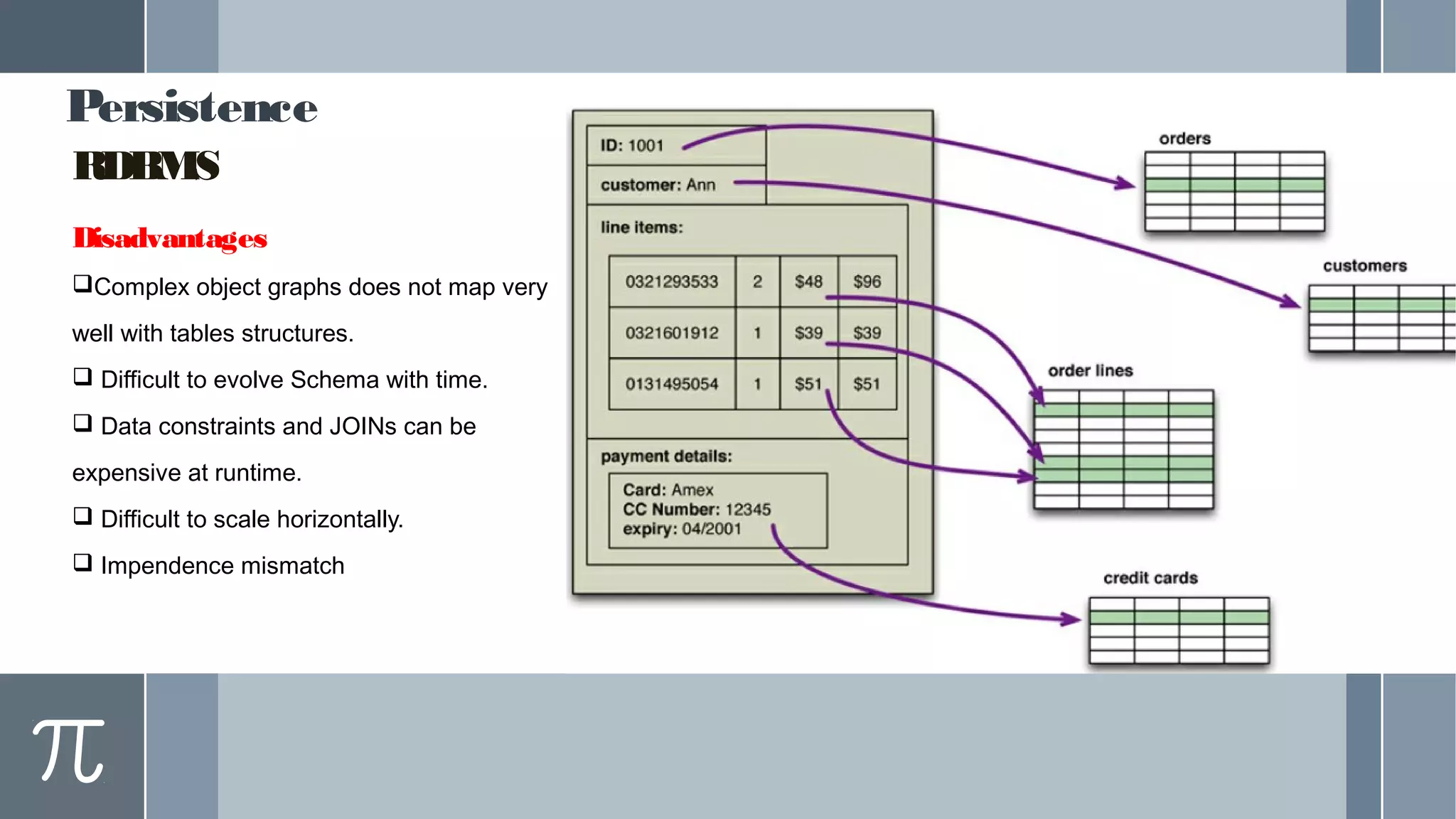
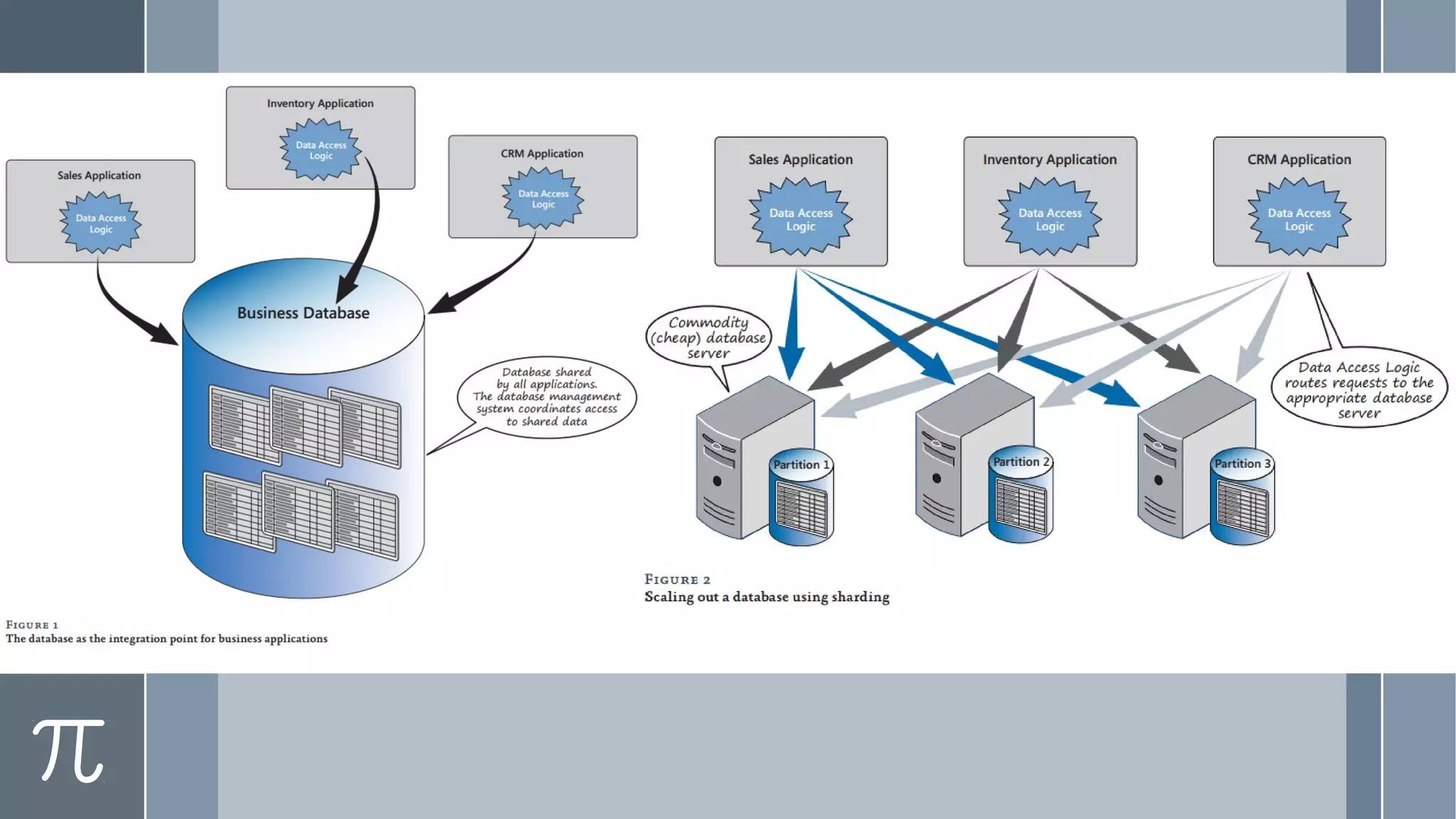
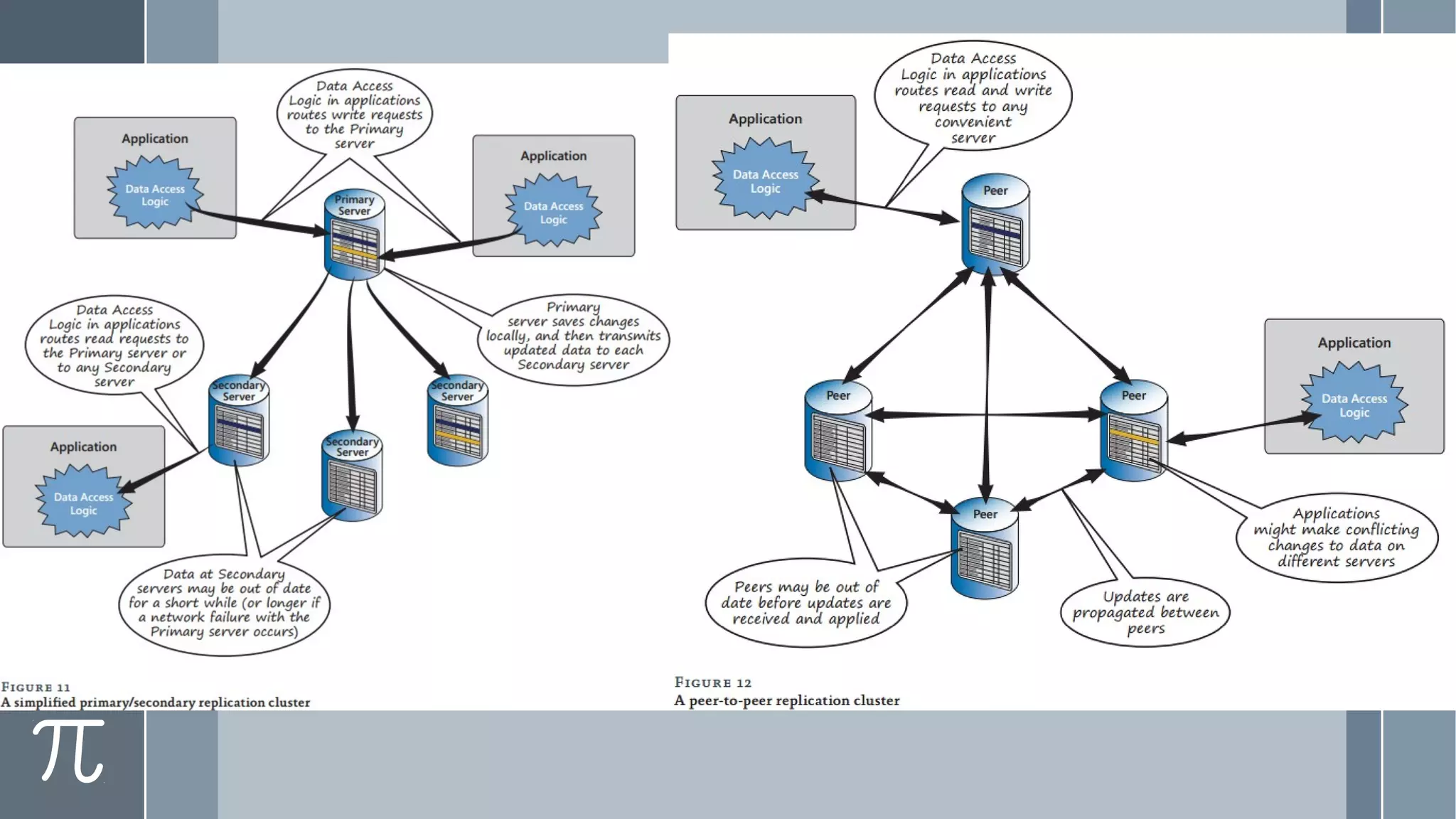
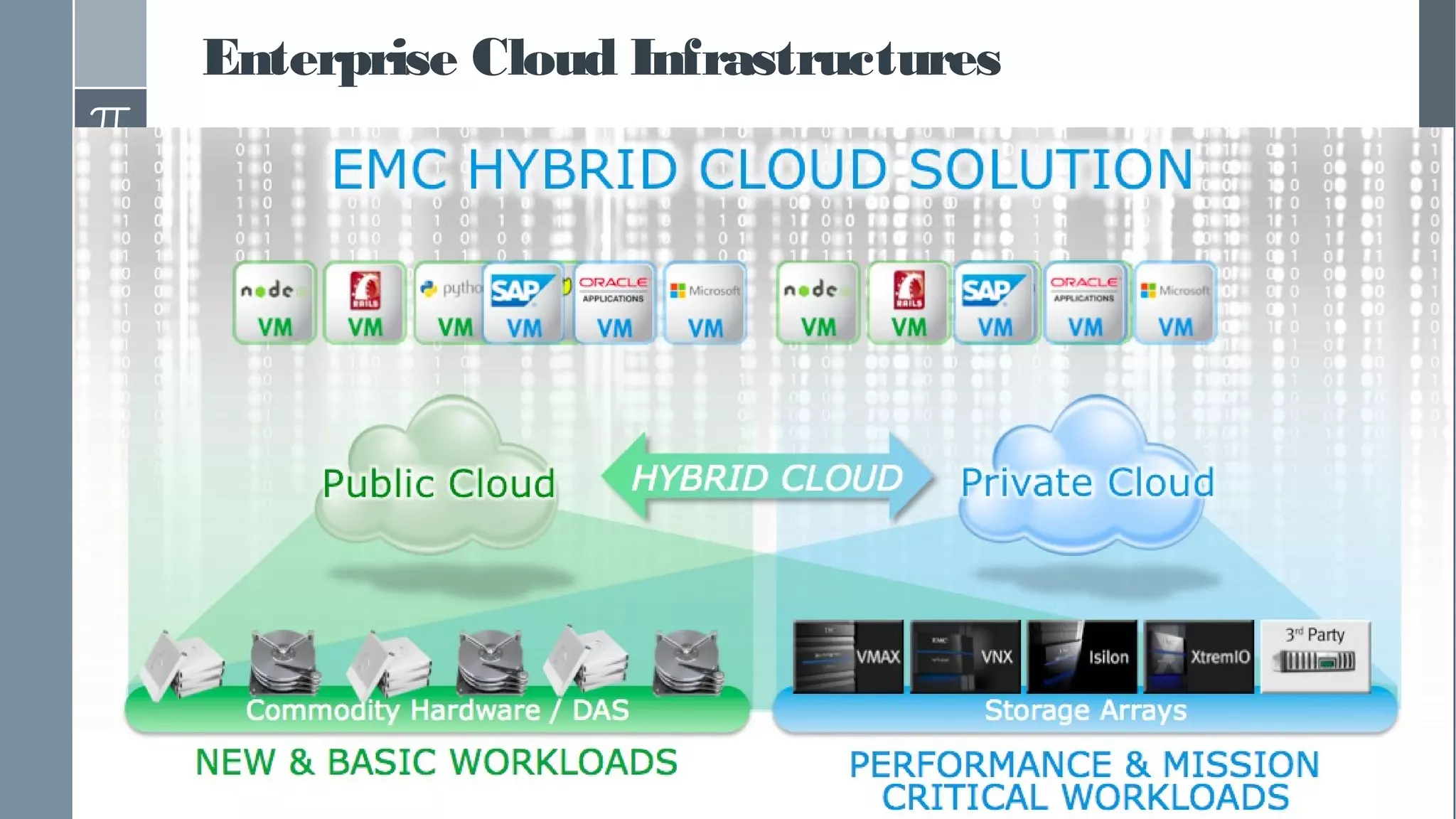
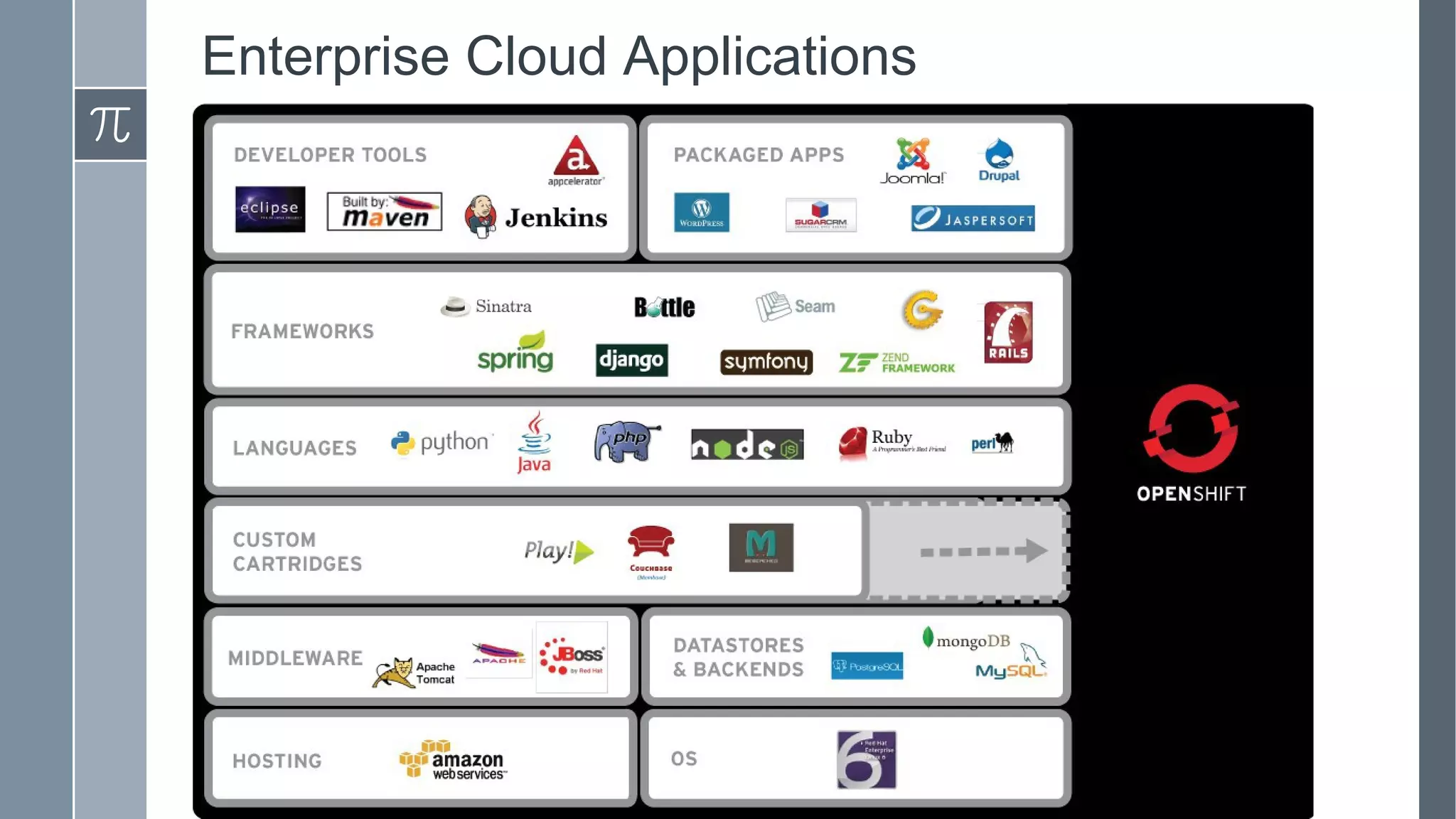
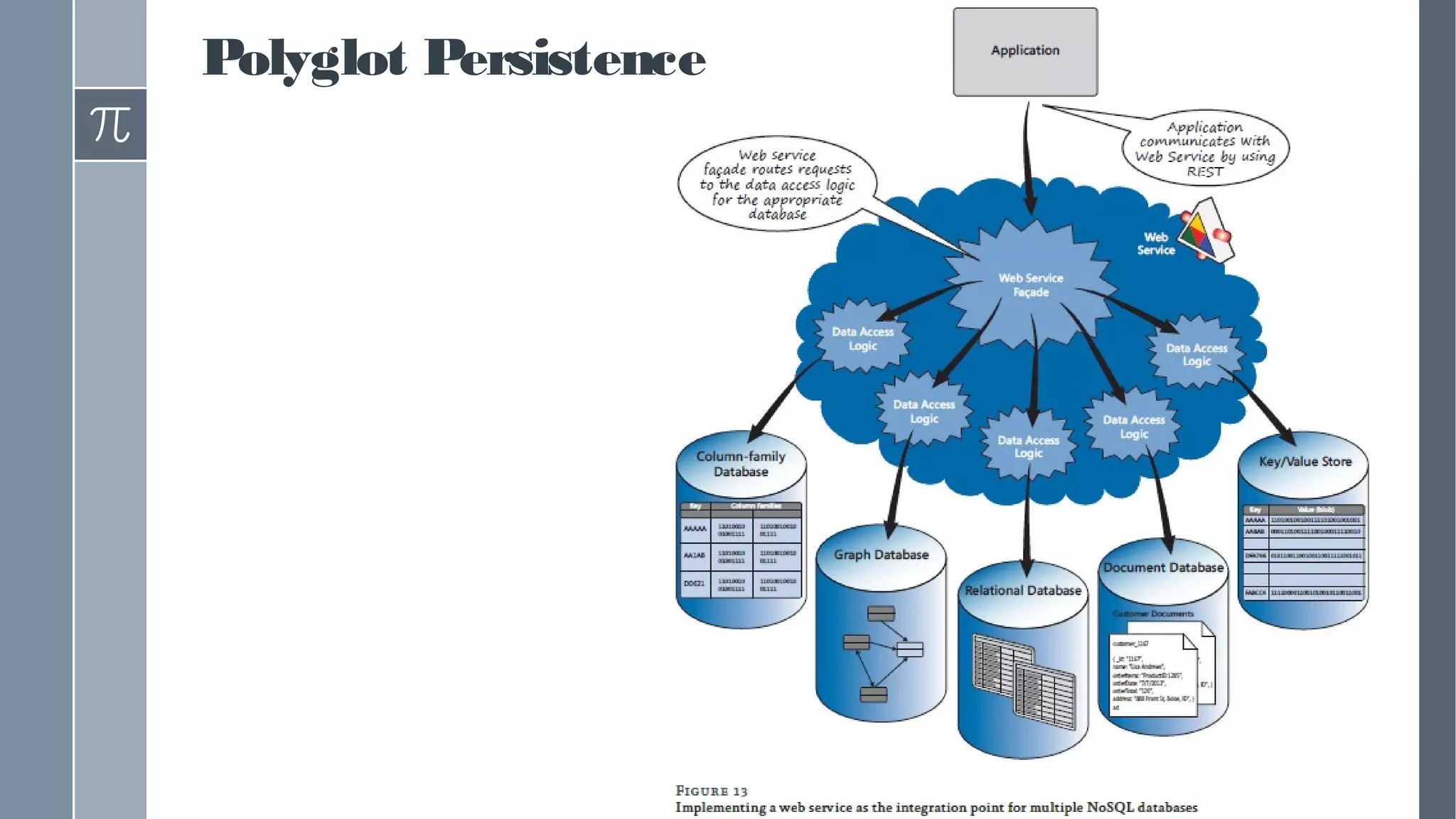
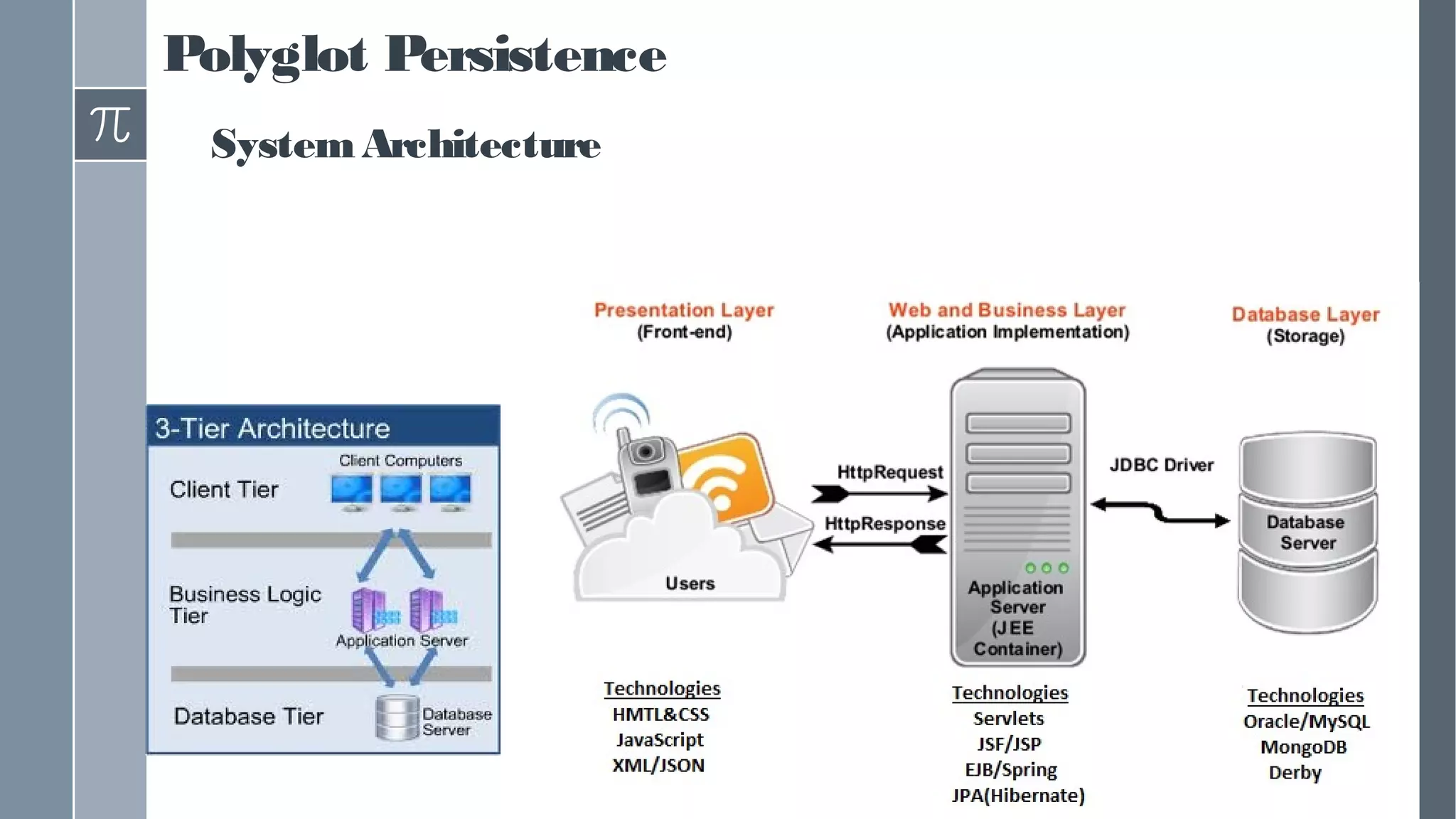
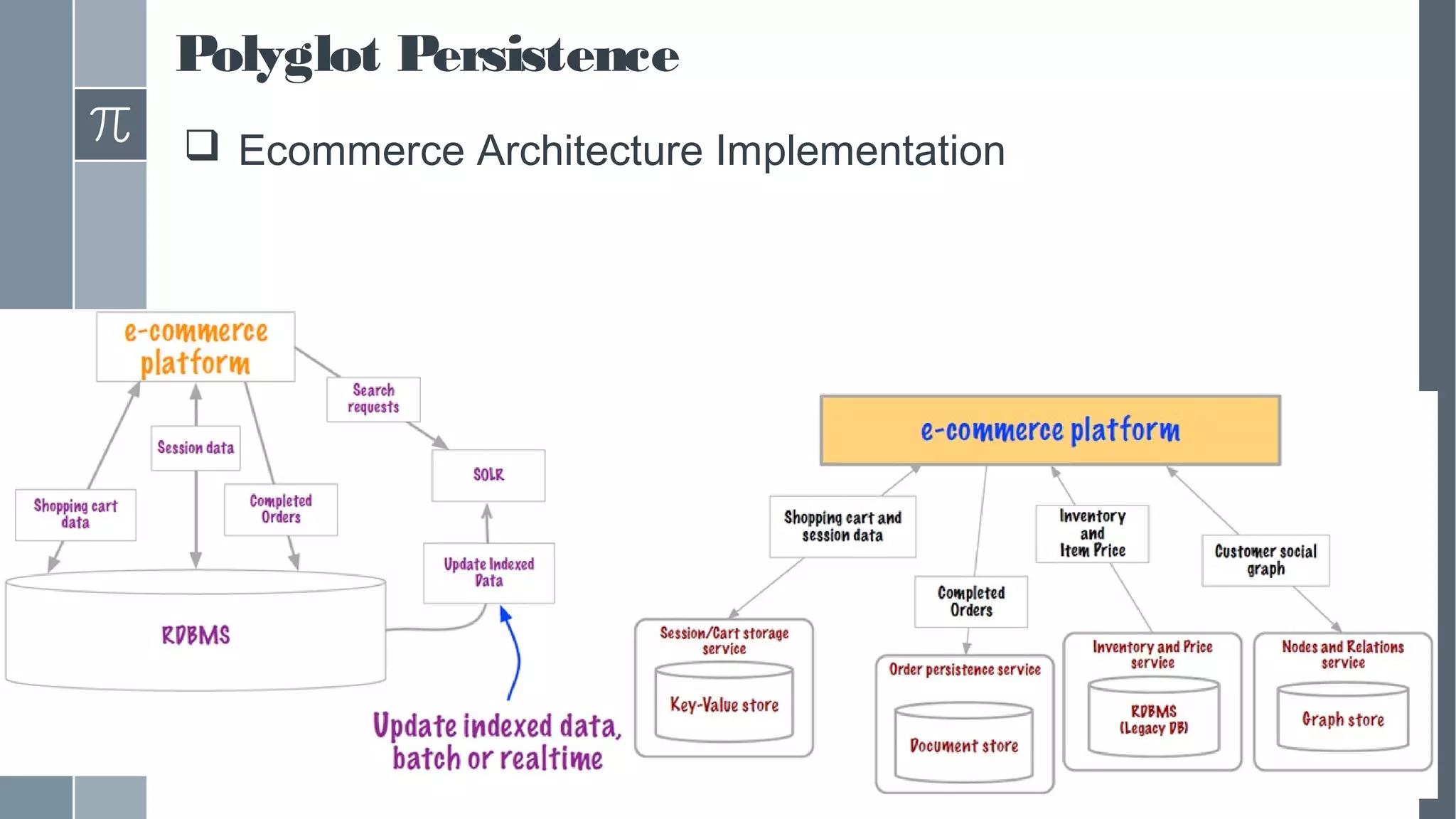
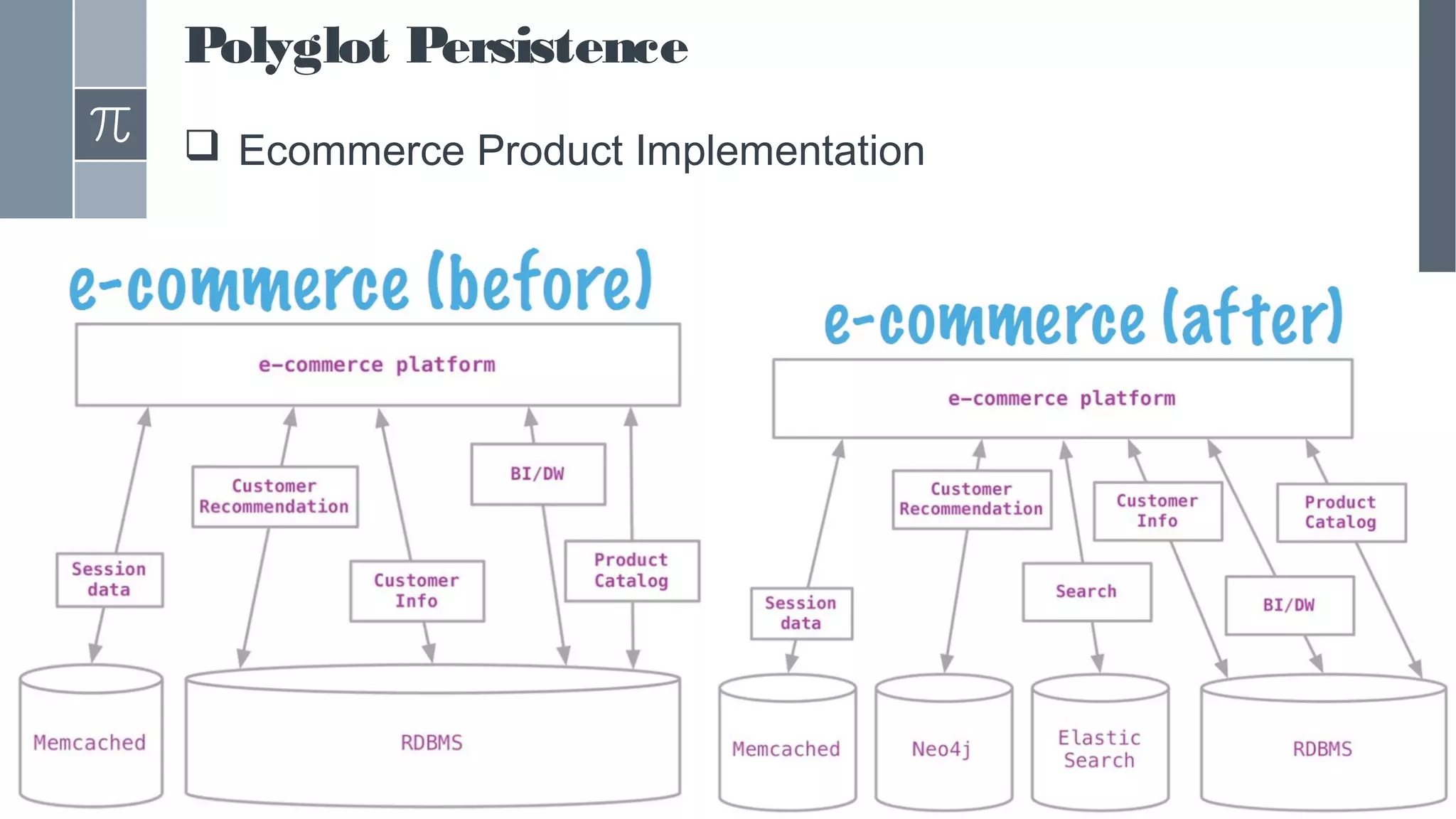
This document discusses polyglot persistence in enterprise cloud applications, detailing the advantages and disadvantages of both RDBMS and NoSQL databases. It highlights the importance of choosing suitable data storage technologies based on application needs and outlines the challenges and benefits of implementing a polyglot persistence architecture. Various references and insights from experts in the field are also included to provide further context on the topic.