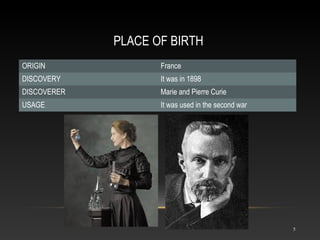
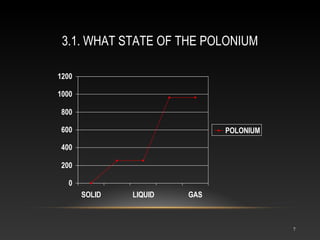
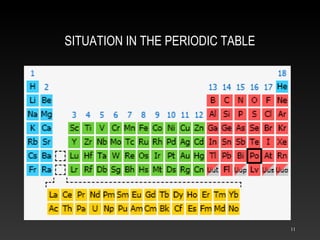
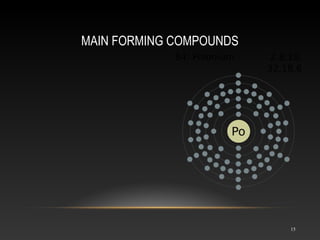
Polonium is a rare radioactive element discovered in 1898 by Marie and Pierre Curie. It is a metal that exists in solid form and belongs to the group of poor metals in the periodic table. Polonium is obtained through irradiation of bismuth with neutrons or protons since it is only found naturally in trace amounts in uranium ores. Its main uses are in compact heat sources for space probes and removing static electricity from photographic film through its radioactive emissions.