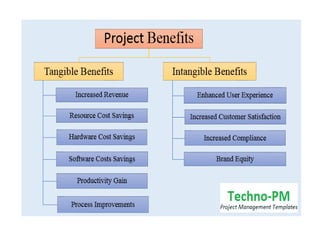
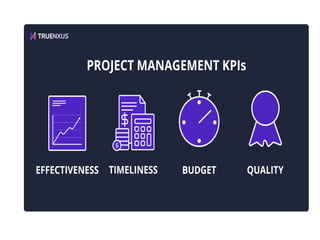
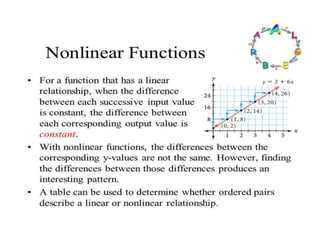
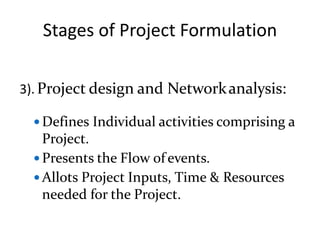
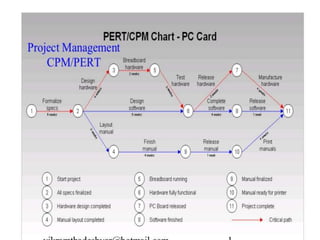
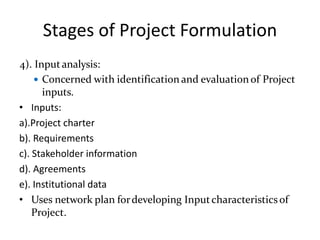
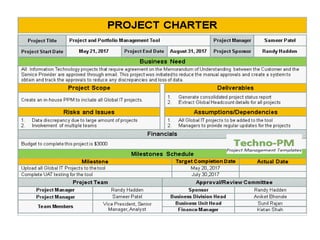
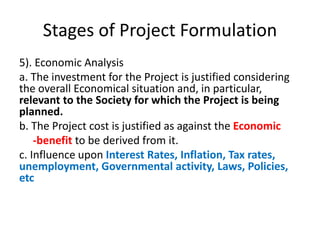
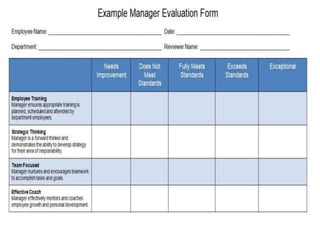
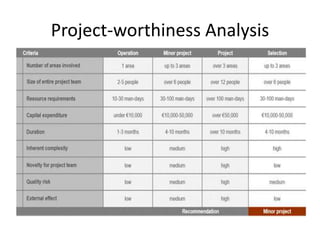
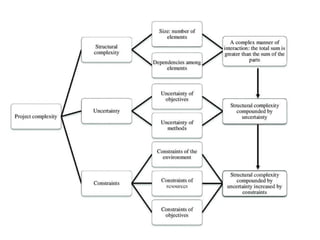
This document discusses project management and project selection methods. It defines a project, outlines the project management lifecycle which includes initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and control, and closure. It then discusses two main methods for selecting projects - benefit measurement methods and constrained optimization methods. Benefit measurement methods include discounted cash flow, cost benefit analysis, payback period, net present value, opportunity cost, scoring models, and economic model. Constrained optimization methods include linear programming, nonlinear programming, integer programming, dynamic programming, and multiple objective programming.