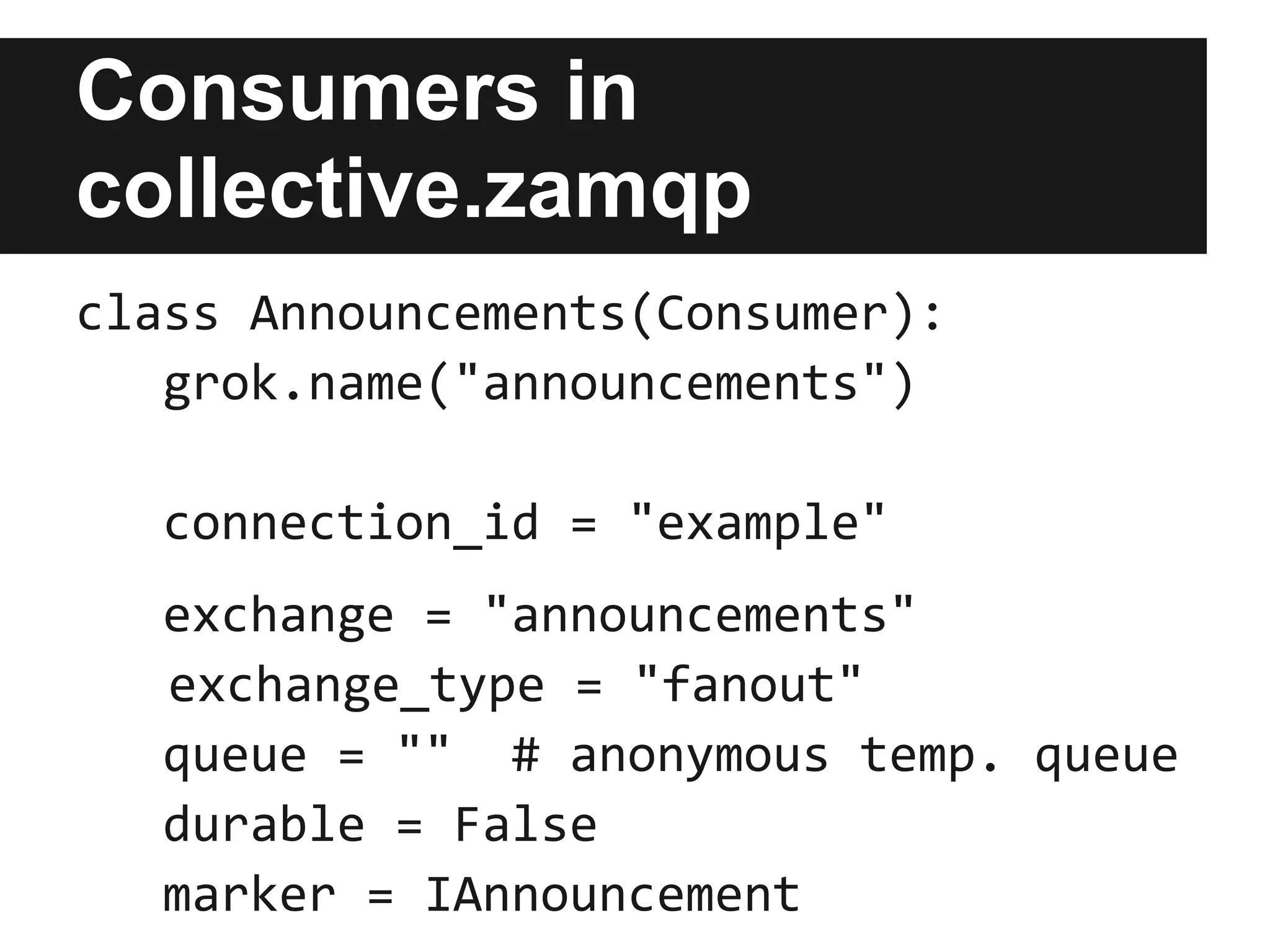
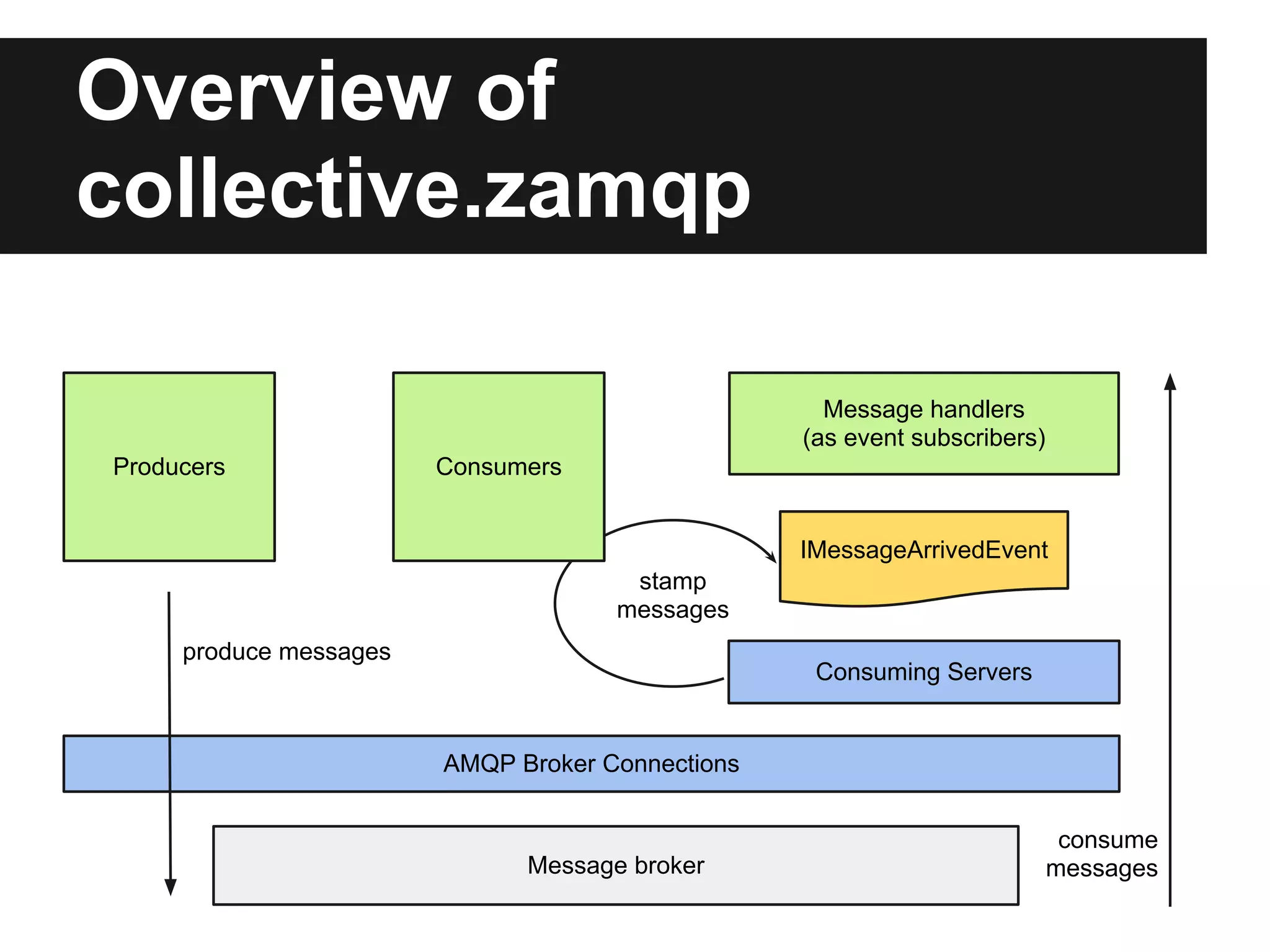
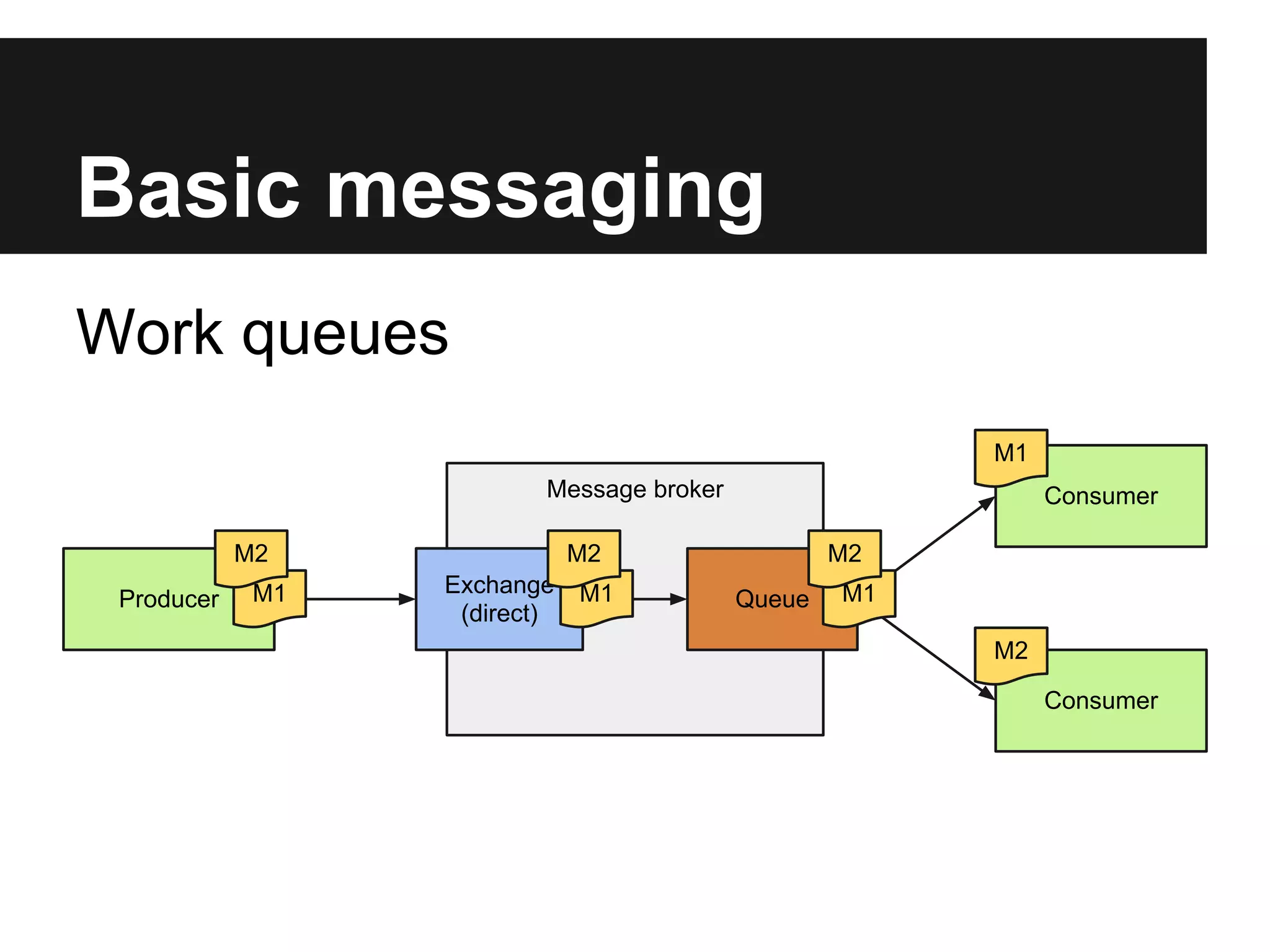
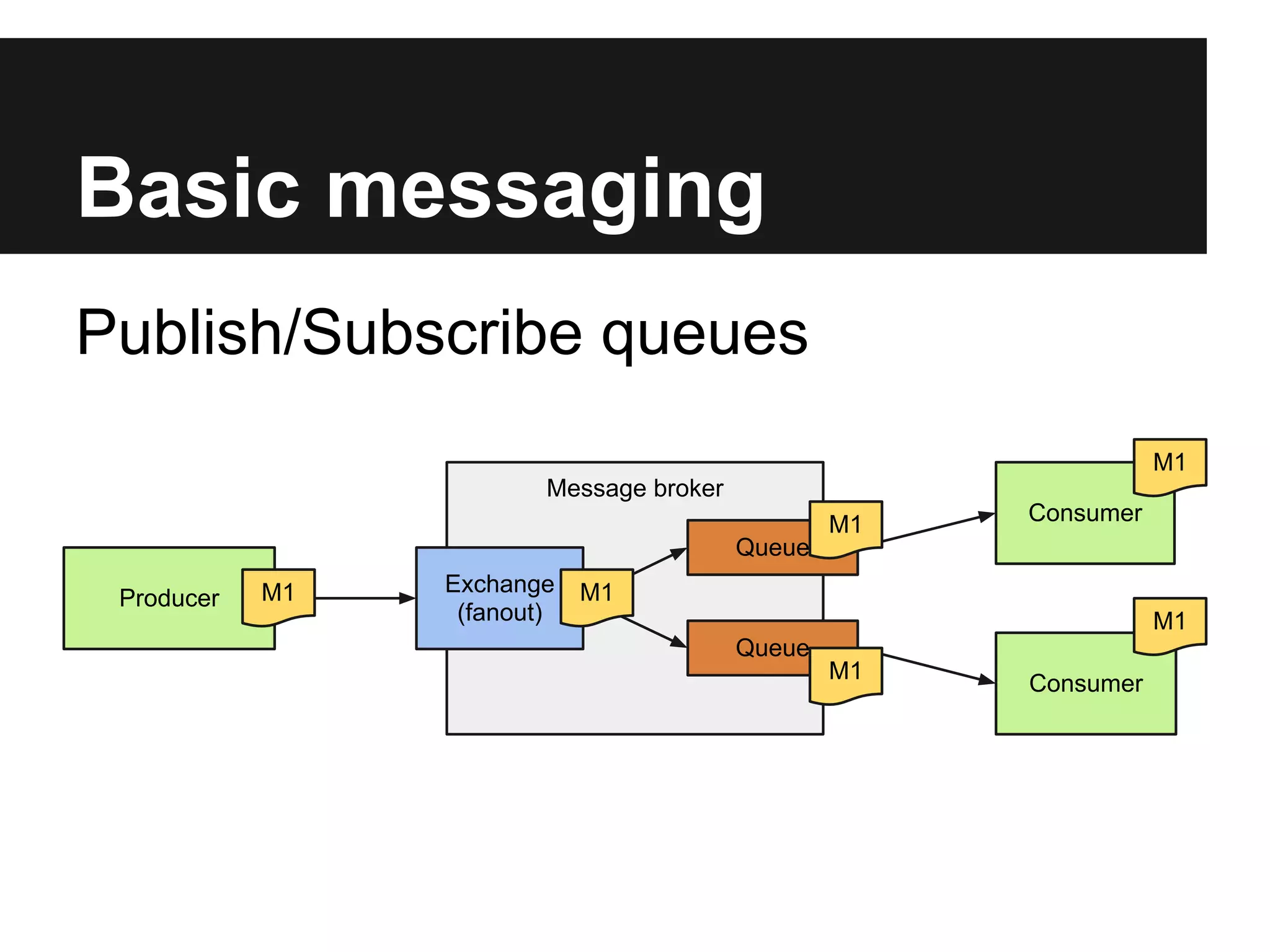
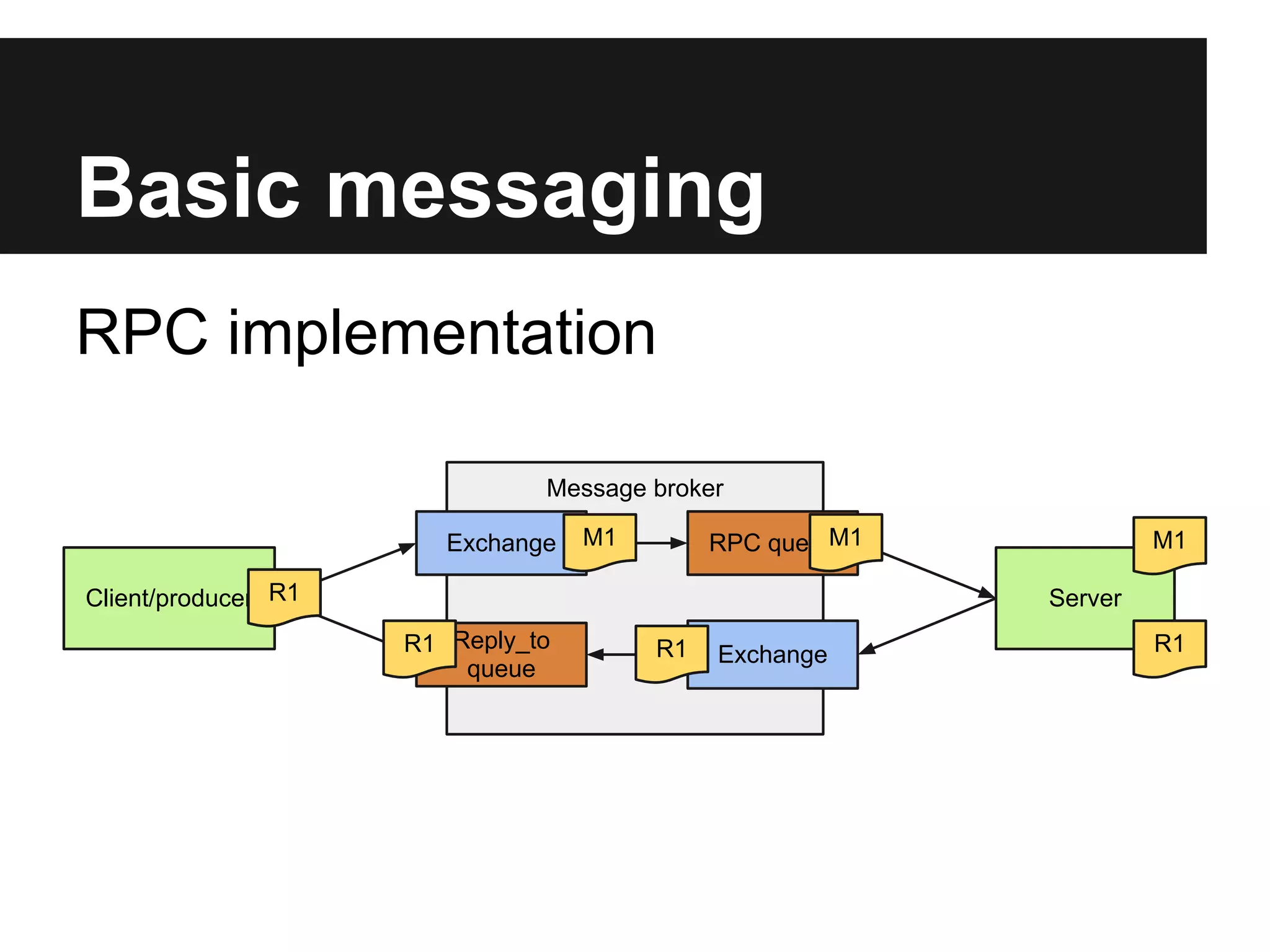
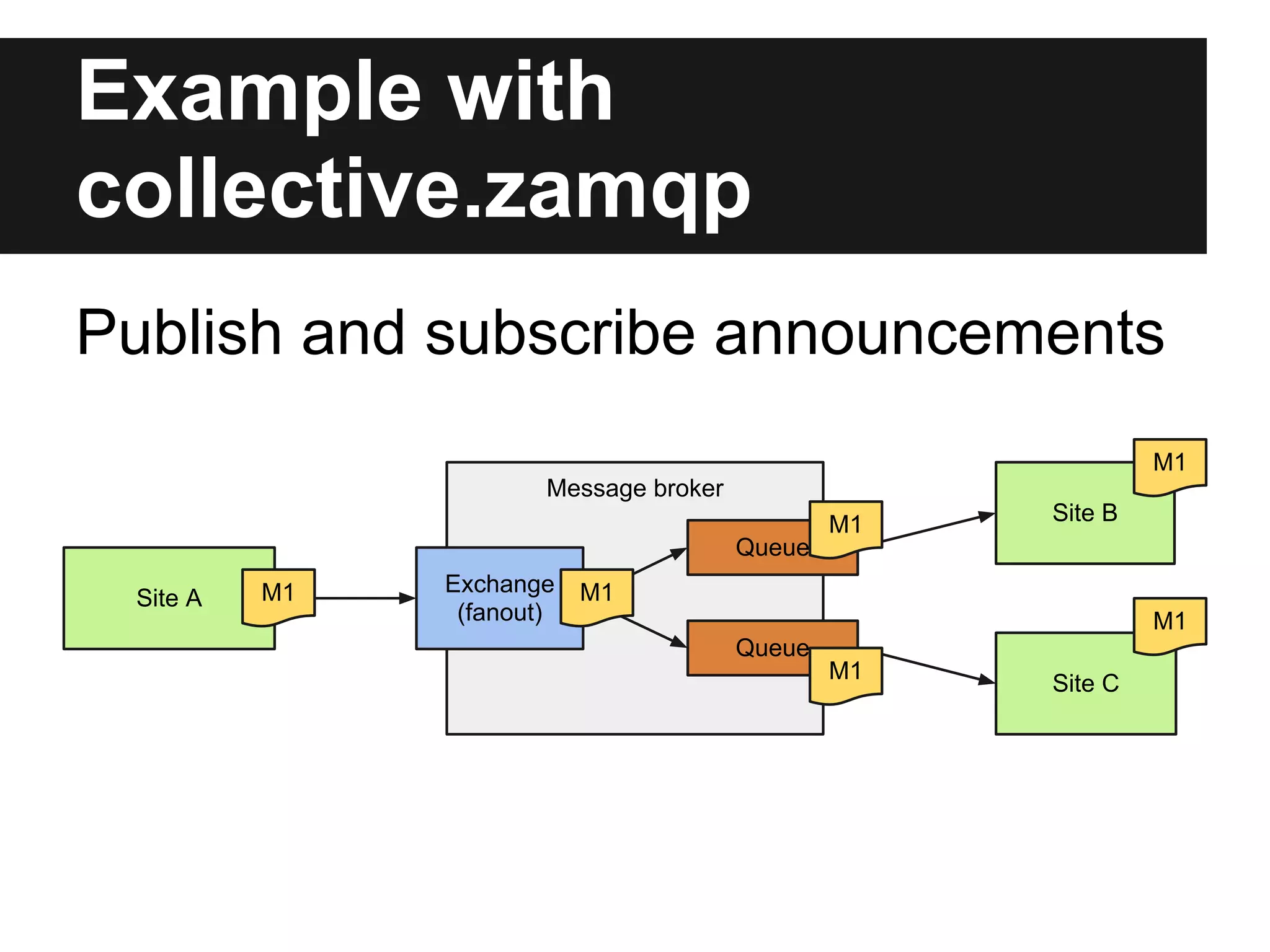
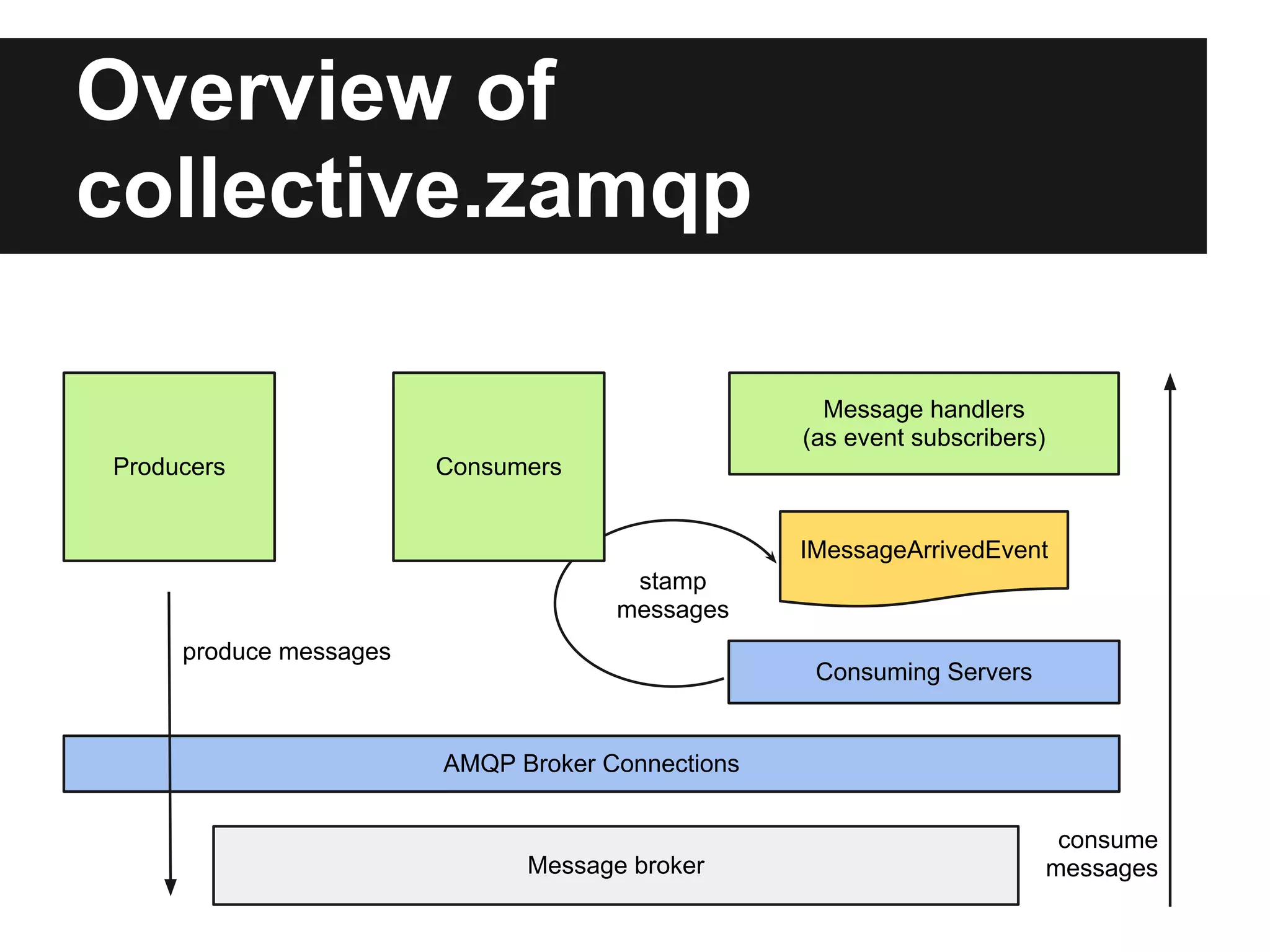
This document discusses using RabbitMQ and message queues with Plone. It provides an overview of message queues and how they can provide reliable, scalable solutions for running asynchronous tasks and integrating services. It introduces AMQP and describes how collective.zamqp can be used to easily produce, consume, and handle messages with Plone. Examples are given of using collective.zamqp to implement publish/subscribe and request/response patterns between Plone sites.











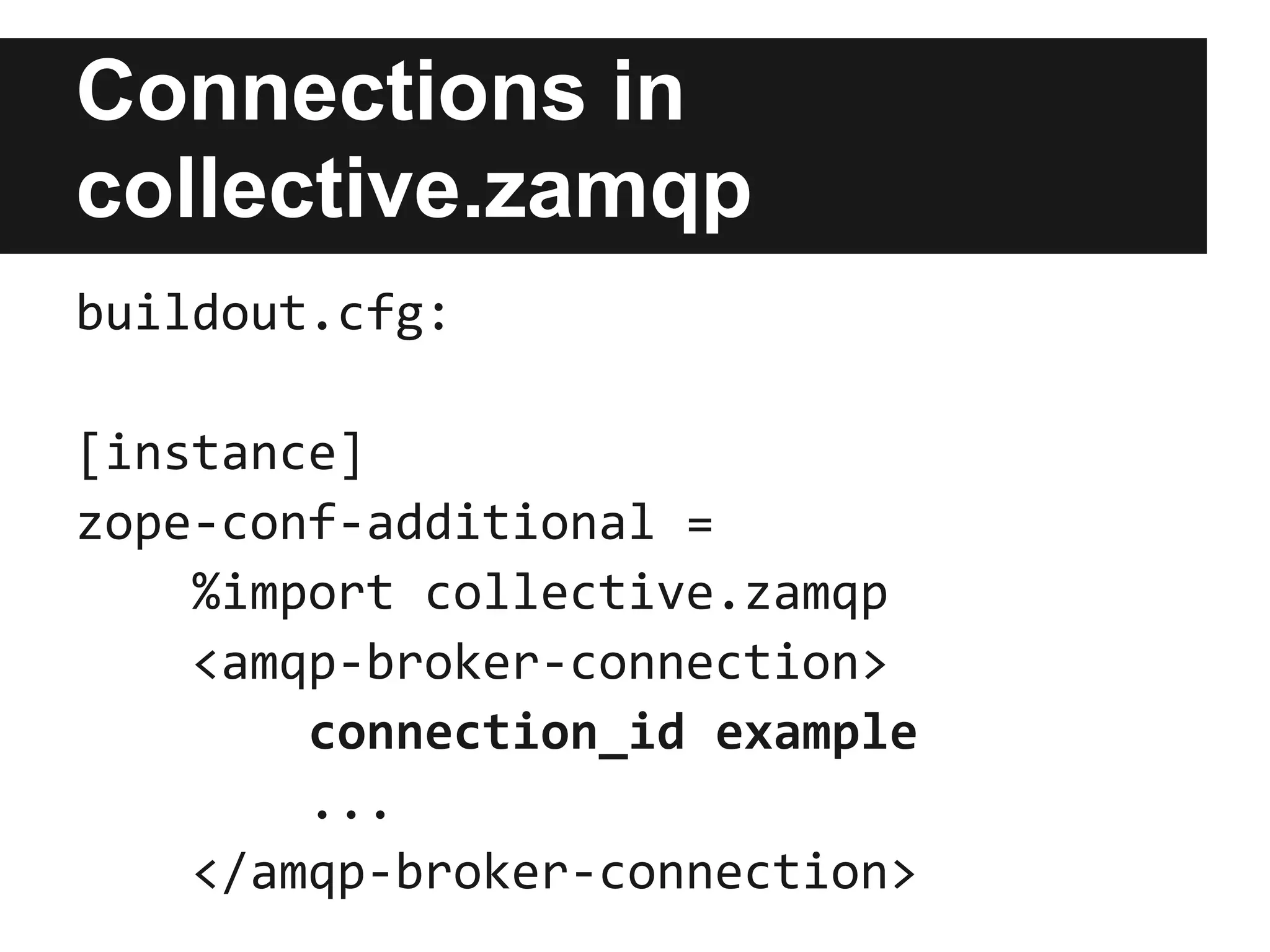
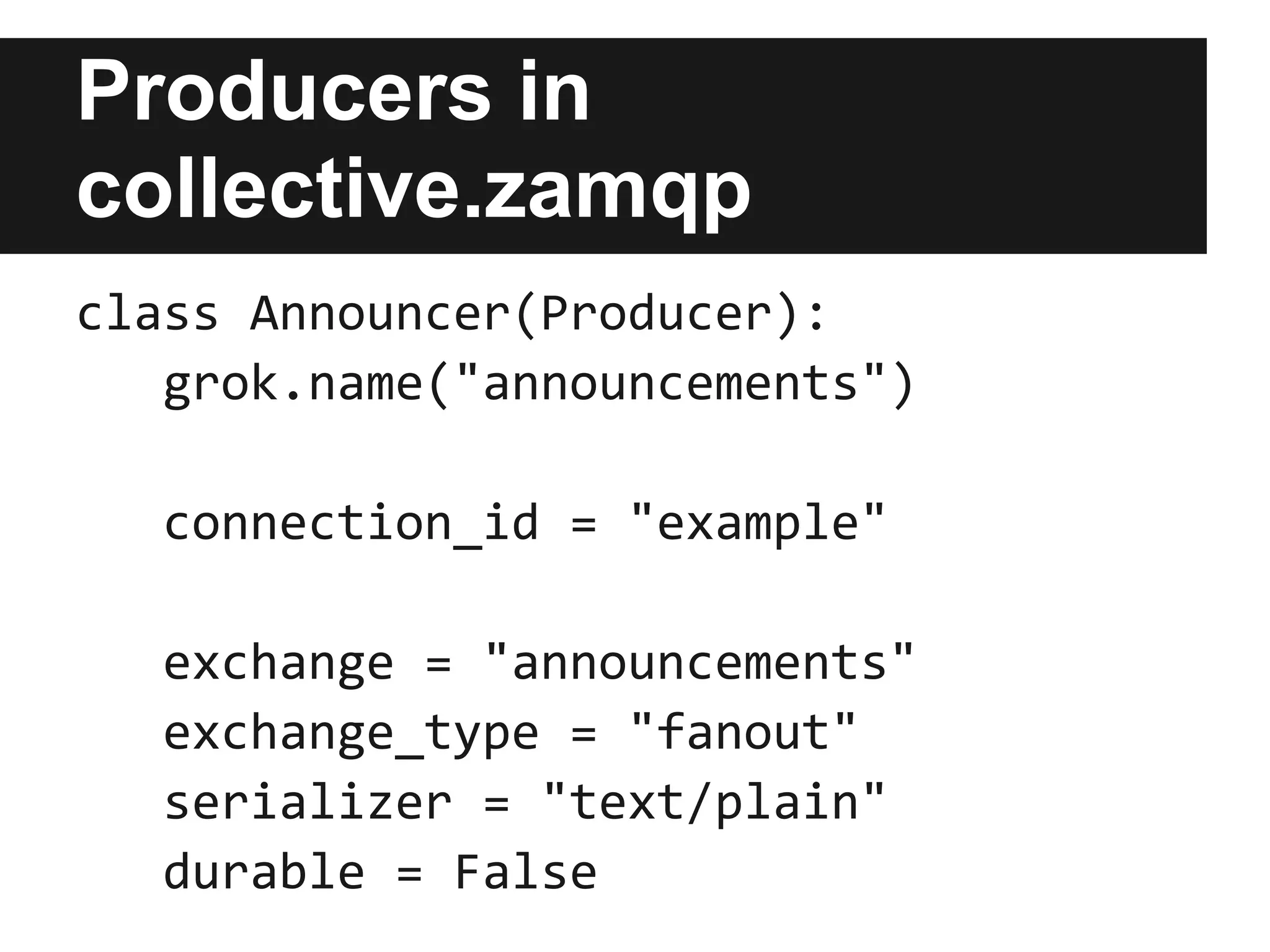
![Connections in
collective.zamqp
buildout.cfg:
[instance]
zope-conf-additional =
%import collective.zamqp
<amqp-broker-connection>
connection_id example
...
</amqp-broker-connection>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/plonerabbitmqandmessagingthatjustworks-121012035633-phpapp02/75/Plone-rabbit-mq-and-messaging-that-just-works-19-2048.jpg)