The document outlines a step-by-step approach to resource description using FRBR-based methods at Jane Austin University of Hawaii, emphasizing data structure from the RDA registry and visualization of records. It discusses workflow enhancement through the use of cache instead of traditional databases to enable better data management and automation. Key topics include data provenance, continuous improvement of data quality, and the importance of human versus machine roles in data handling.

![Why RIMMF?
Well constructed for FRBR-based description
Data structure comes from RDA Registry
Links to RDA Toolkit throughout data building
process
Useful visualization of groups of records
RDF export
Improves discussion of issues with RDA
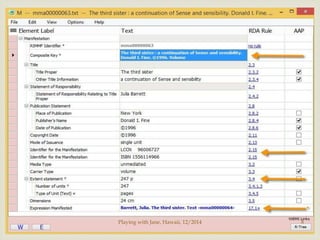
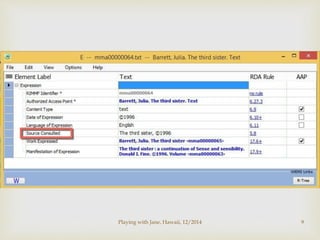
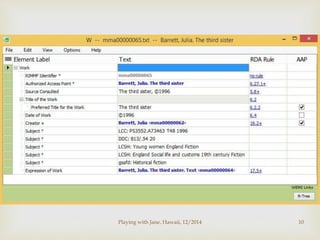
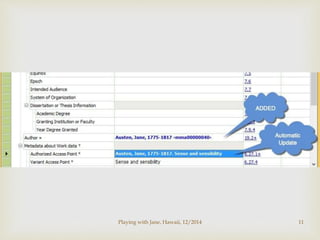
Step-by-step illustration of adding a record [next]
Playing with Jane, Hawaii, 12/2014 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playingwithjane2-141211115443-conversion-gate02/85/Playing-with-Jane-2-320.jpg)

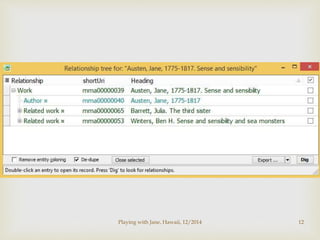
![Issues for Discussion
Record sharing
Identification
RDF
Data Aggregation
Looking more clearly at workflow and maintenance
Provenance: who, what when, [where?]
Playing with Jane, Hawaii, 12/2014 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playingwithjane2-141211115443-conversion-gate02/85/Playing-with-Jane-13-320.jpg)
![Workflow
Obtain data (possibly as ‘records’)
Store data as statements in cache
Evaluate data by source or collection
Improve data using specific services, as determined
by evaluation
Publish improved data
[Rinse, repeat]
Playing with Jane, Hawaii, 12/2014 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/playingwithjane2-141211115443-conversion-gate02/85/Playing-with-Jane-15-320.jpg)


