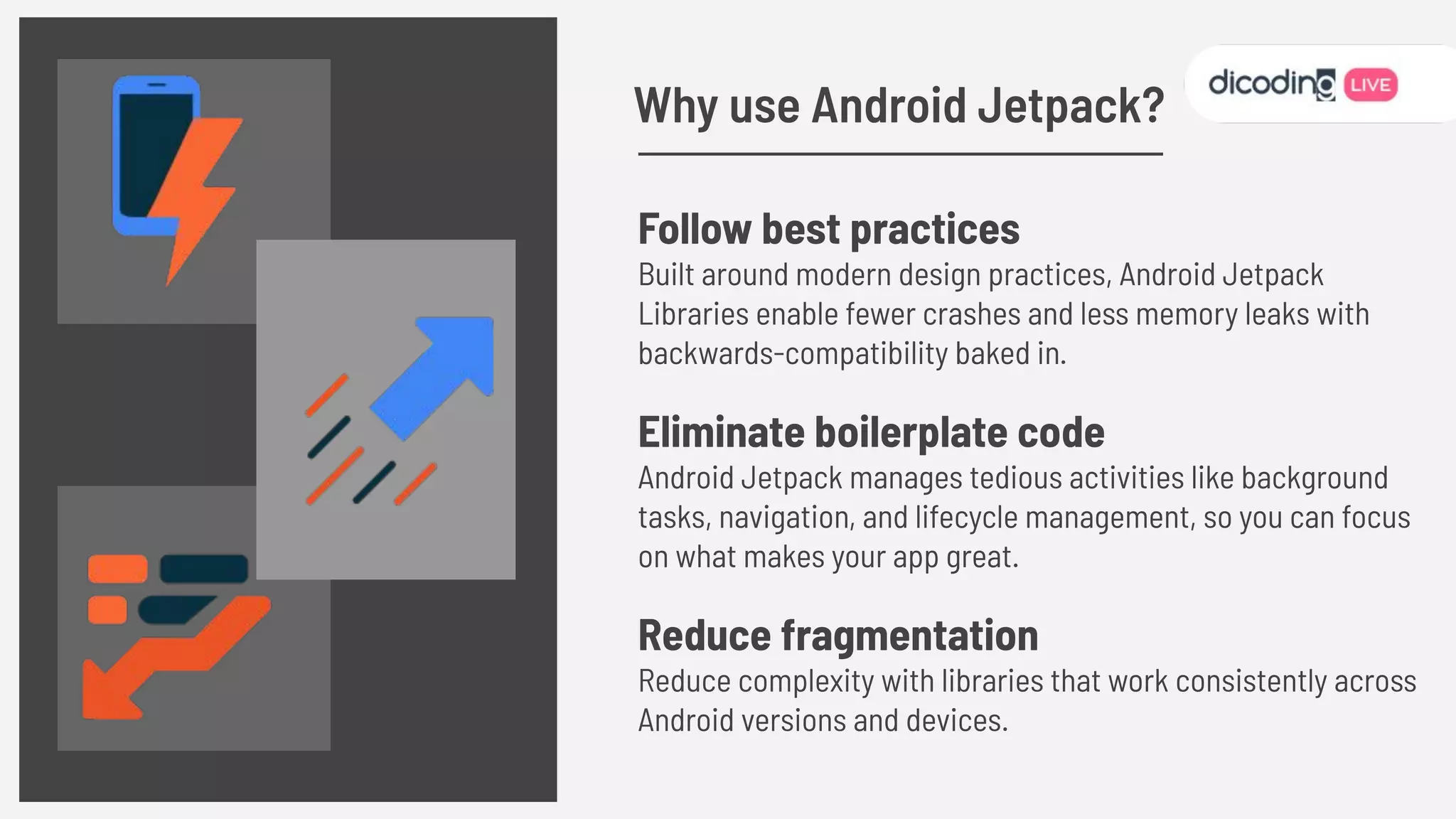
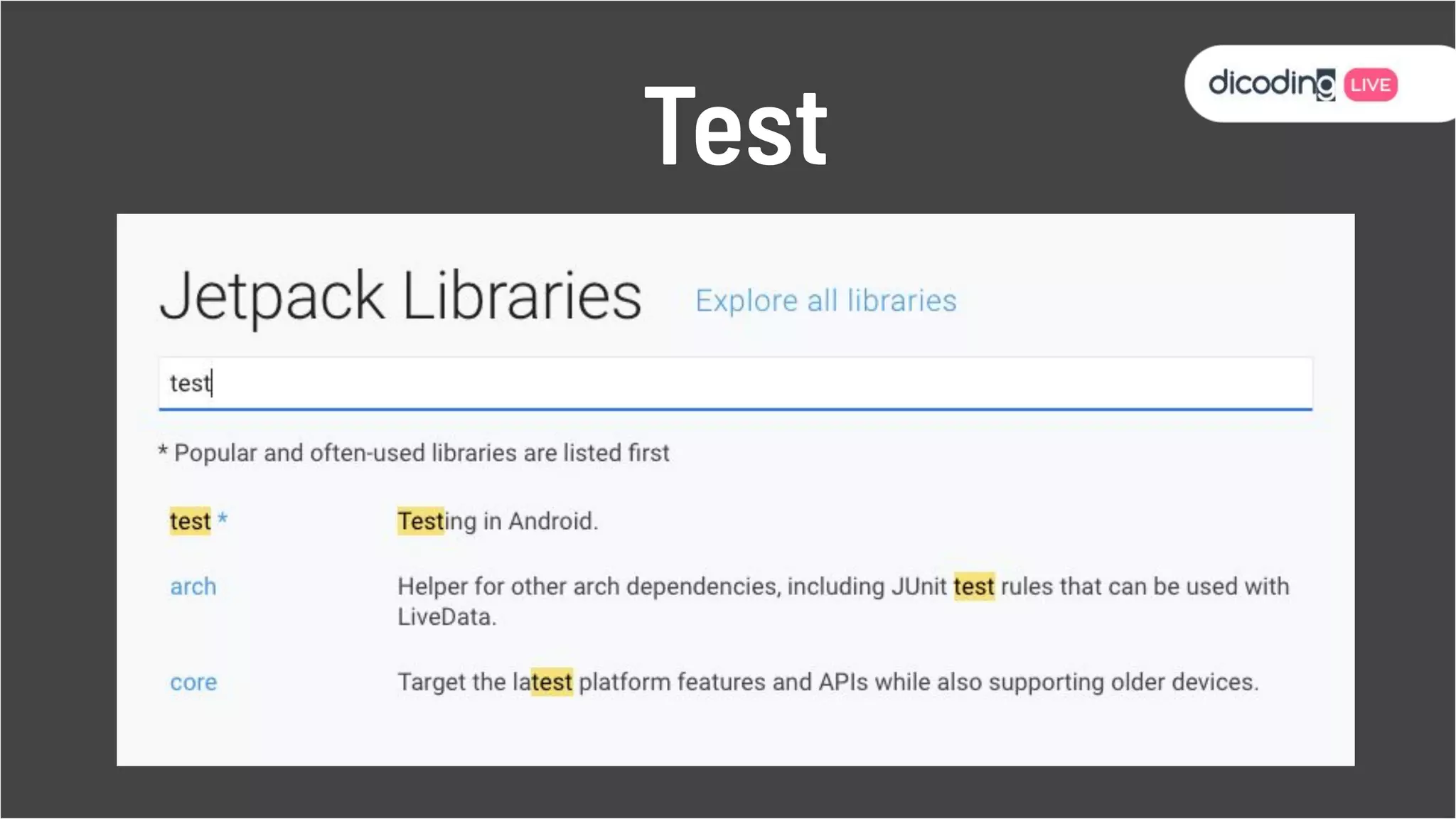
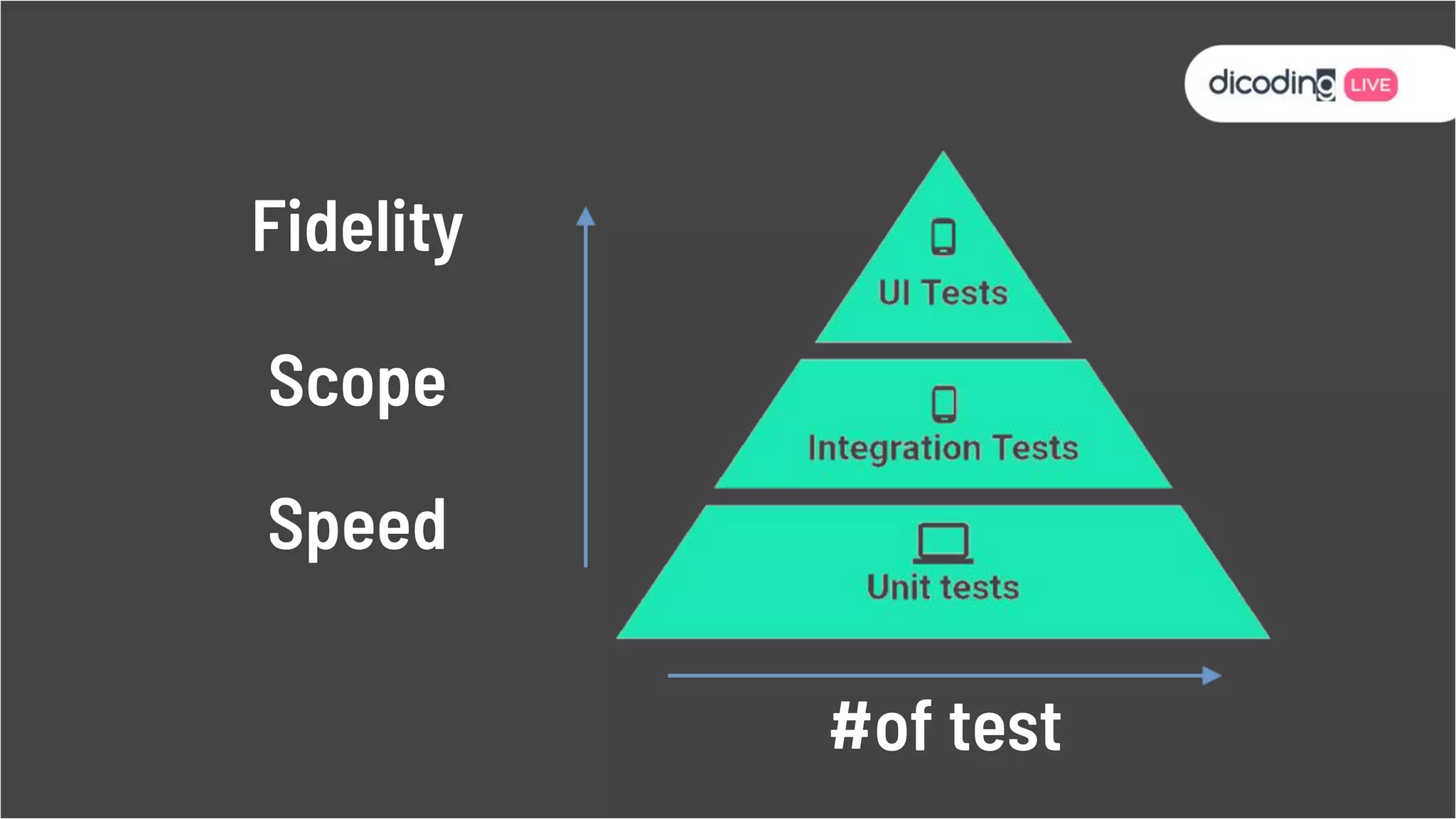
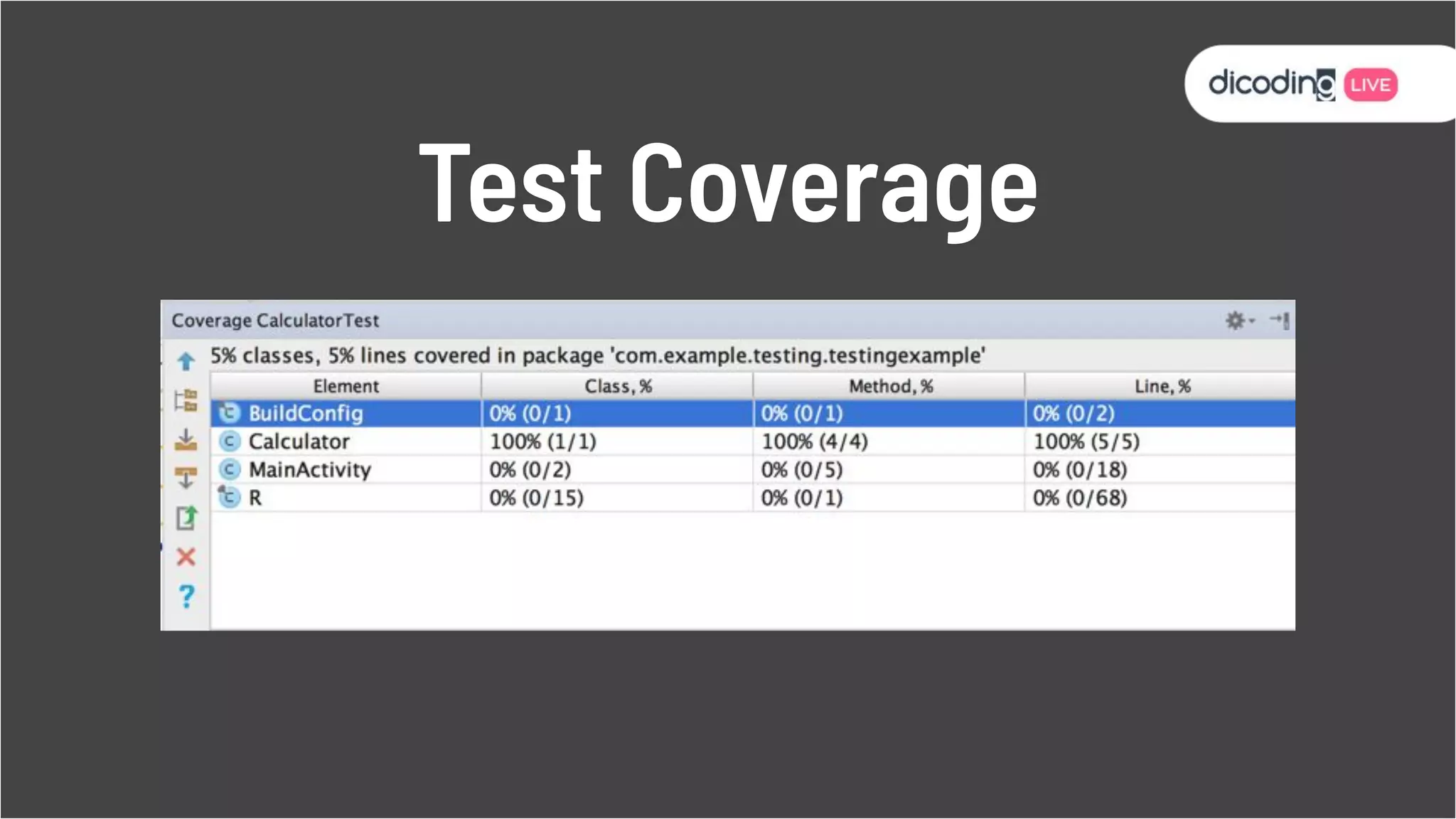
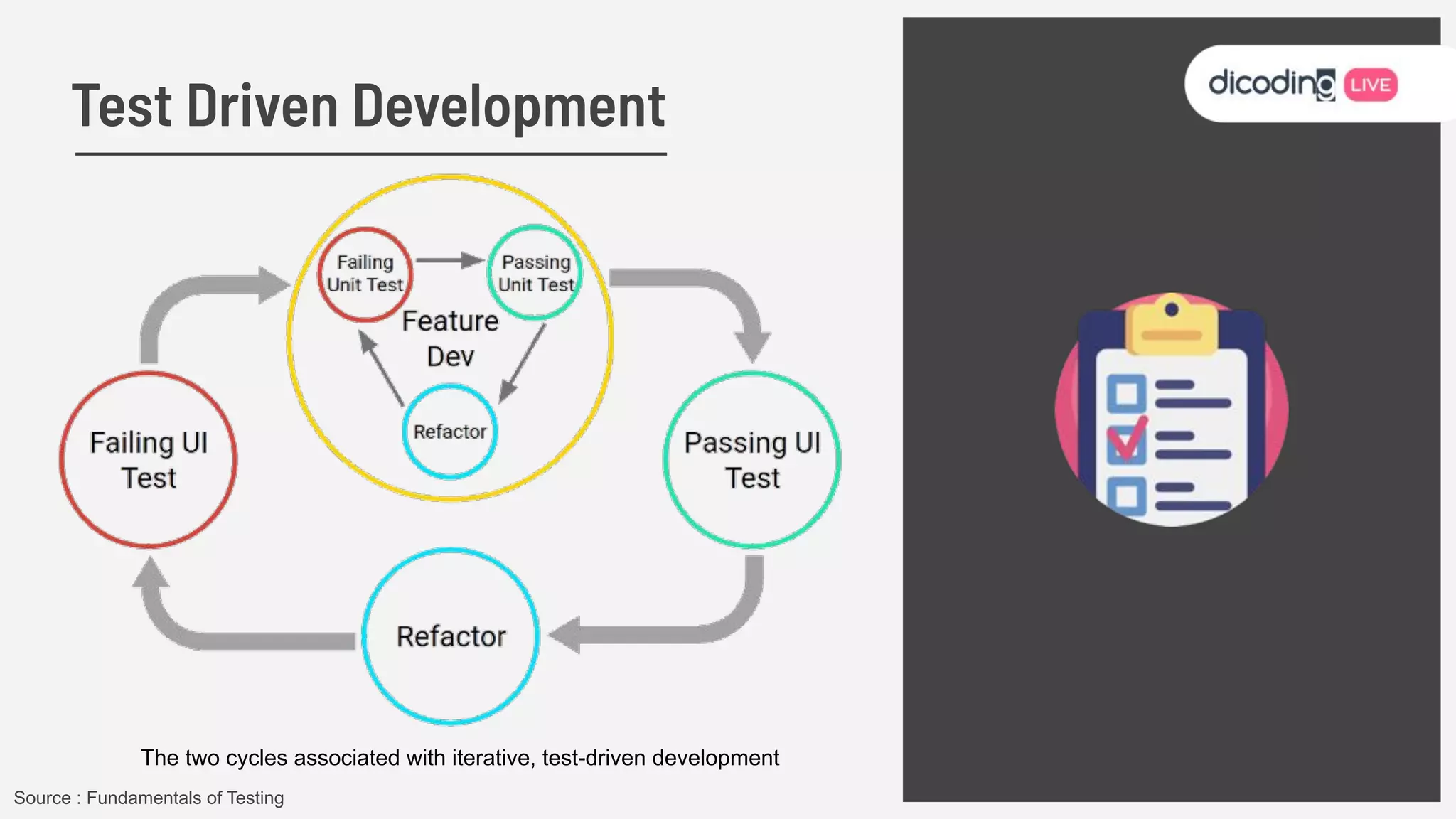
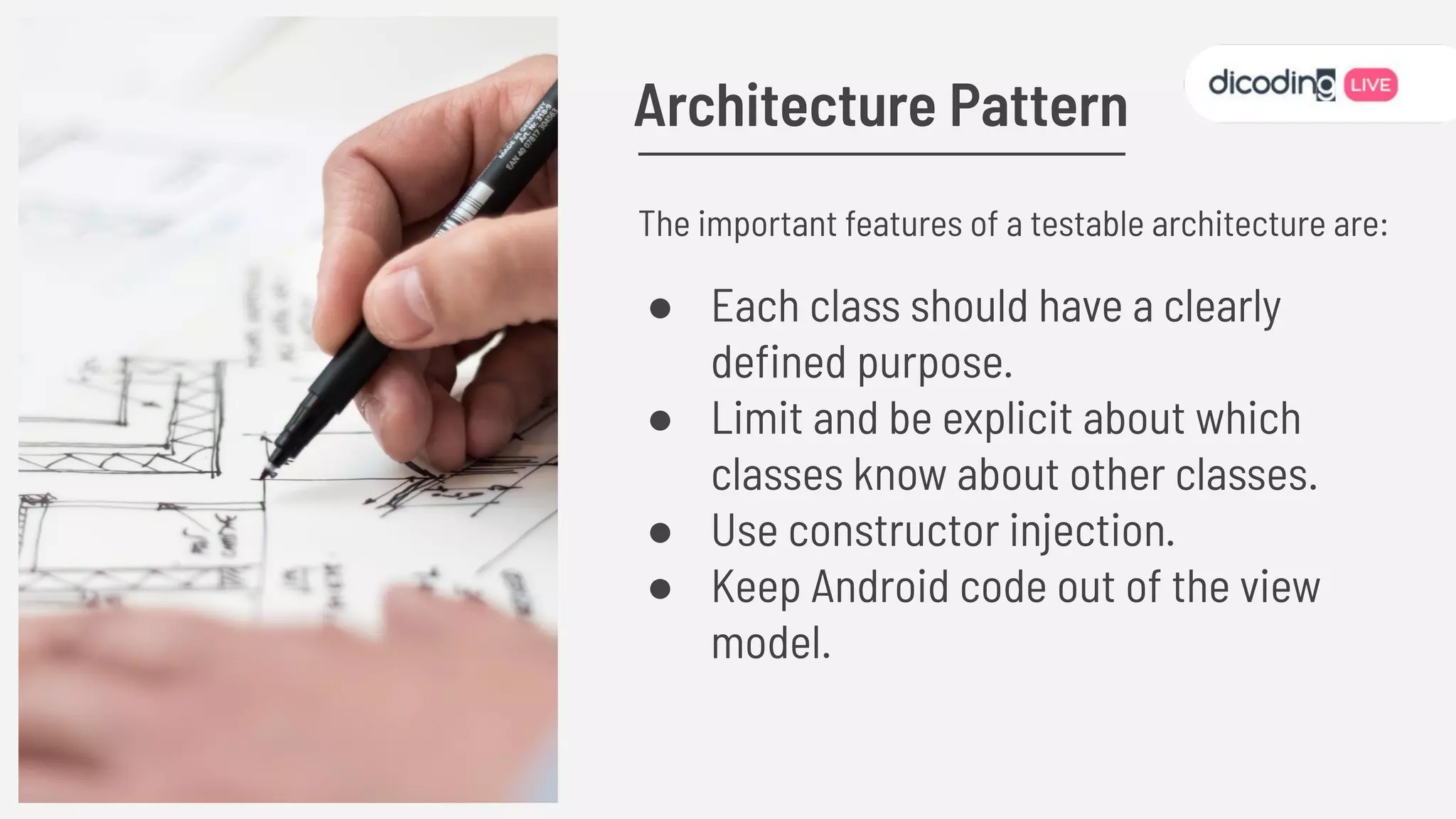
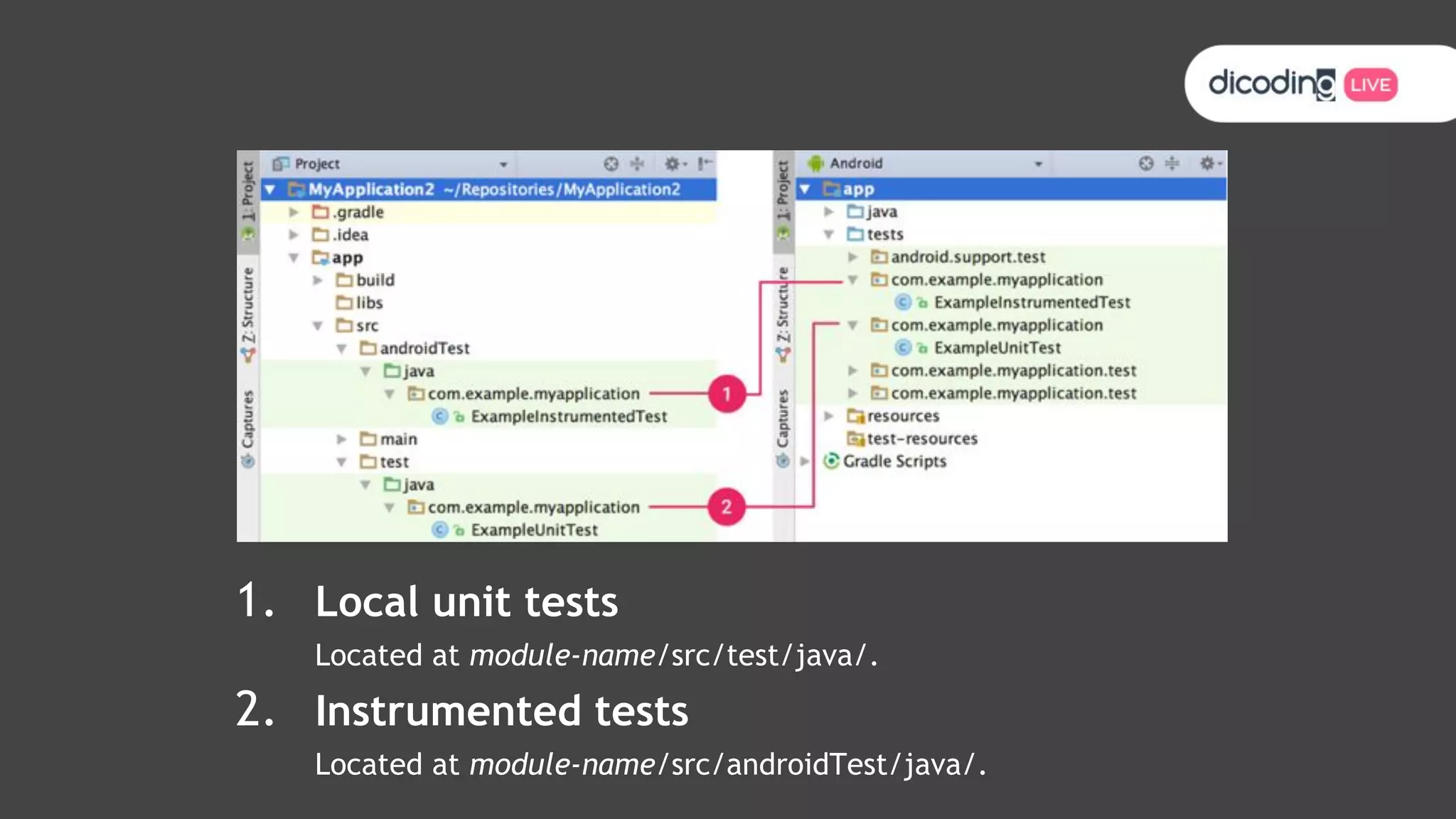
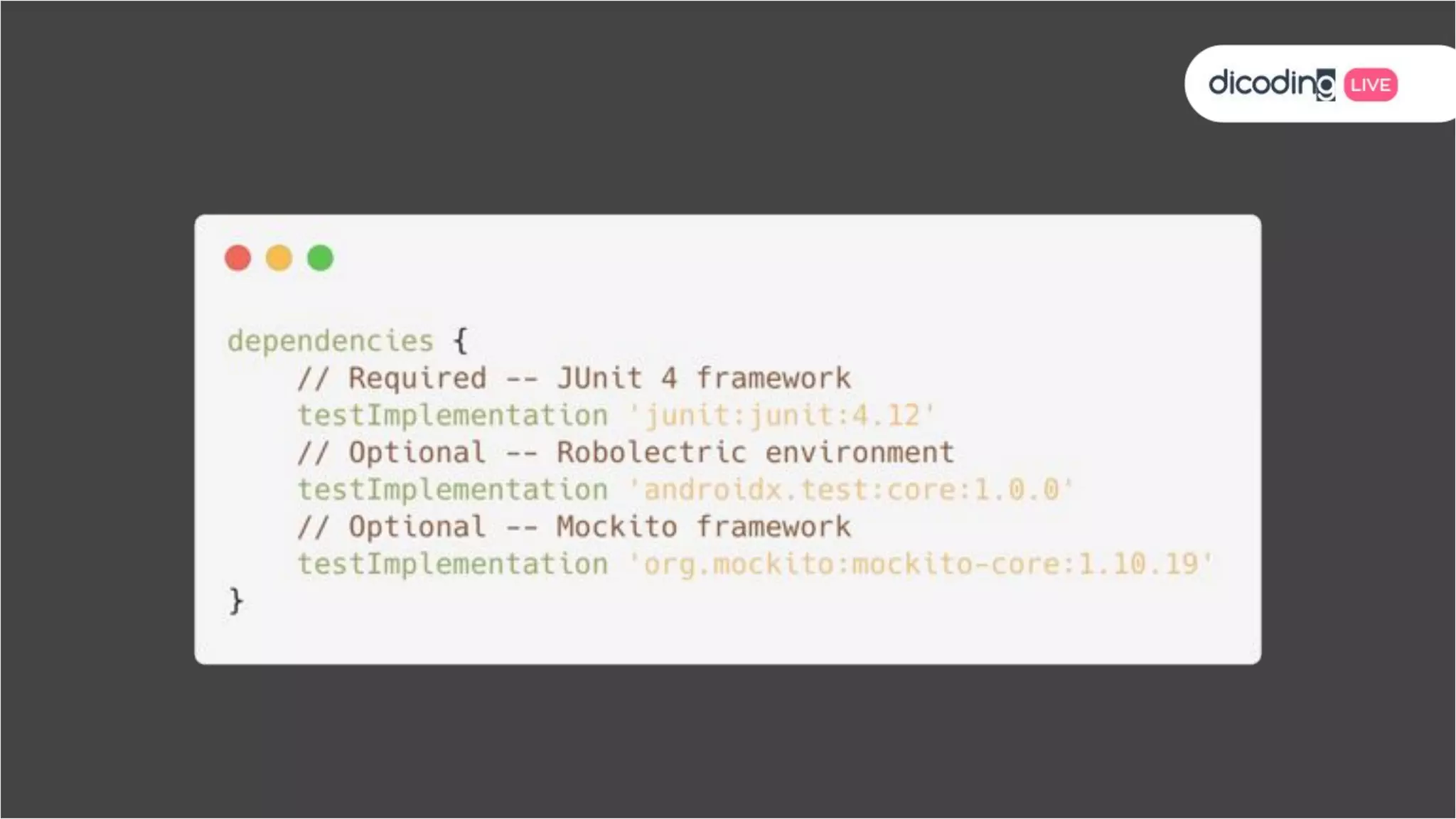
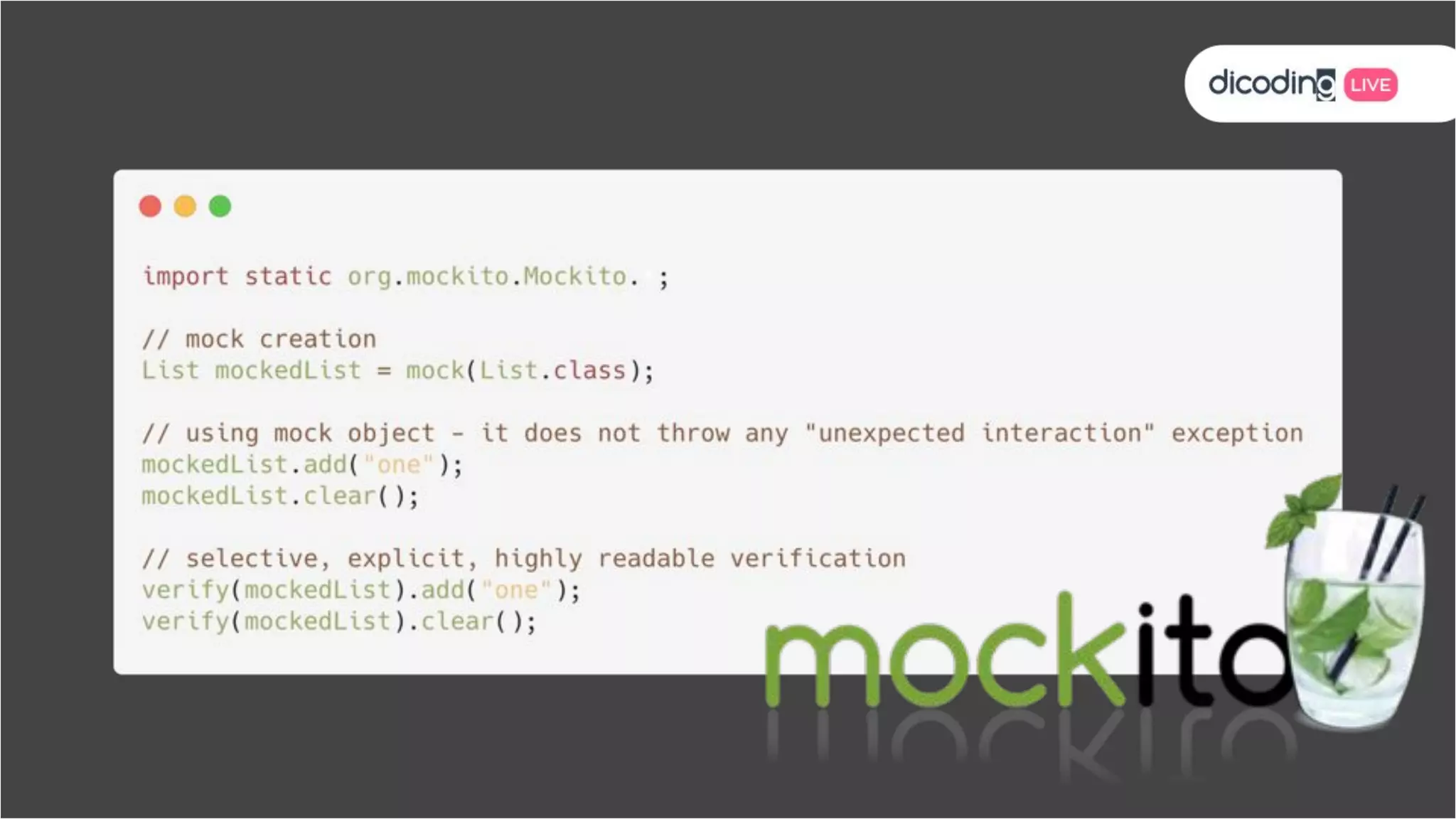
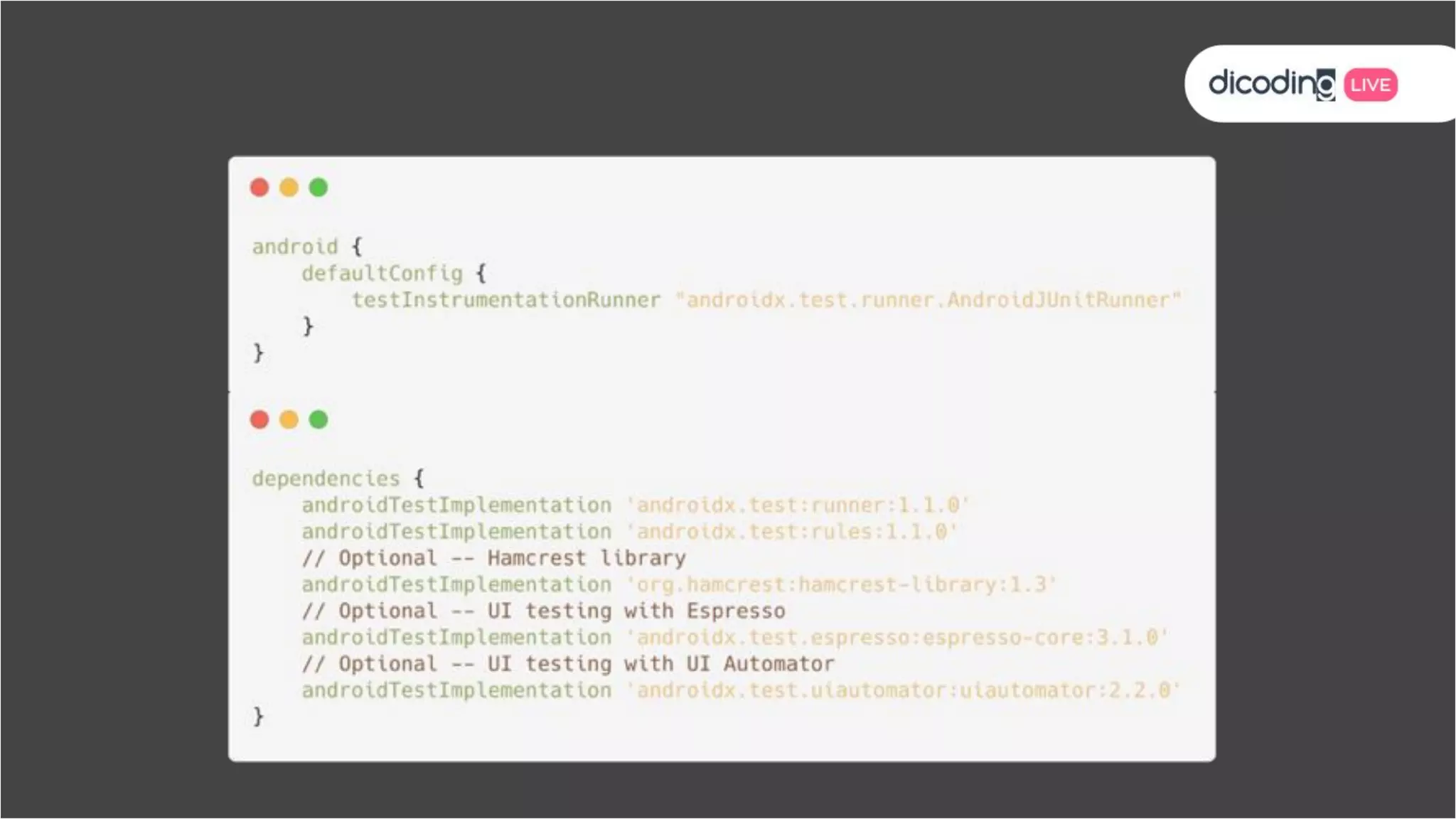
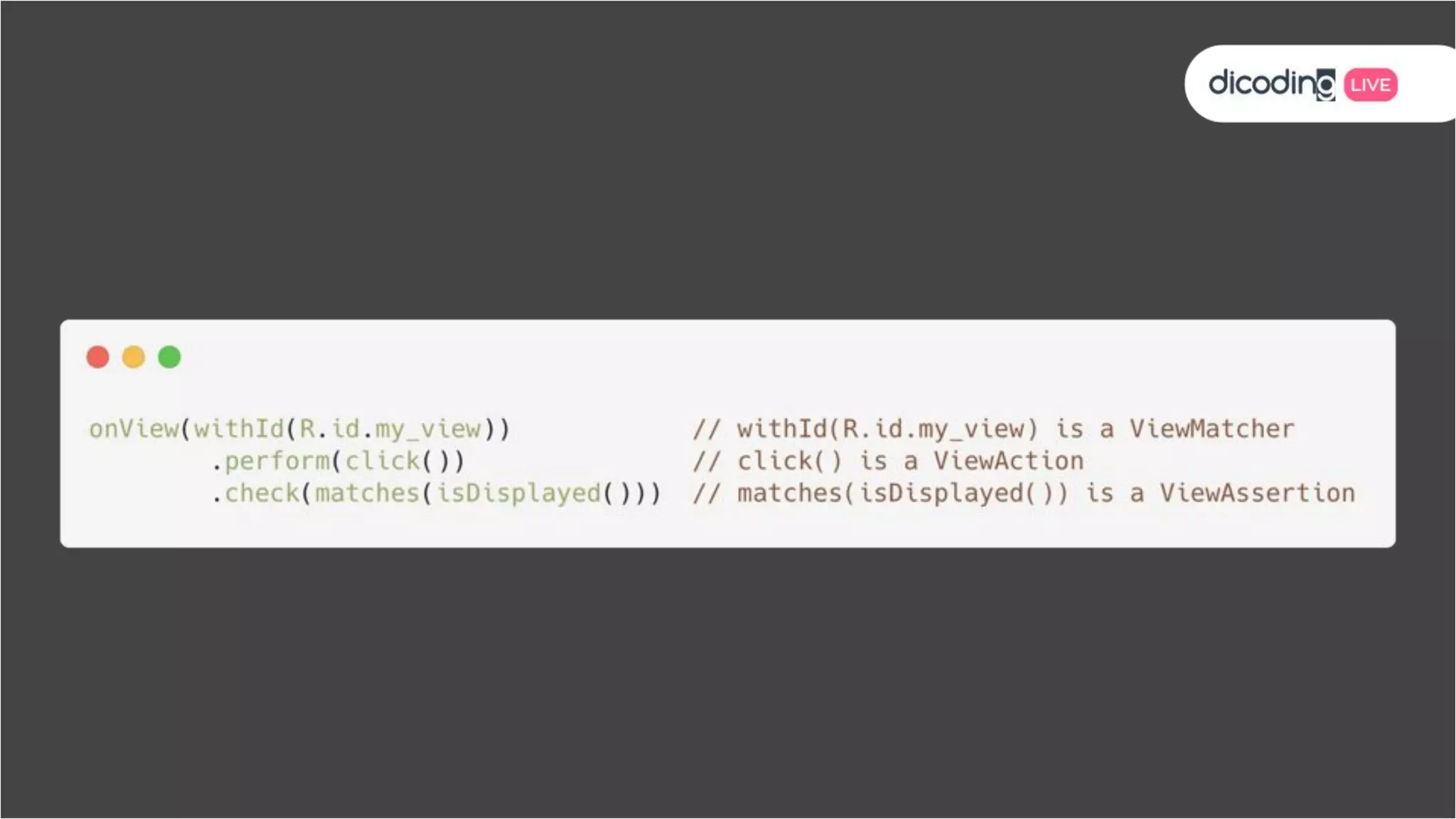
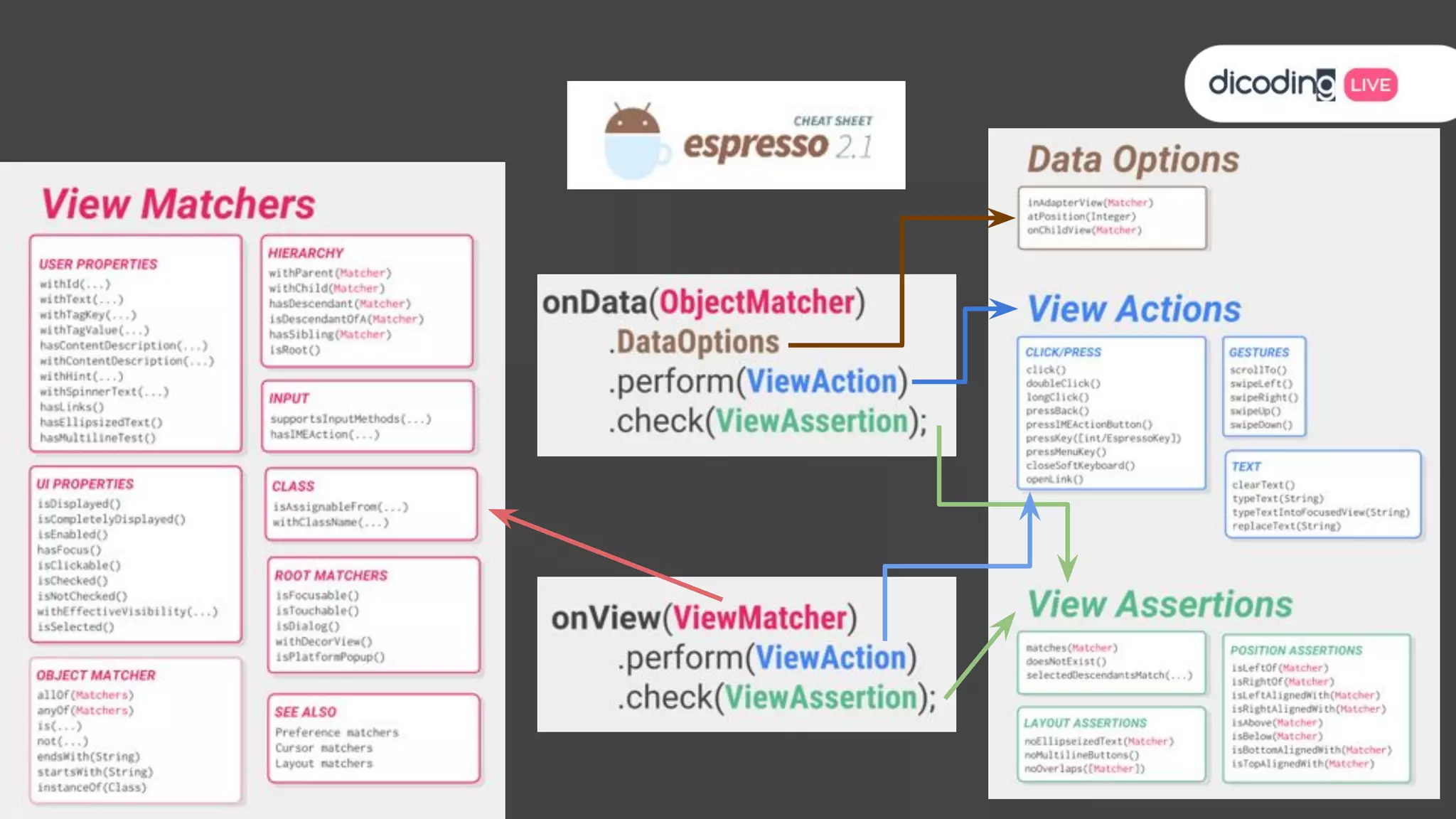
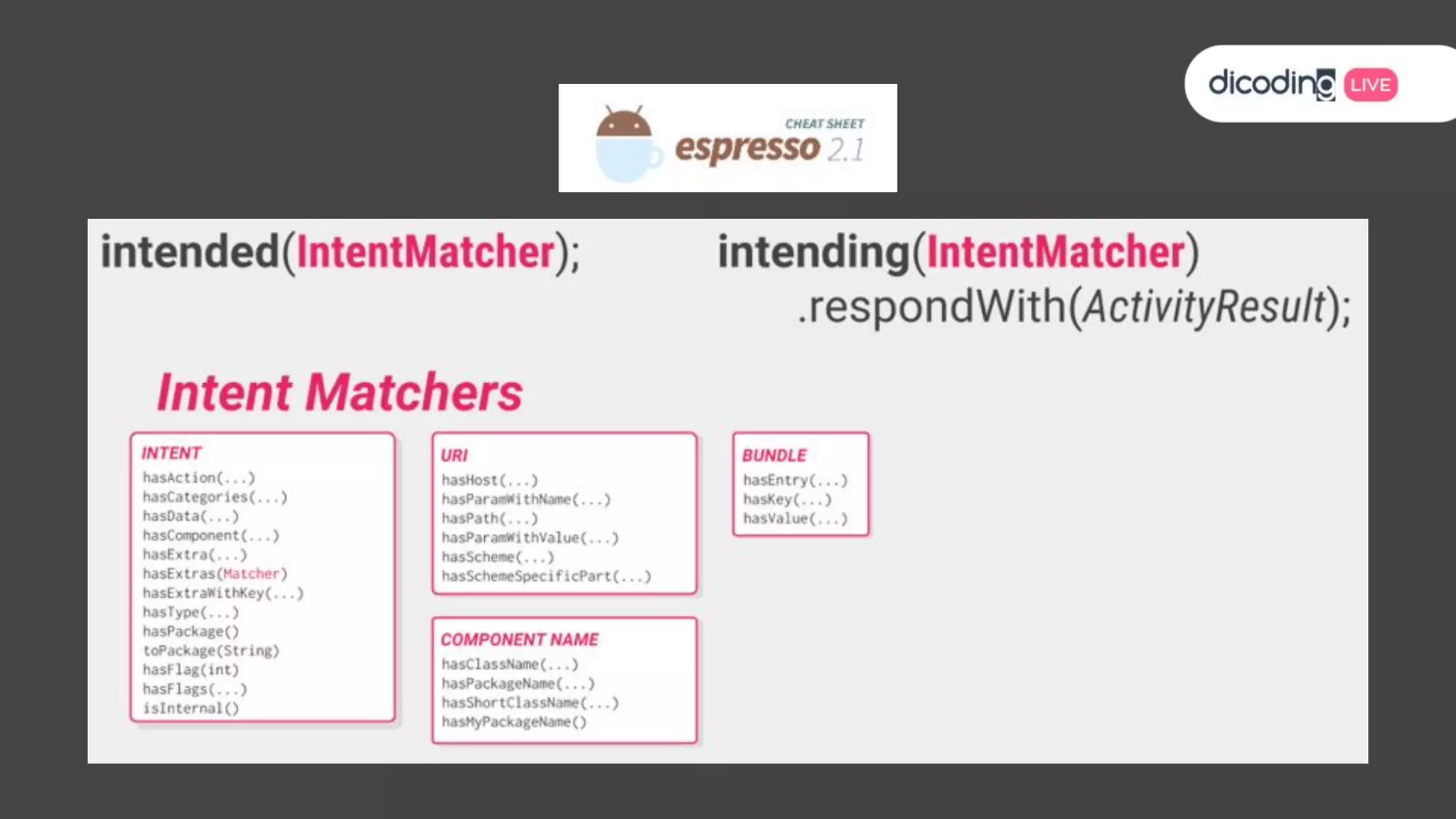
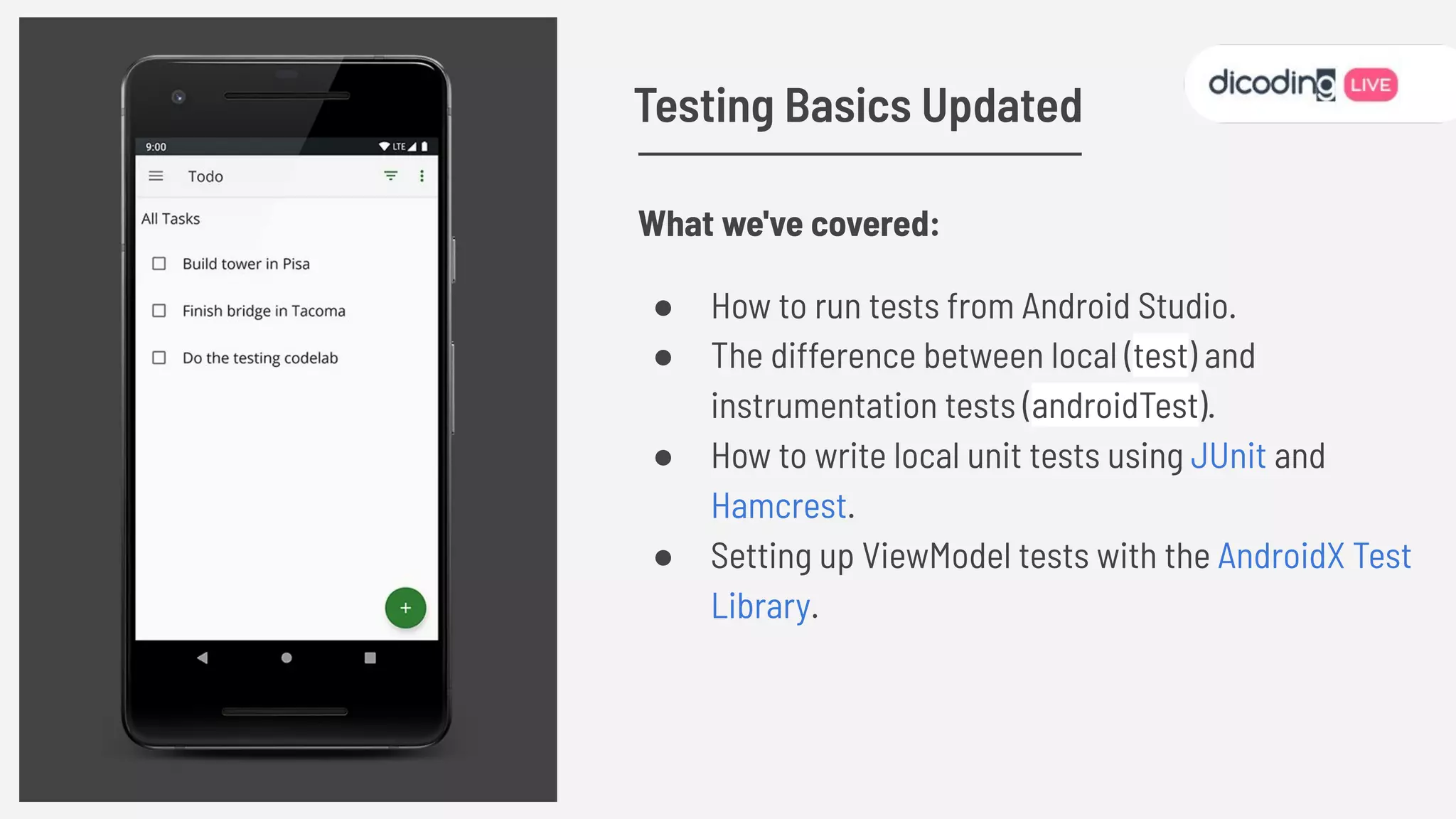
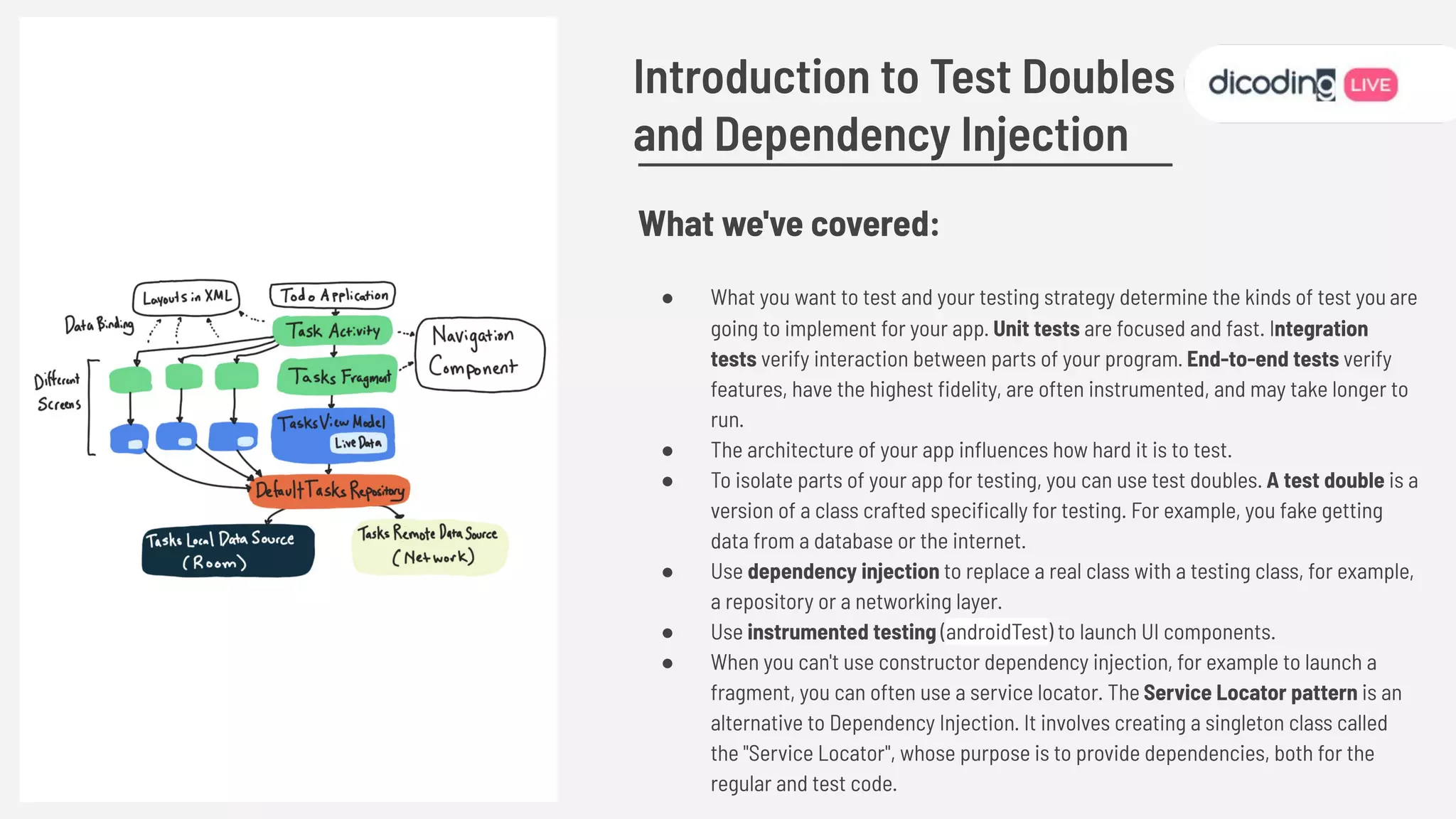
The document outlines best practices for testing in Android development, emphasizing the use of Android Jetpack libraries to simplify code management and reduce bugs. It discusses the importance of test-driven development (TDD) and various testing methodologies, including unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests, highlighting the advantages of a well-structured testing approach. Additionally, it covers the use of dependency injection and test doubles to create a testable architecture, ultimately aiming to improve code quality and development efficiency.