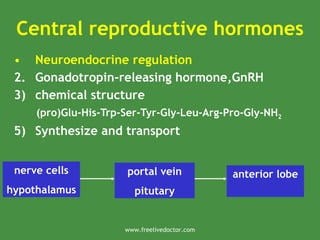
The document discusses the physiology of the female reproductive system. It covers the stages of development from birth through menopause. It describes the menstrual cycle and how it is regulated by hormones like estrogen and progesterone produced by the ovaries and hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian axis. The ovarian cycle and changes in the endometrium across the proliferative and secretory phases are also summarized.