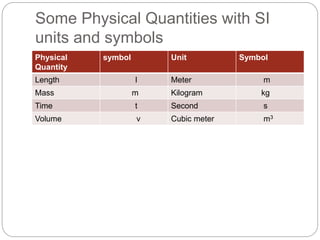
This document outlines a physics lesson plan on measurement of physical quantities. It will discuss physical quantities and examples, the international system of units (SI units), and prefixes. Students will learn to define physical quantities, describe the SI, apply prefixes to interpret units, and interconvert smaller and larger units. The lesson will take 40 minutes and include activities on the whiteboard, projector, and homework assignments involving unit conversions.