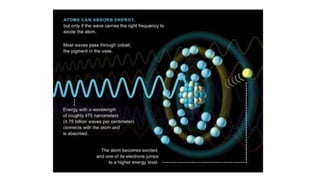
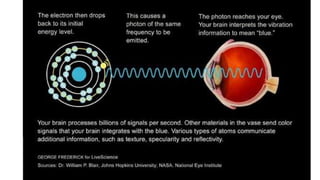
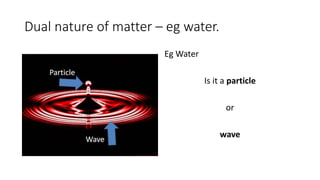
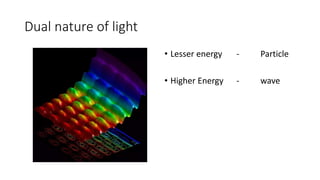
1. Theories of light have evolved over centuries from ray models to wave and particle models. Ibn al-Haytham in the 11th century correctly identified vision as light rays reflecting off objects rather than emanating from the eyes.
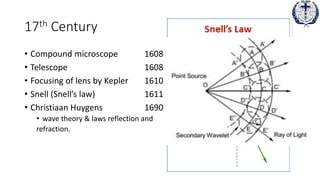
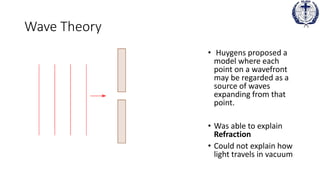
2. In the 17th century, advances like the telescope and microscope led to discoveries of laws of reflection and refraction by scientists like Snell and Huygens, who proposed the wave theory of light.
3. Newton's particle theory was widely accepted until Maxwell showed in the 19th century that light is an electromagnetic wave, not requiring a medium, though it couldn't explain all phenomena like the photoelectric effect. Einstein later explained this with his quantum theory, describing