The document summarizes key differences between PHP 4 and PHP 5, with a focus on object-oriented programming features. Some of the major changes covered include:
- Objects are now passed by reference by default in PHP 5.
- PHP 5 introduces classes, visibility, abstract classes, interfaces and type hints to improve object-oriented support.
- New magic methods like __construct(), __destruct() and __toString() are available in PHP 5.
- The MySQL extension is replaced by the improved MySQLi extension in PHP 5. Prepared statements and bound parameters are introduced.
![PHP 5 Bootcamp for PHP 4 Programmers Adam Trachtenberg eBay Technical Evangelist [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php5bootcamp-12827559844205-phpapp01/75/PHP-5-Boot-Camp-1-2048.jpg)




















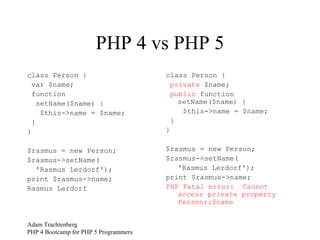












![Accessors class Person { private $data; public function __get($property) { return $this->data[$property]; } public function __set($property, $value) { $this->data[$property] = $value; } } $rasmus = new Person; $rasmus->name = 'Rasmus Lerdorf'; print $rasmus->name; Rasmus Lerdorf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php5bootcamp-12827559844205-phpapp01/85/PHP-5-Boot-Camp-37-320.jpg)








![MySQL vs MySQLi $db = mysql_connect( $server, $user, $pass); mysql_select_db( $db, "users"); $r = mysql_query( "SELECT user FROM users", $db); while ($row = mysql_fetch_assoc($r)) { print $row['user']; } mysql_free_result($r); mysql_close($db);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php5bootcamp-12827559844205-phpapp01/85/PHP-5-Boot-Camp-46-320.jpg)
![MySQL vs MySQLi $db = mysql_connect( $server, $user, $pass); mysql_select_db( $db, "users"); $r = mysql_query( "SELECT user FROM users", $db); while ($row = mysql_fetch_assoc($r)) { print $row['user']; } mysql_free_result($r); mysql_close($db); $db = mysql i _connect( $server, $user, $password , "users" ); $r = mysql i _query( $db, "SELECT user FROM users"); while ($row = mysql i _fetch_assoc($r)) { print $row['user']; } mysql i _free_result($r); mysql i _close($db);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php5bootcamp-12827559844205-phpapp01/85/PHP-5-Boot-Camp-47-320.jpg)

![Procedural vs OO $db = mysqli_connect( $server, $user, $password, "users"); $r = mysqli_query( $db, "SELECT user FROM users"); while ($row = mysqli_fetch_assoc($r)) { print $row['user']; } mysqli_free_result($r); mysqli_close($db); $db = new mysqli ( $server, $user, $password, "users"); $r = $mysqli->query ( "SELECT user FROM users"); while ($row = $r->fetch_assoc ()) { print $row['user']; } $r->close(); unset($db);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php5bootcamp-12827559844205-phpapp01/85/PHP-5-Boot-Camp-49-320.jpg)






















![Reading: DOM: PHP 4 $dom = domxml_open_file('address-book.xml'); foreach ($dom->get_elements_by_tagname('person') as $person) { $firstname = $person-> get_elements_by_tagname('firstname'); $firstname_text = $firstname[0]->first_child(); $firstname_text_value = $firstname_text-> node_value(); print "$firstname_text_value\n"; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php5bootcamp-12827559844205-phpapp01/85/PHP-5-Boot-Camp-75-320.jpg)

![What’s different? studlyCaps get_elements_by_tagname() getElementsByTagname() DOM node list vs array $firstname[0] $firstname->item(0) Methods vs Properties first_child() firstChild Object vs Resource](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/php5bootcamp-12827559844205-phpapp01/85/PHP-5-Boot-Camp-77-320.jpg)