This document provides an overview of PHP, including:
- PHP stands for Hypertext Preprocessor and is a popular open-source scripting language used for web development.
- PHP features include easy learning, a large function library, ability to embed code directly into HTML, and compatibility with many databases and servers.
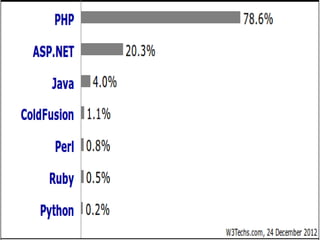
- PHP can be used for e-commerce sites, content management, community building, and more. Its history began in 1995 and it is now used on over 10 million websites.
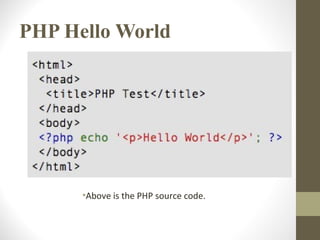
- The document discusses PHP implementations, basics of PHP syntax and control structures, and provides an example of a simple "Hello World" PHP program. It also notes some potential security issues to be aware of.