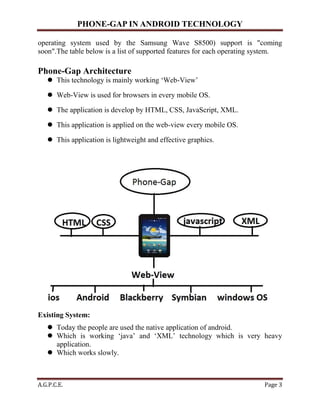
PhoneGap is a mobile development framework that allows developers to create hybrid applications using HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript, circumventing the need for device-specific languages. It utilizes Apache Cordova's underlying technology, enabling access to native device features while maintaining a lightweight app structure. Adobe's acquisition of PhoneGap in 2011 facilitated its evolution and integration into a broader range of mobile operating systems.


![PHONE-GAP IN ANDROID TECHNOLOGY
Proposed System:
The proposed system is Phone-Gap Technology which overcome on that all
the drawbacks.
By using this technology we can create application which is lightweight and
important thing is that this application is working on multiple Mobile OS.
Conclusion
The conclusion is that 50% of mobile application is not required database.
This application is build by using Phone-Gap so we can have lightweight
and more effective application.
There are no of Mobile OS are available so we can provide a multi platform
applivation
References
1. "PhoneGap License". Phonegap.com. Retrieved 2013-10-09.
2. "FAQ | PhoneGap Build | Edge Tools & Services | Adobe & HTML".
Html.adobe.com. Retrieved 2013-10-09.
3. "Adobe Announces Agreement to Acquire Nitobi, Creator of PhoneGap".
Adobe.com. 2011-10-03. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
4. "Andre Charland's Answers on PhoneGap". Quora. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
5. Jose Fermoso (April 5, 2009). "PhoneGap Seeks to Bridge the Gap Between
Mobile App Platforms". GigaOM. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
6. "Apache Cordova gets a new look - The H Open Source: News and
Features". H-online.com. 2012-02-22. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
7. Apache Callback Project Incubation Status[dead link]
8. / (2013-08-15). "Apache Callback Proposal". Wiki.phonegap.com. Retrieved
2013-10-09.
9. Darryl K. Taft (2009-03-13). "PhoneGap Simplifies iPhone, Android,
BlackBerry Development". Eweek.com. Retrieved 2013-10-09.
10.Davis, Lidija (2009-04-02). "PhoneGap: People's Choice Winner at Web 2.0
Expo Launch Pad". Readwriteweb.com. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
11."PhoneGap Apps". Phonegap.com. Retrieved 2012-12-06.
12."PhoneGap and the Apple developer license agreement. « PhoneGap".
Phonegap.com. 2010-04-14. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
13."Create Mobile and Web Apps with HTML5 and JavaScript".
ViziApps.com. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
14. "Mobile Application Platform and Tools". Worklight. 2012-01-16.
Retrieved 2012-04-07.
15. "How PhoneGap plays an important part in our Enterprise offering
« PhoneGap". Phonegap.com. 2011-06-27. Retrieved 2012-04-07.
A.G.P.C.E.
Page 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phonegapinandroidtechnology-131128063743-phpapp01/85/Phone-gap-in-android-technology-4-320.jpg)