1) The document summarizes a 12-year meta-analysis of nearly 700 studies and over 1,600 effects analyzing the impact of testing on student achievement from 1910-2010.
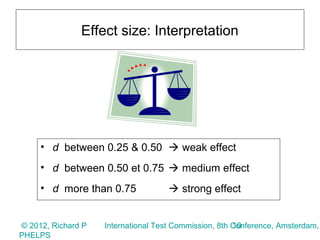
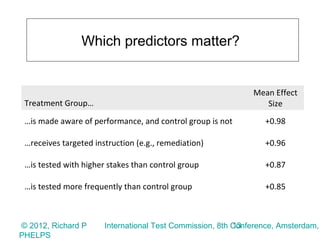
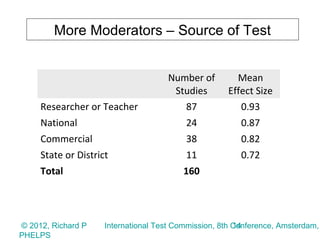
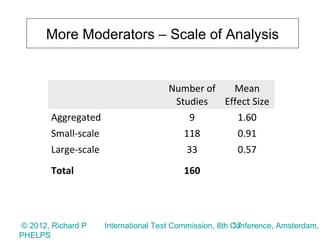
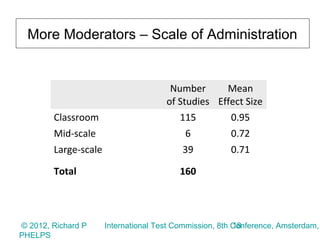
2) The meta-analysis found a medium effect of testing on student achievement (d=0.55) that increased to a strong effect when adjusted for measurement error (d=0.71 to 0.88). Higher stakes testing, more frequent testing, and targeted instruction had larger positive effects.
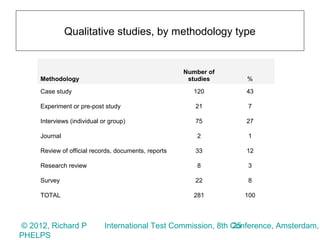
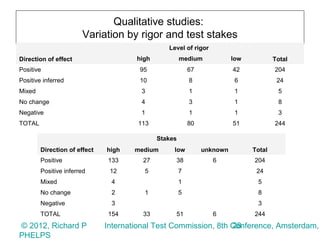
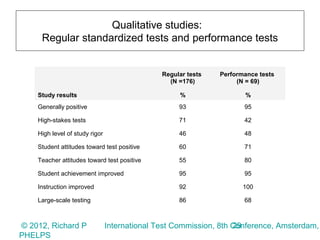
3) Surveys of over 700,000 respondents and qualitative studies also generally found testing improved student achievement and teacher instruction, though results varied by test stakes and rigor.