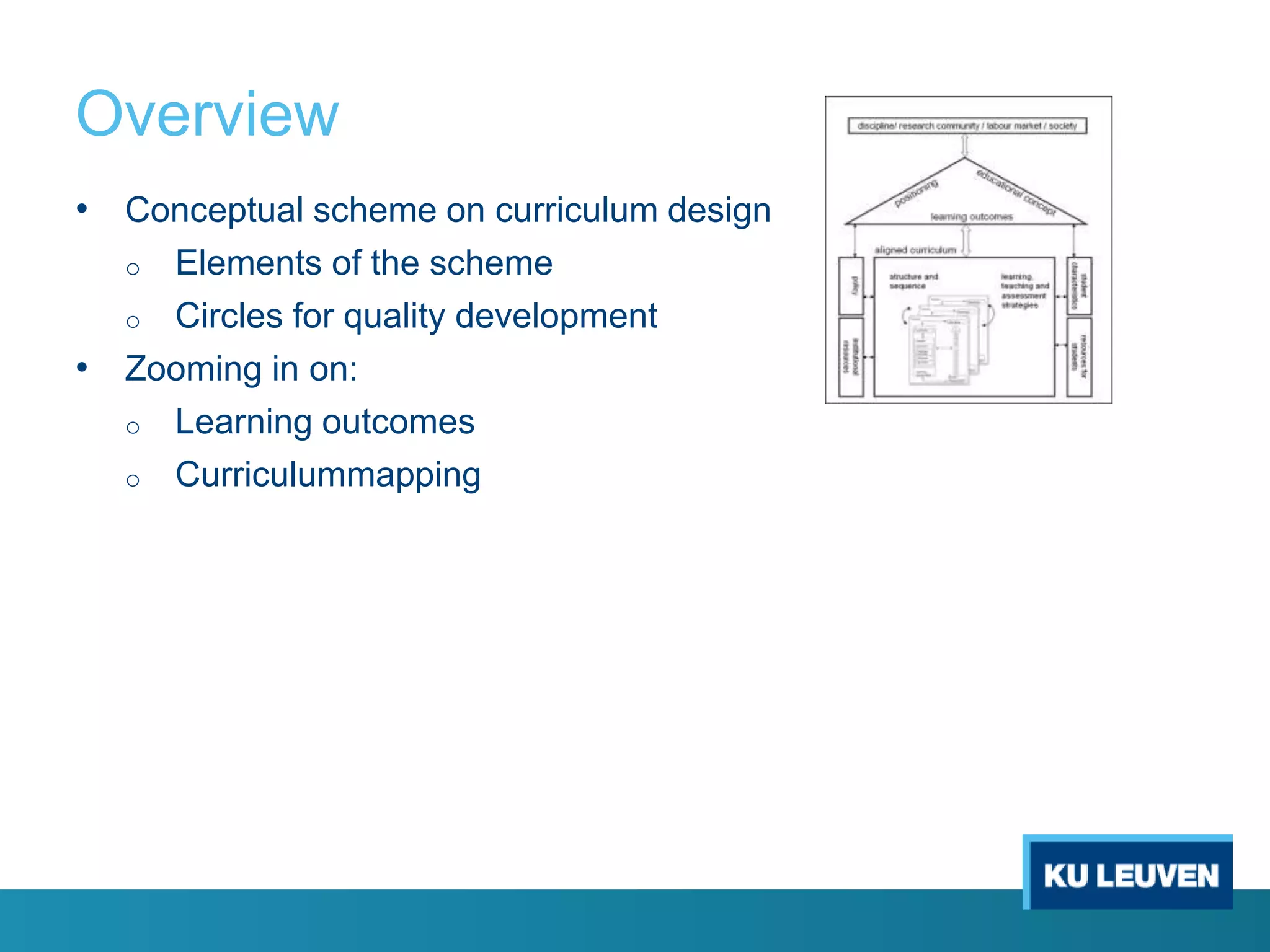
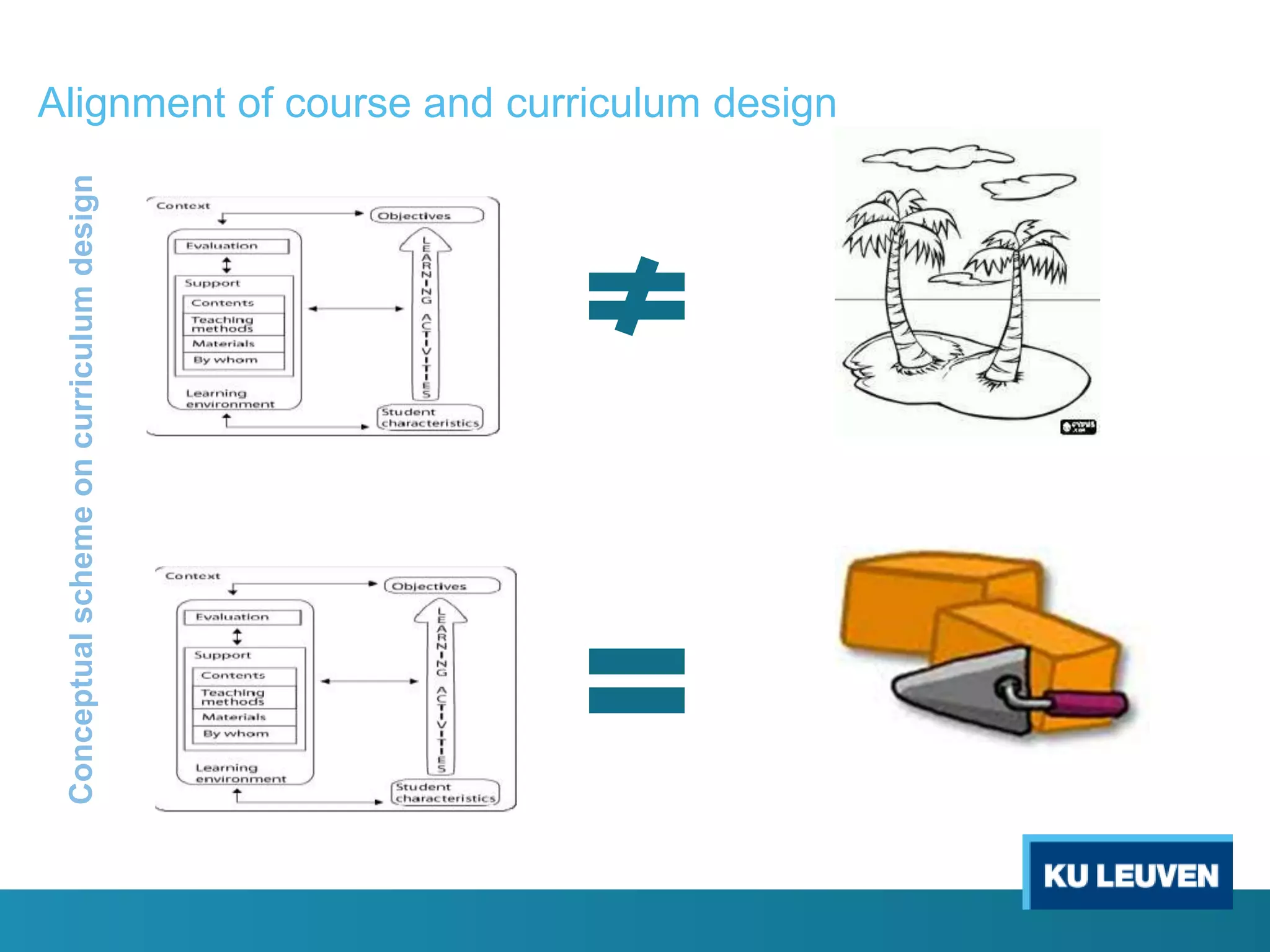
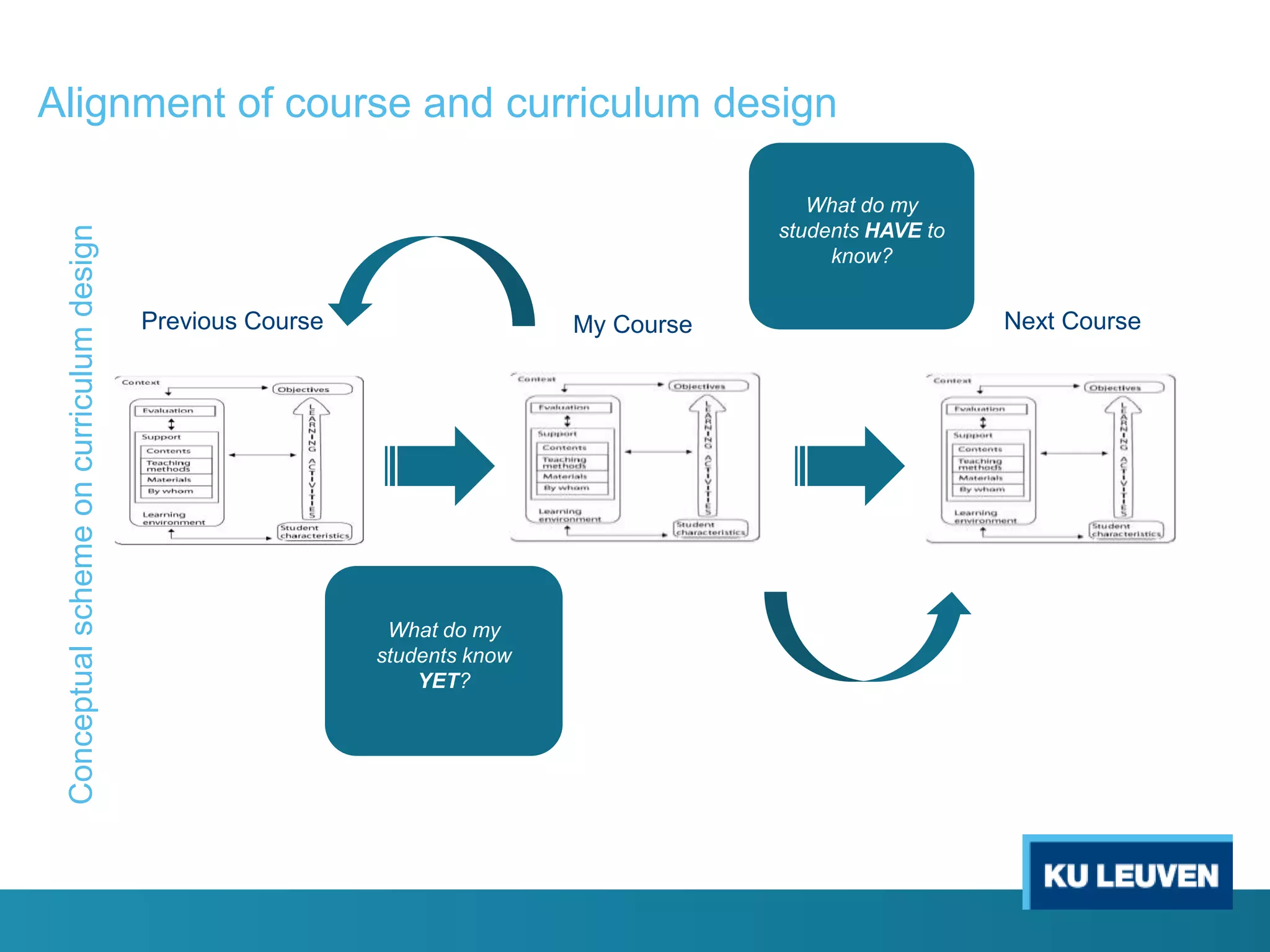
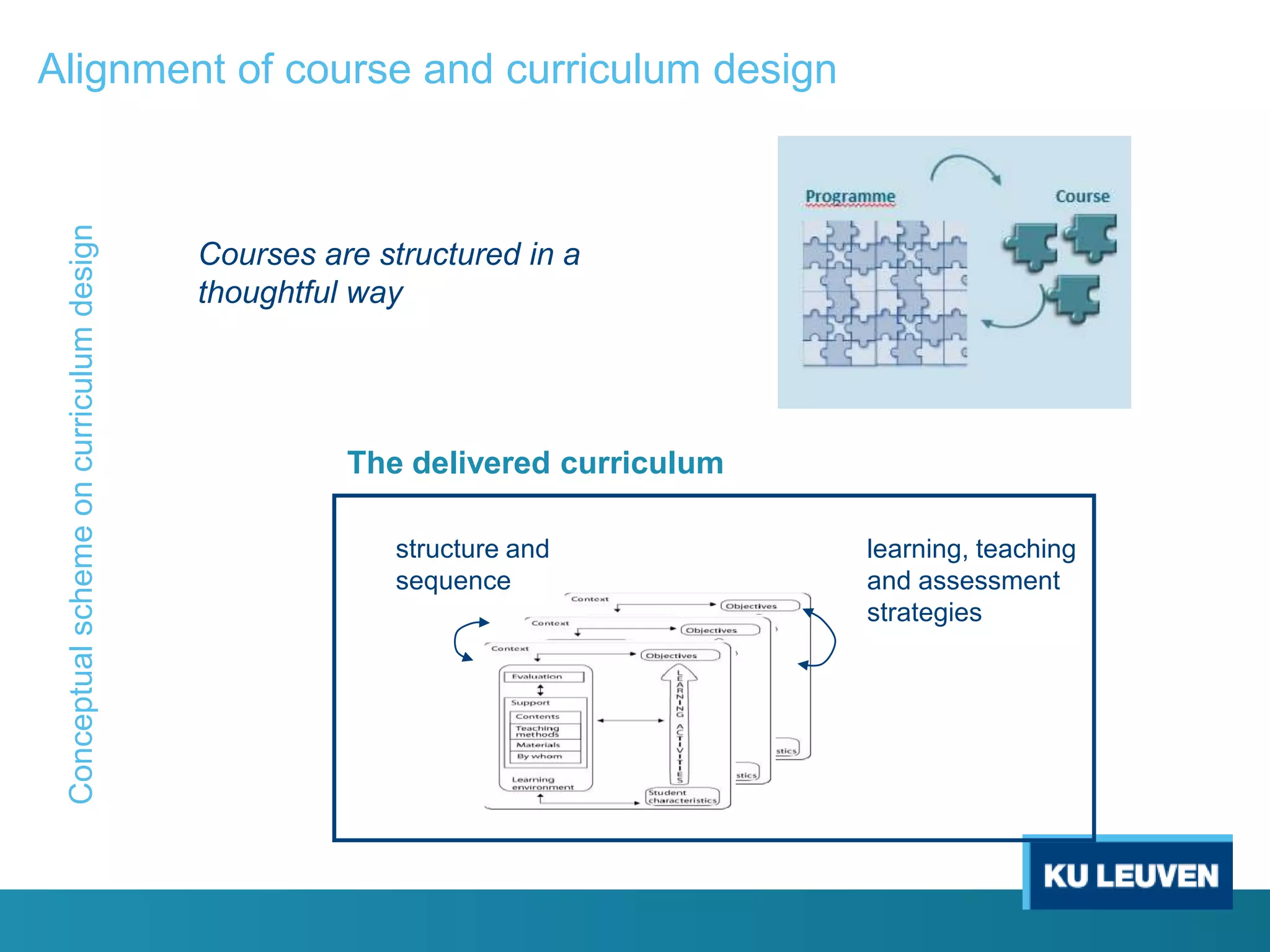
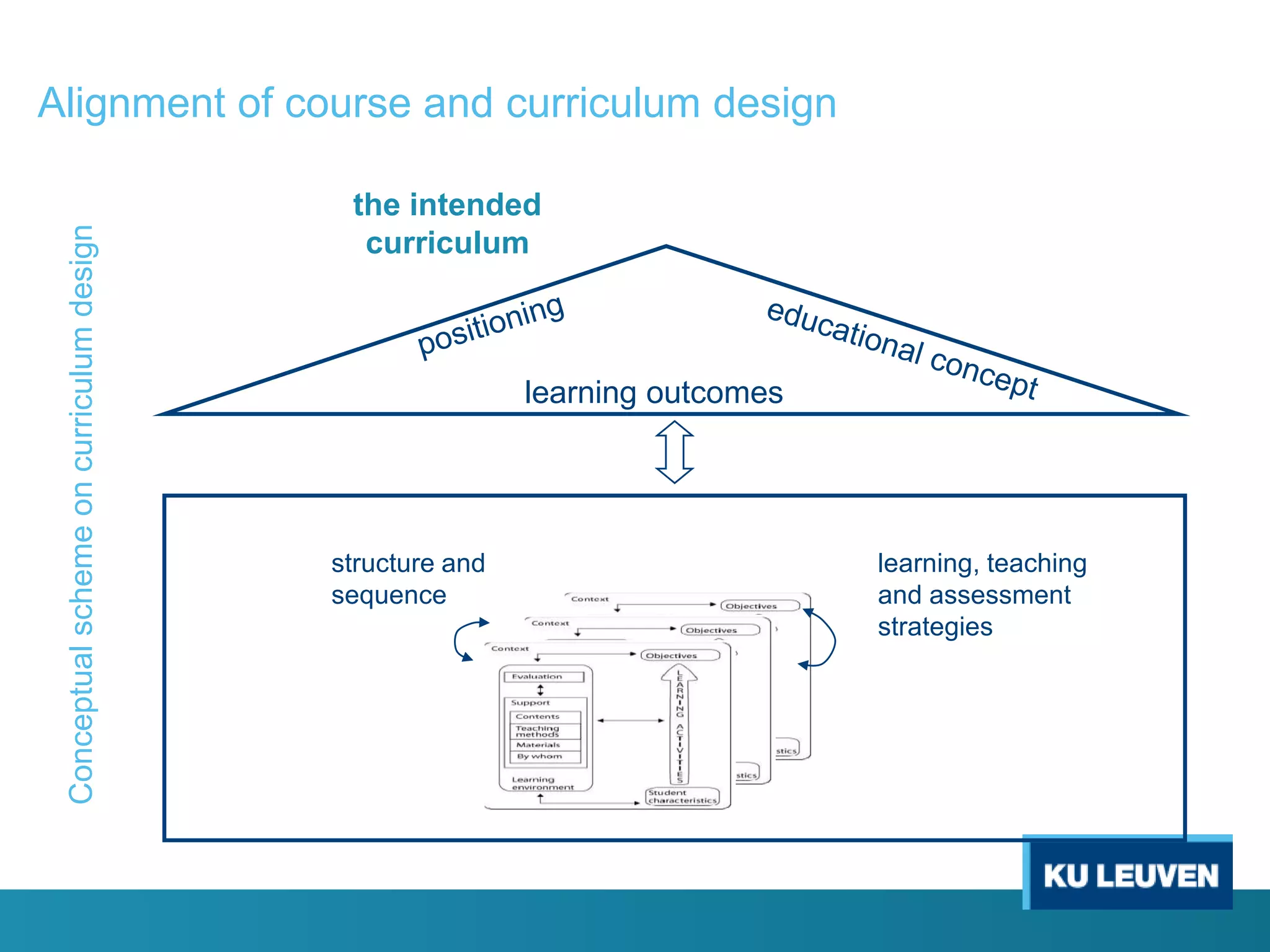
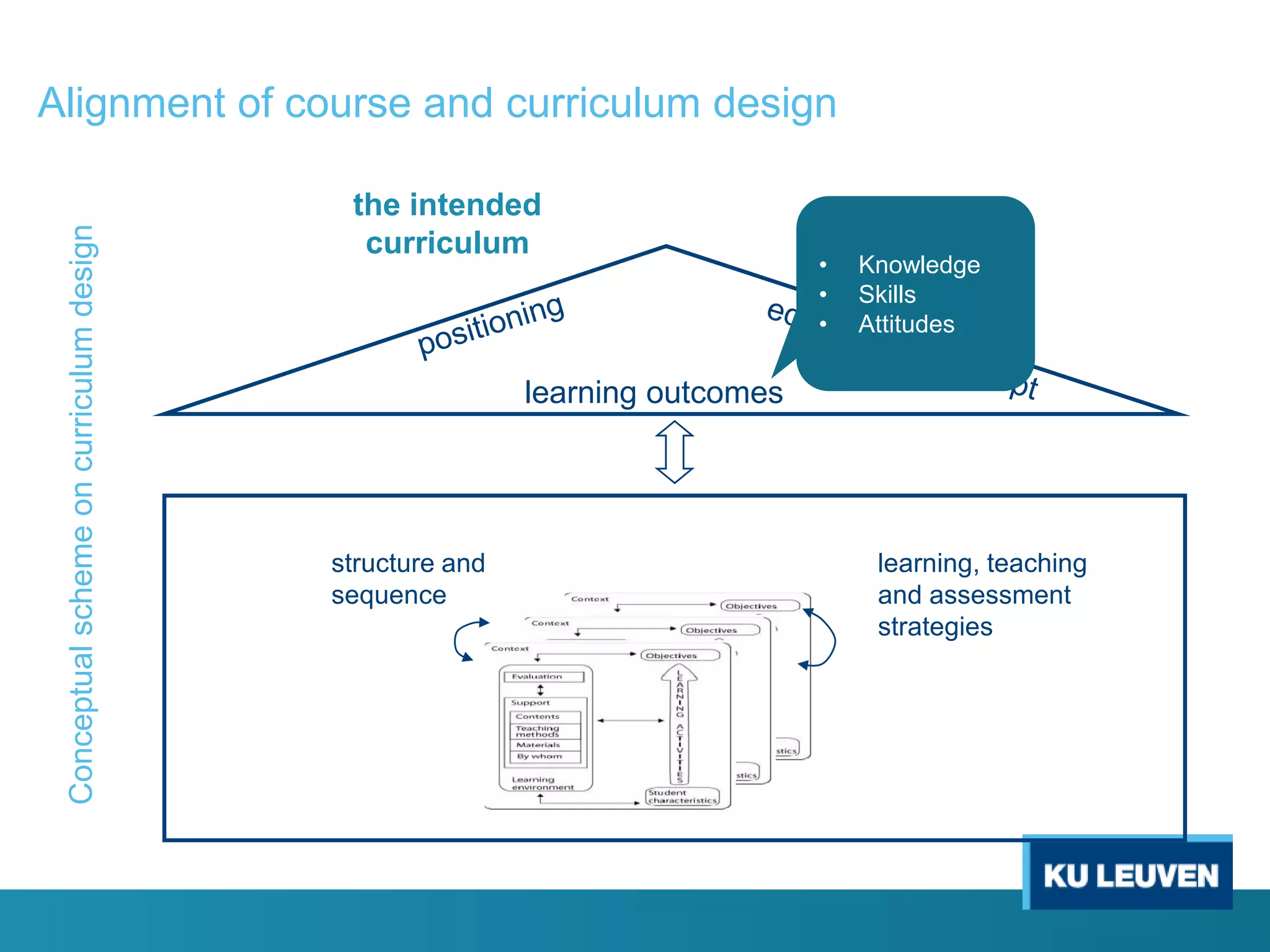
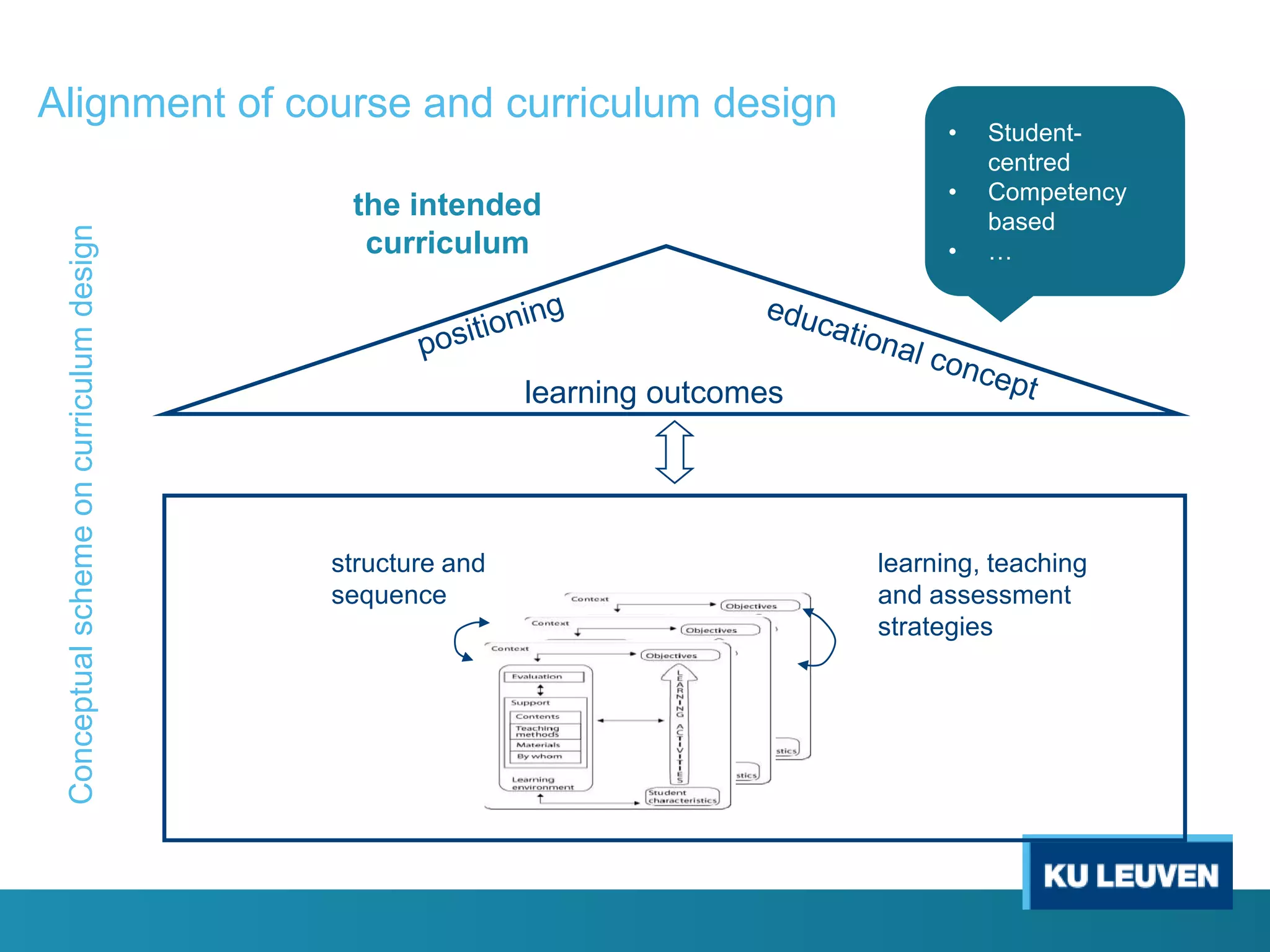
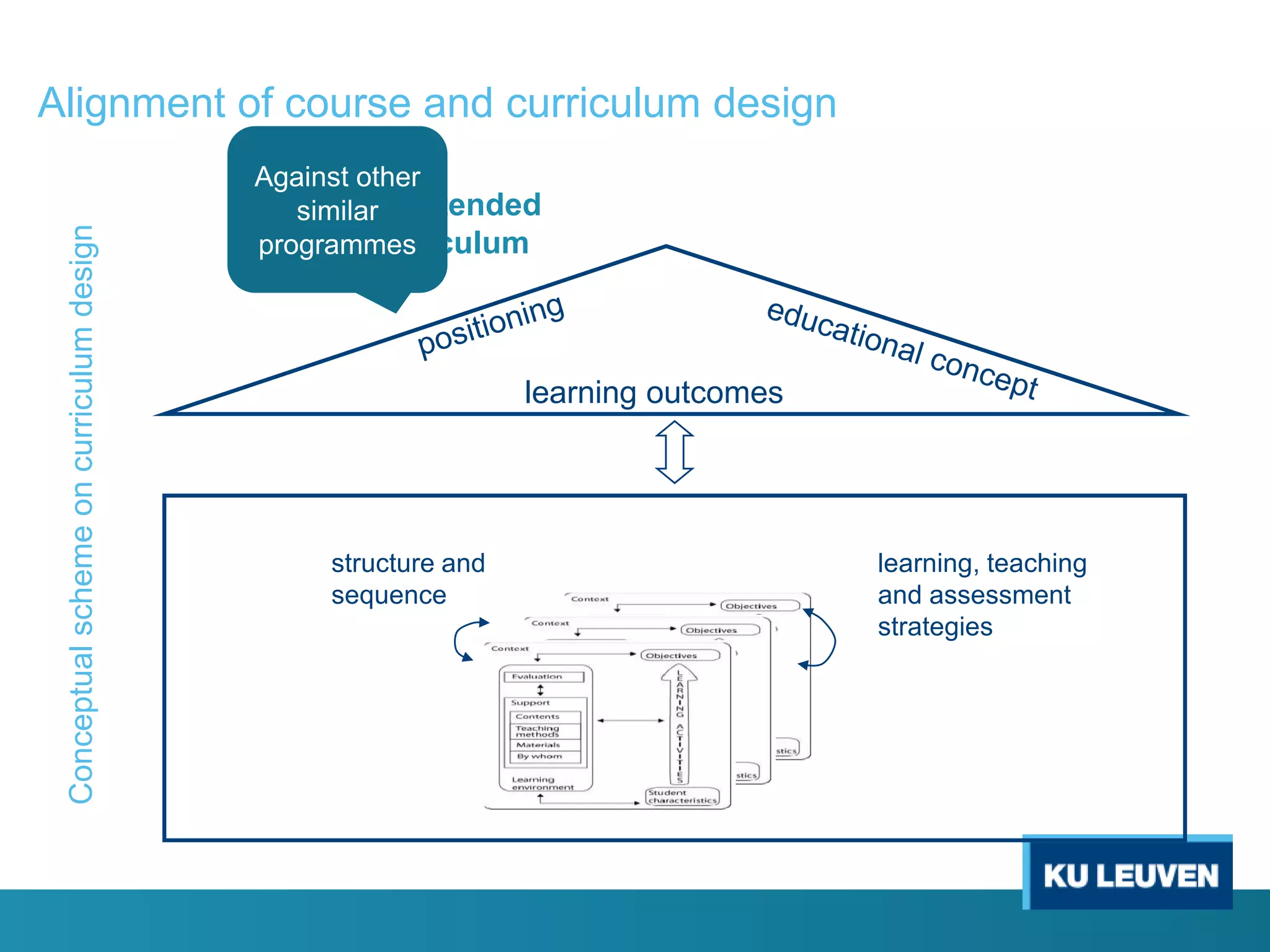
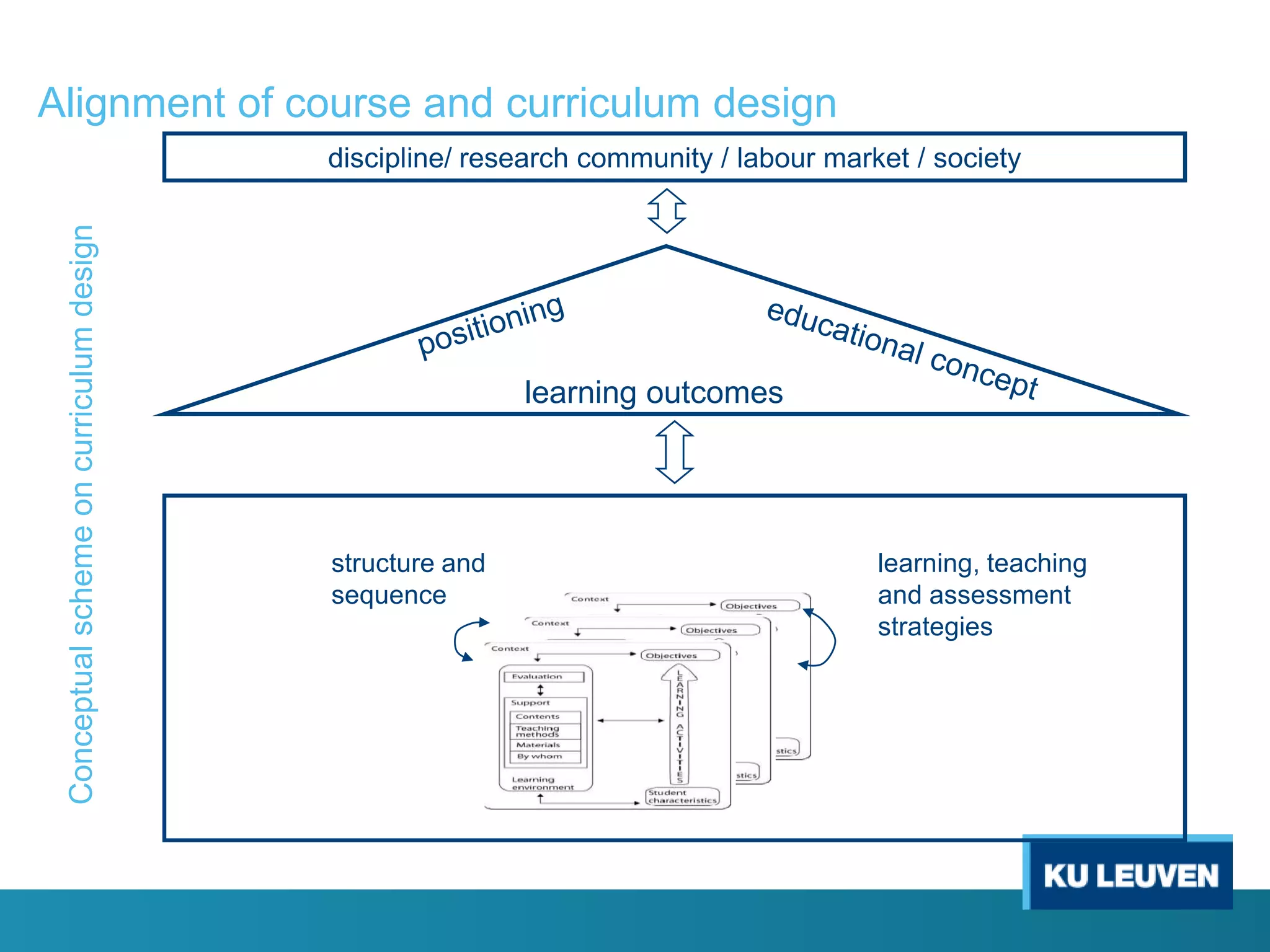
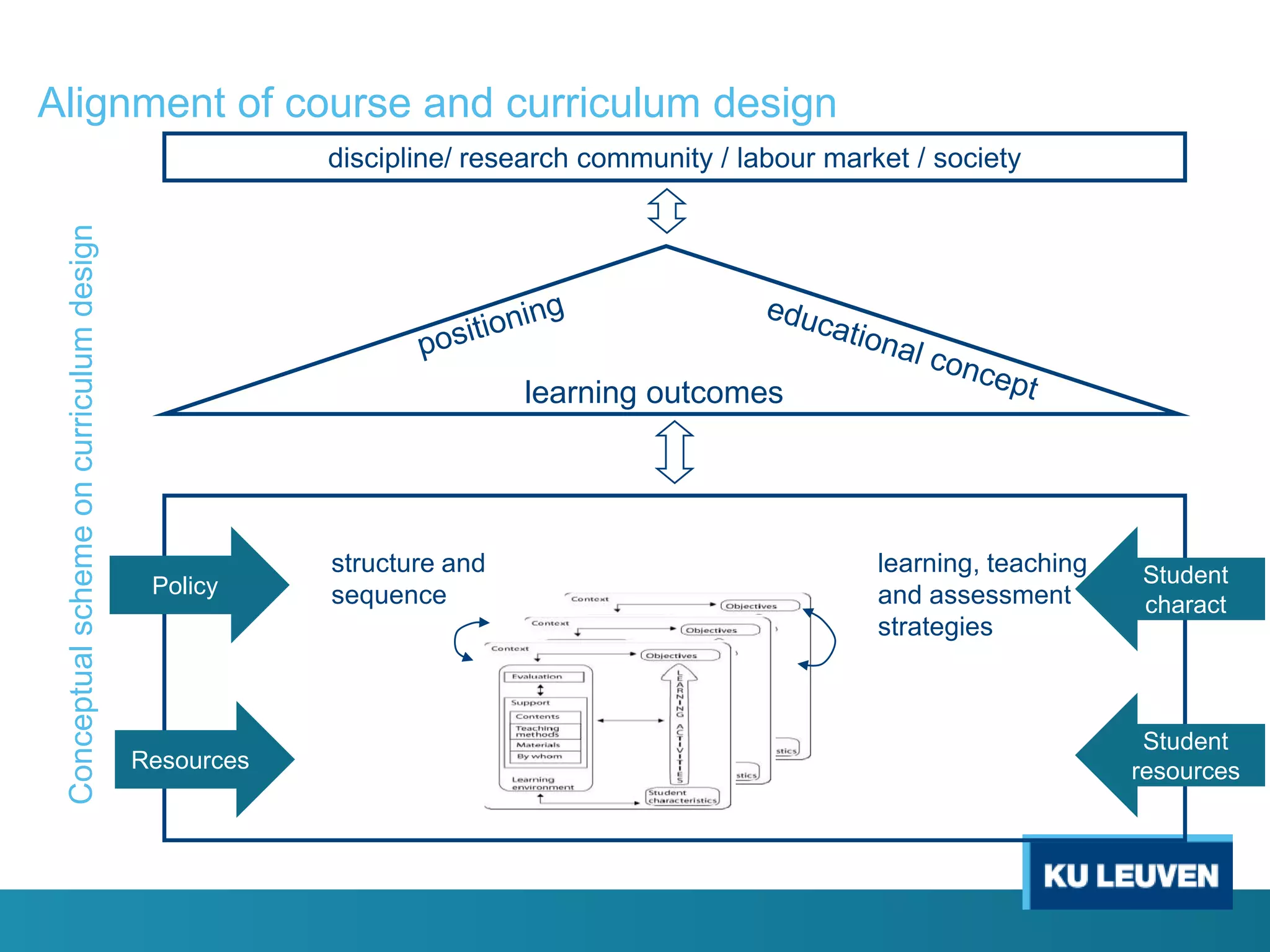
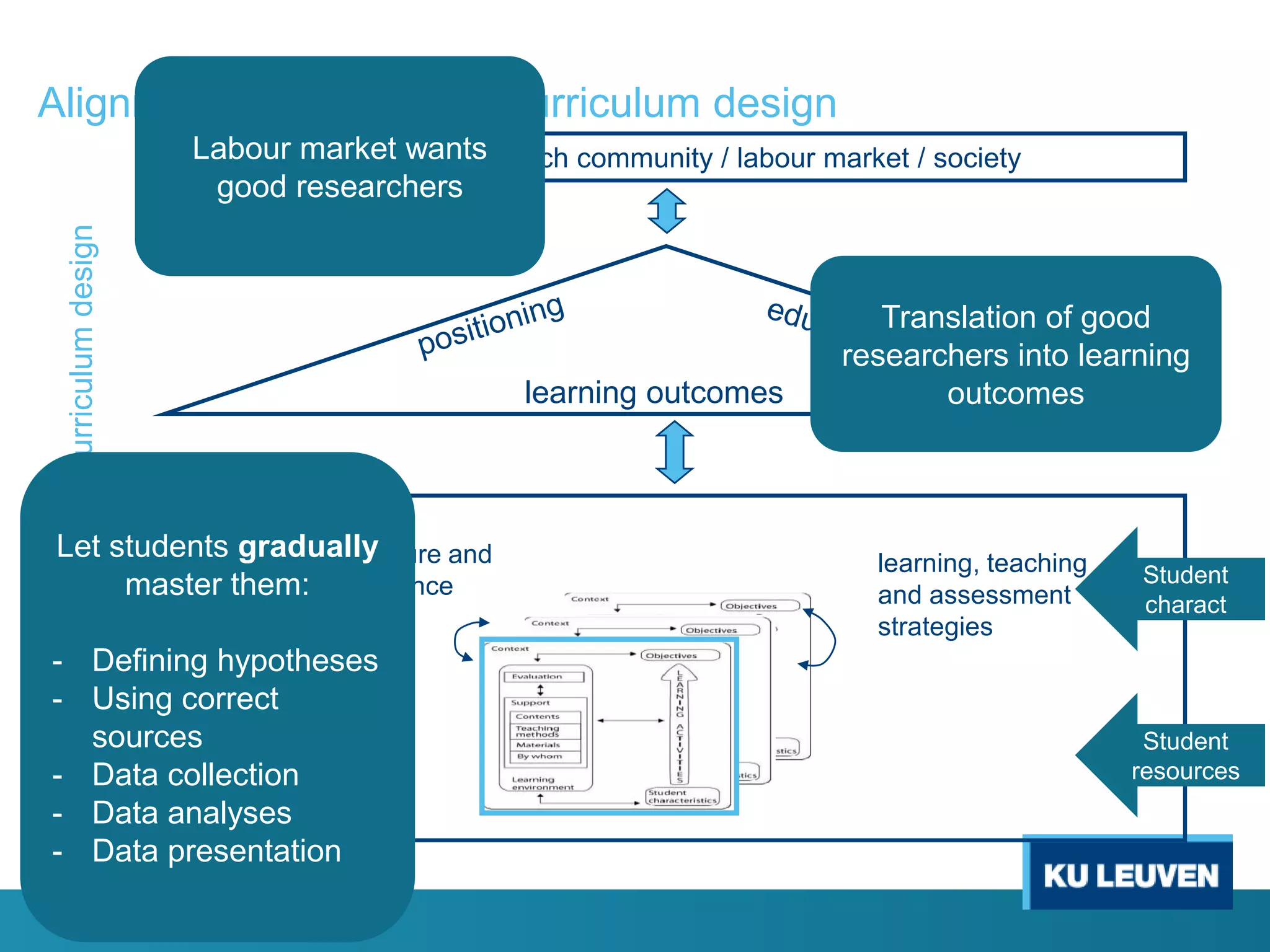
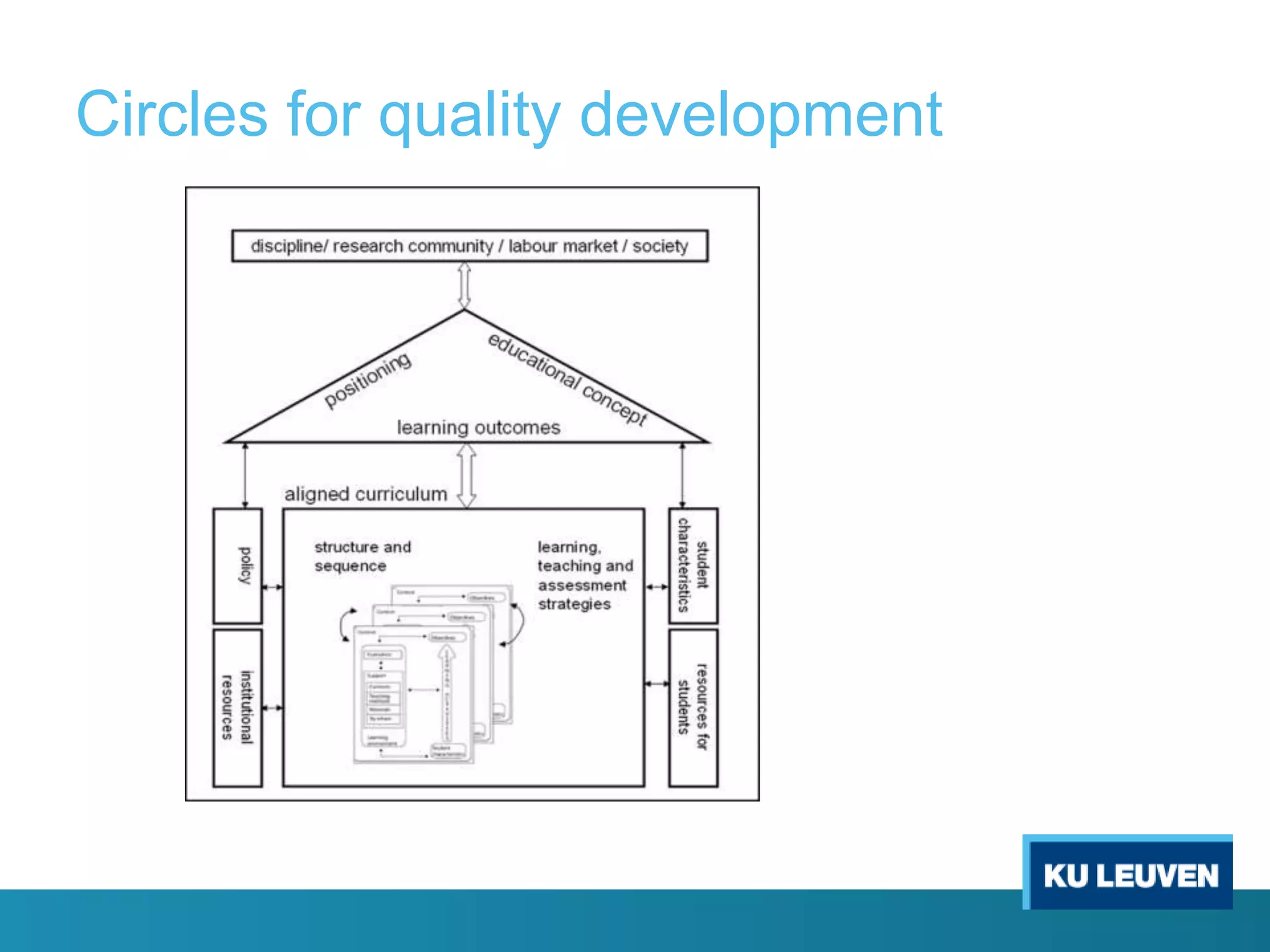
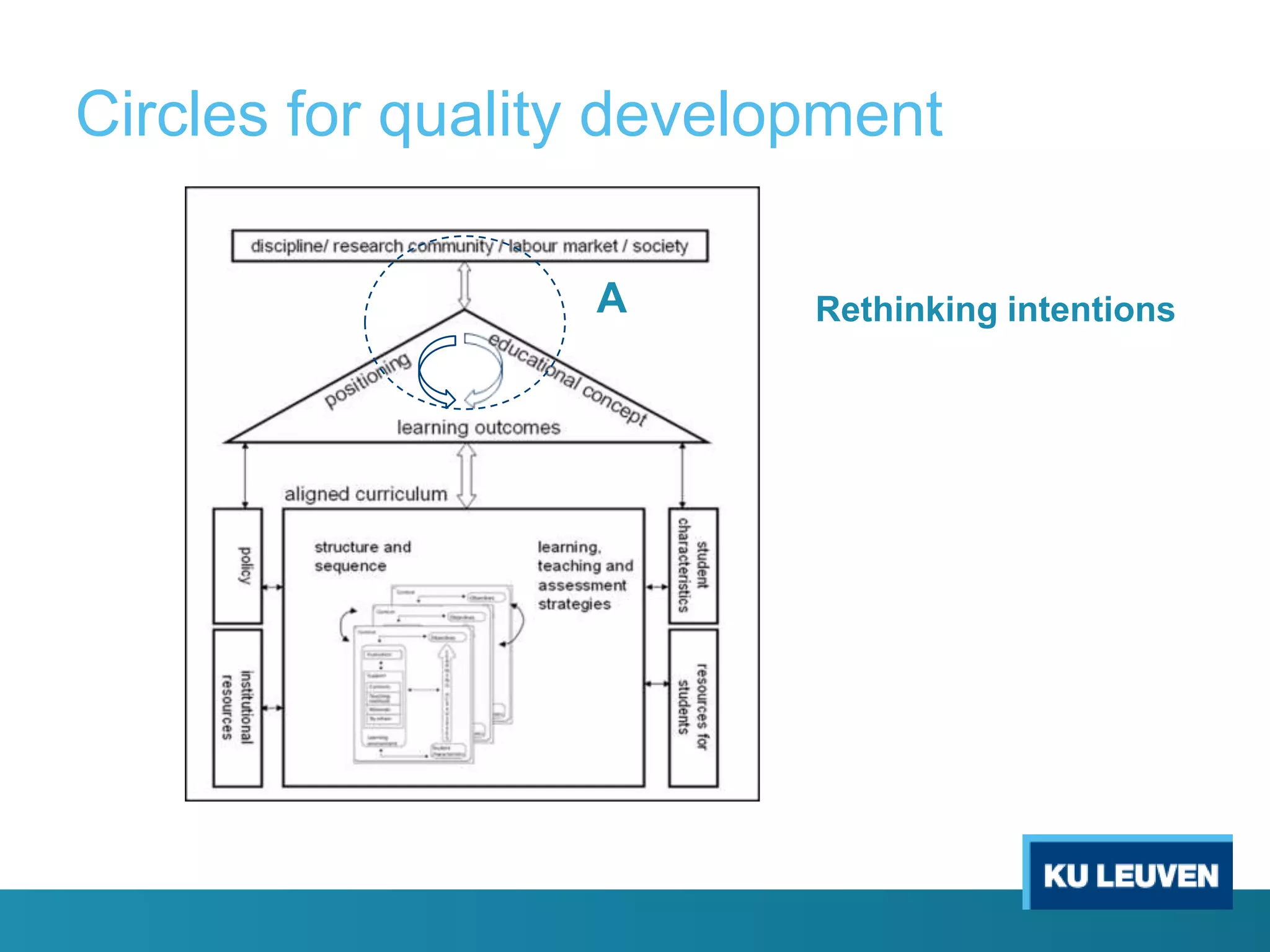
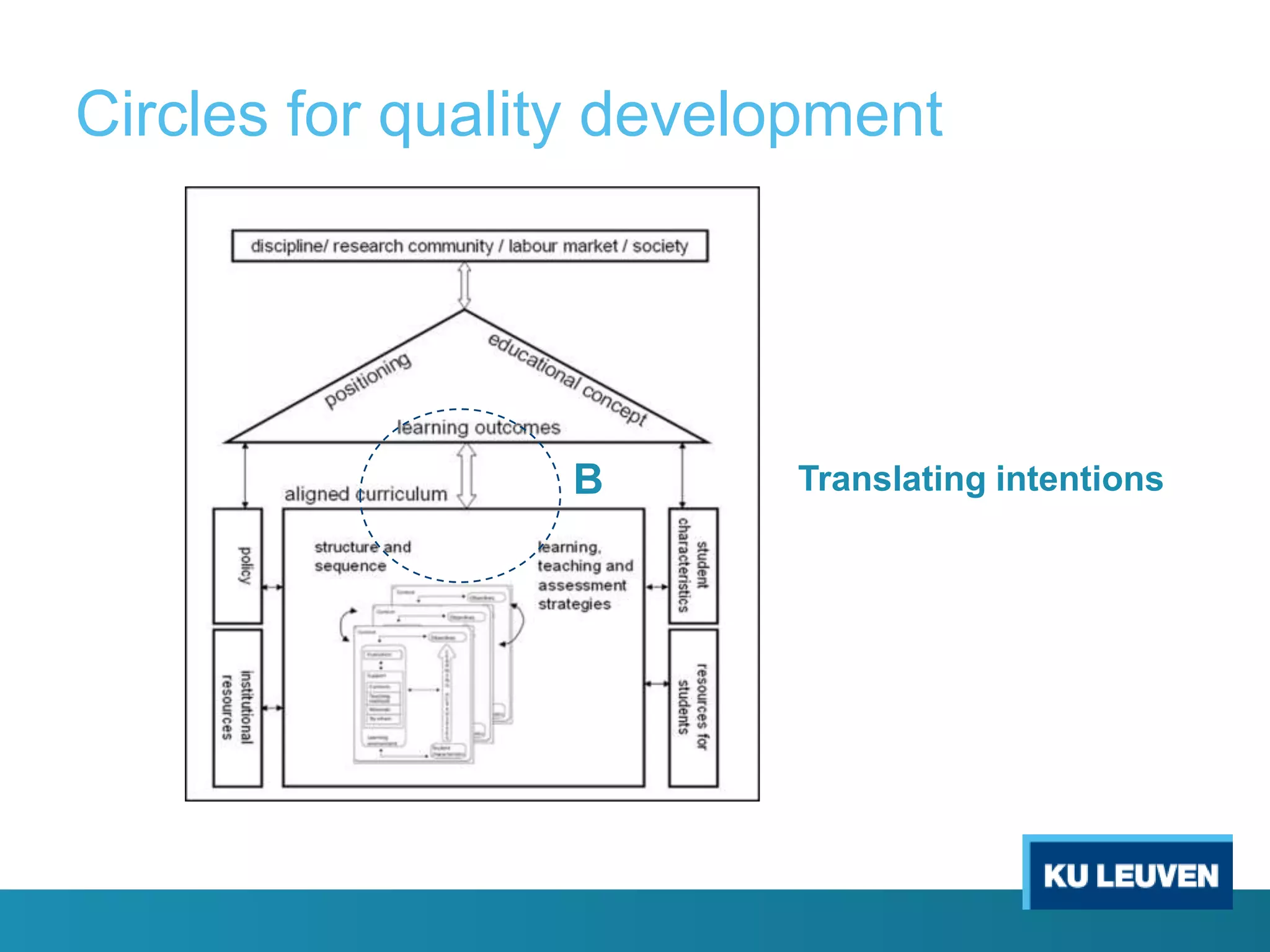
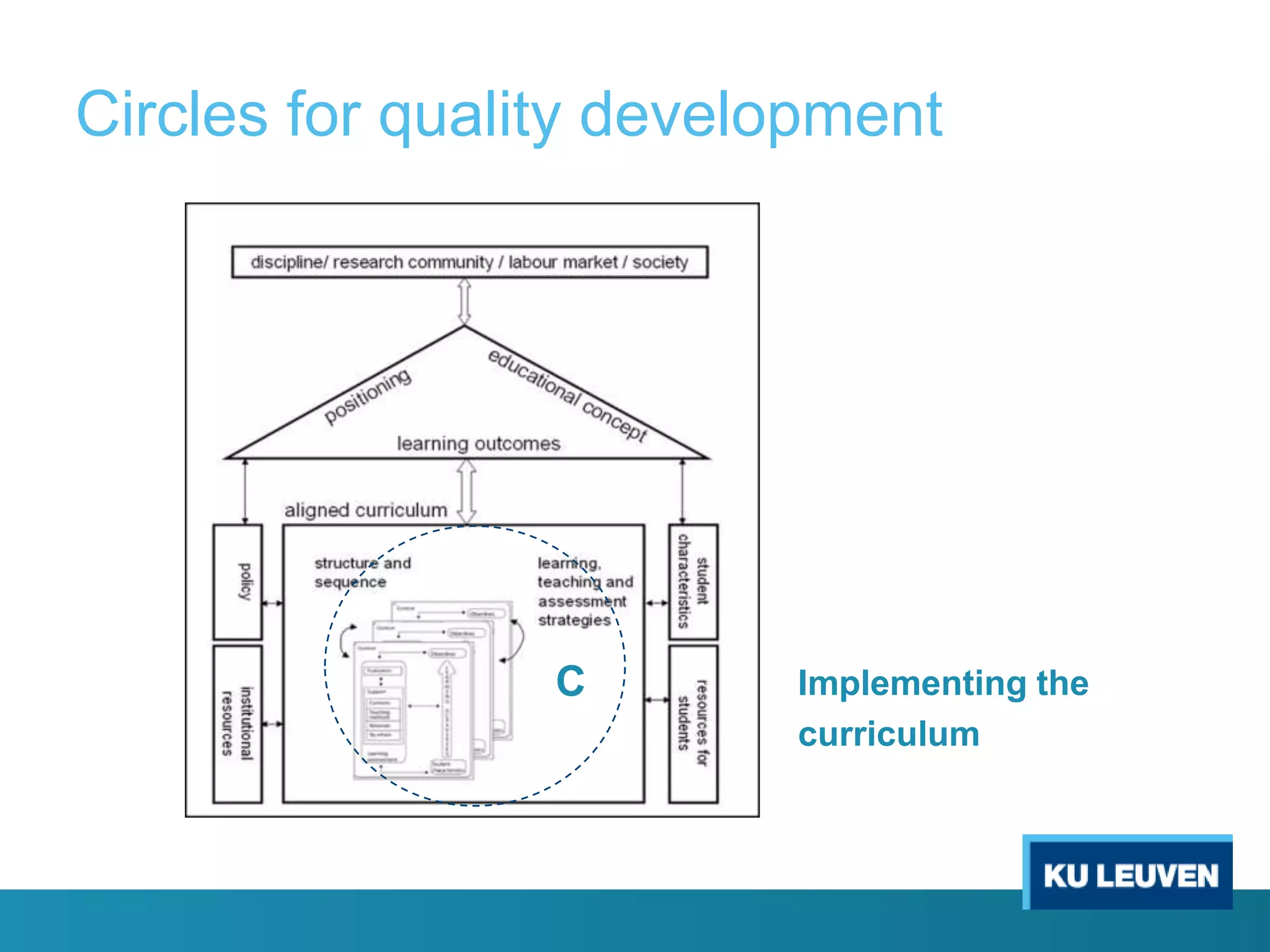
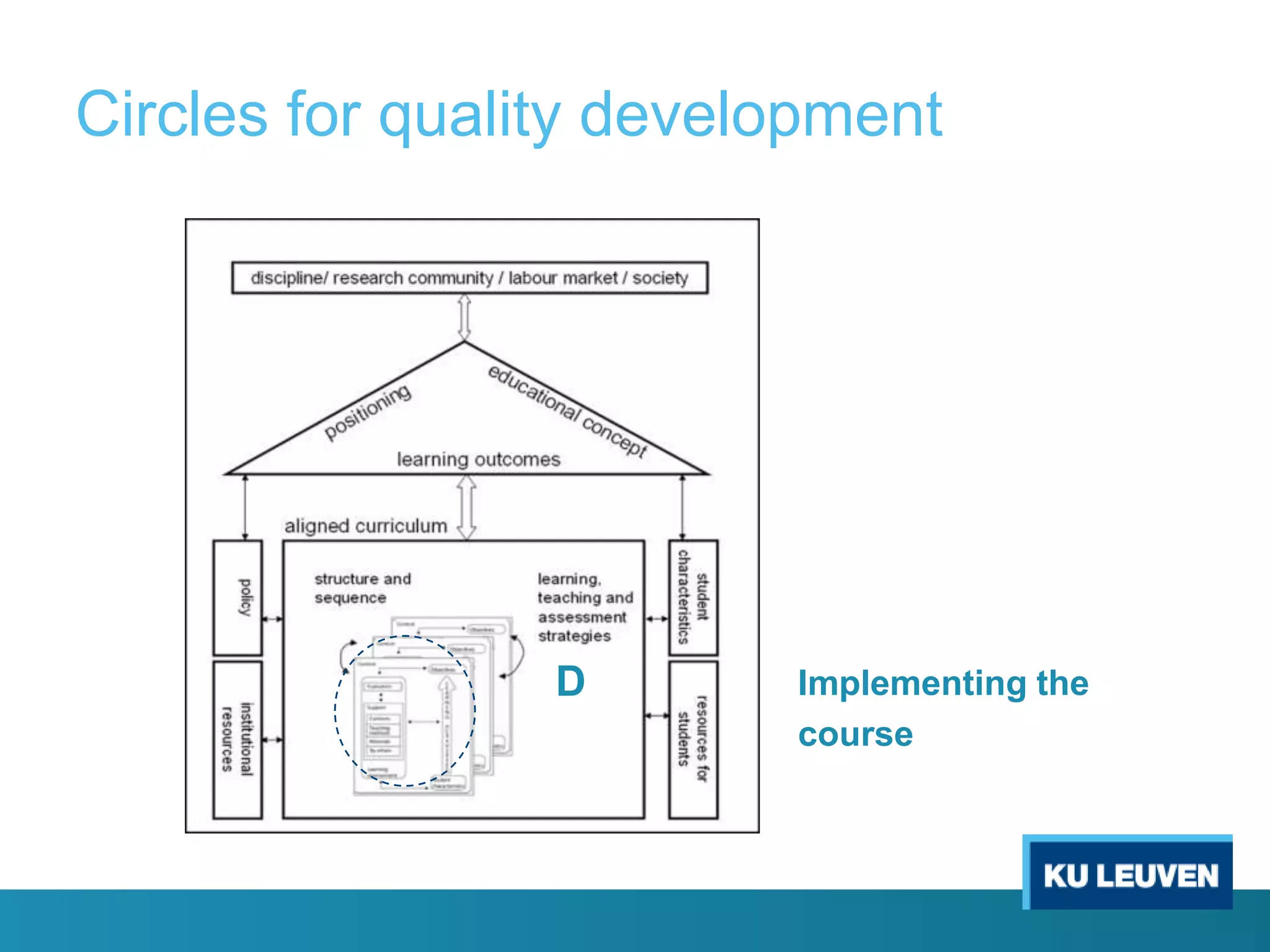
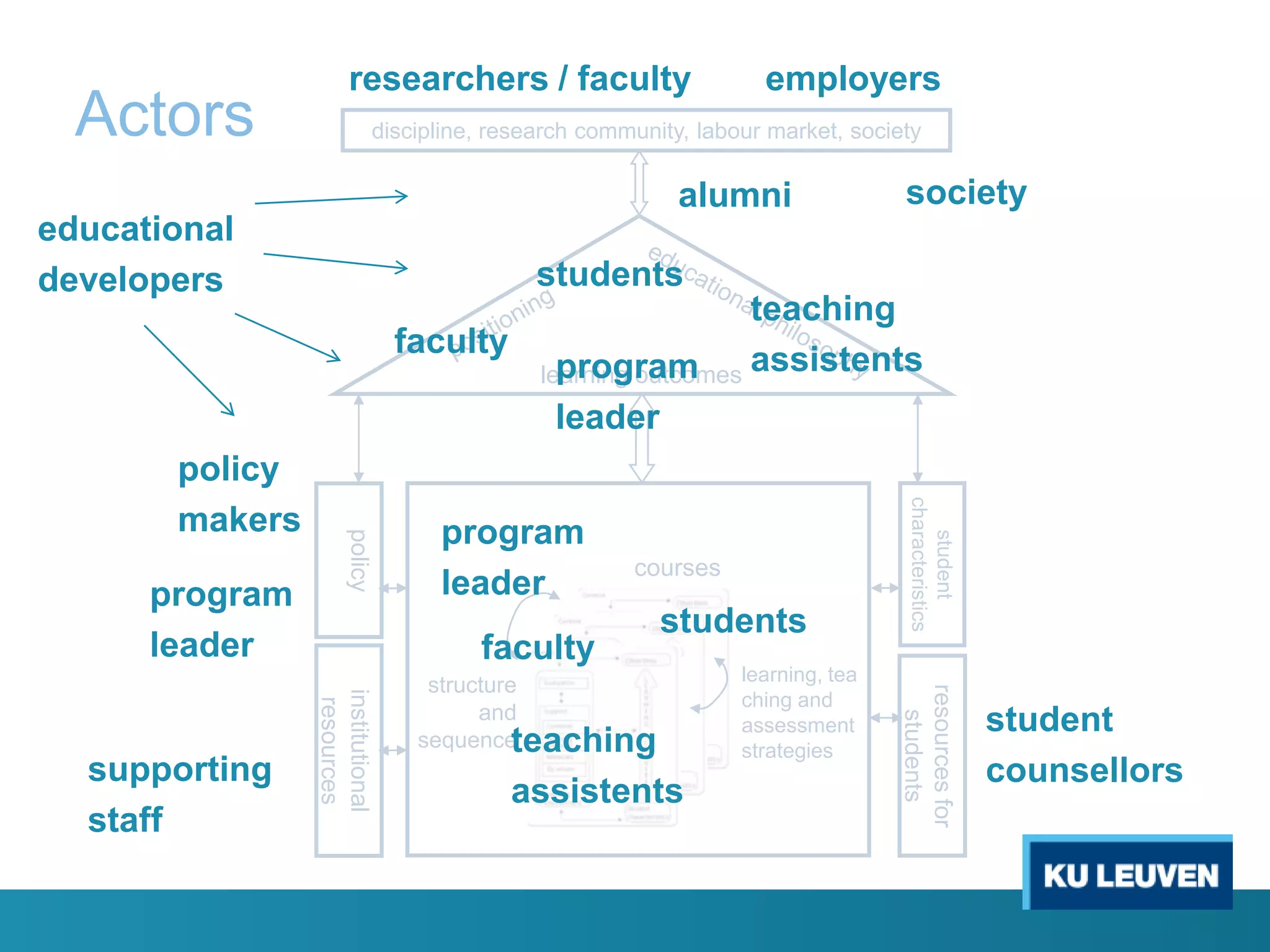
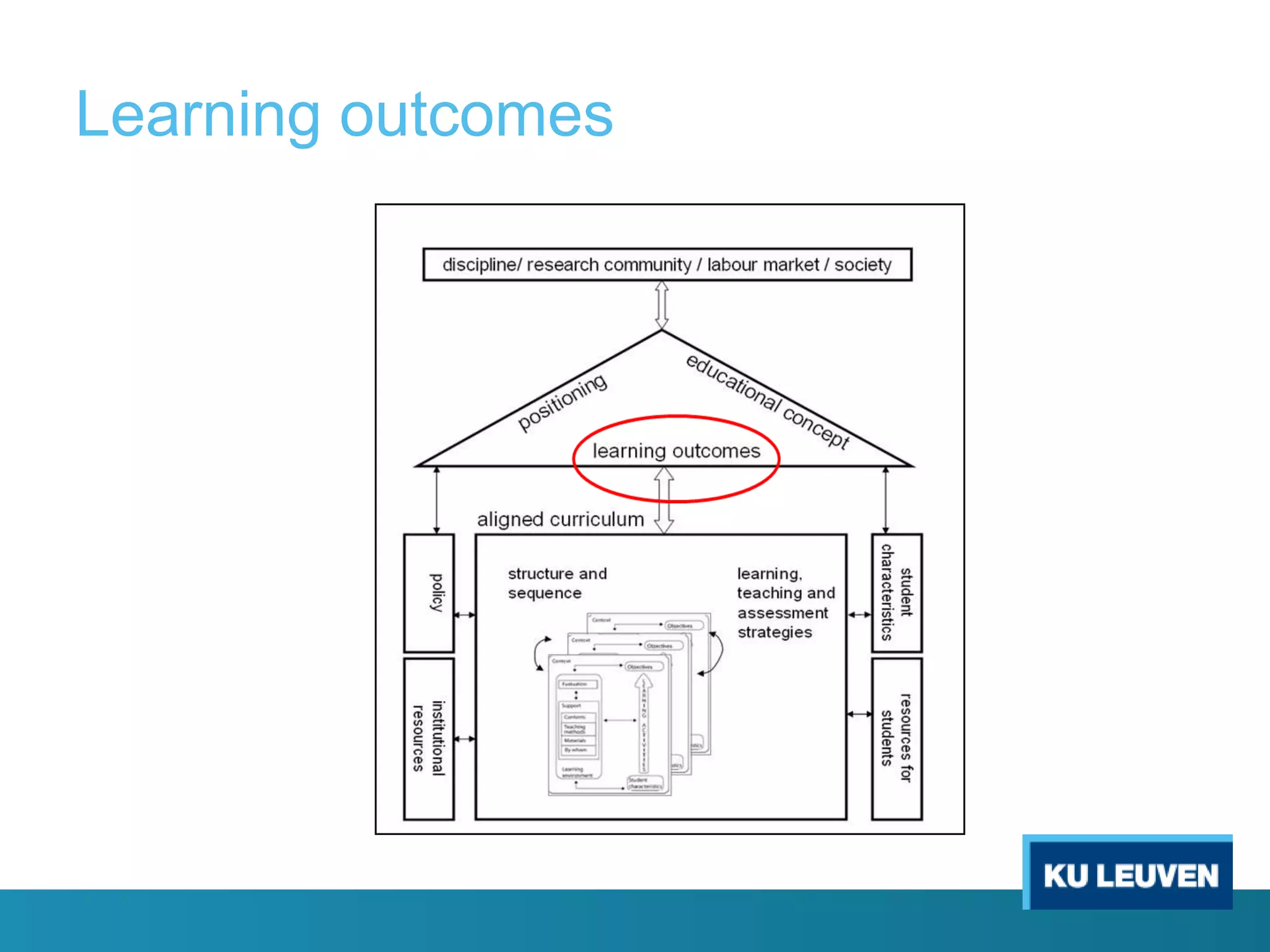
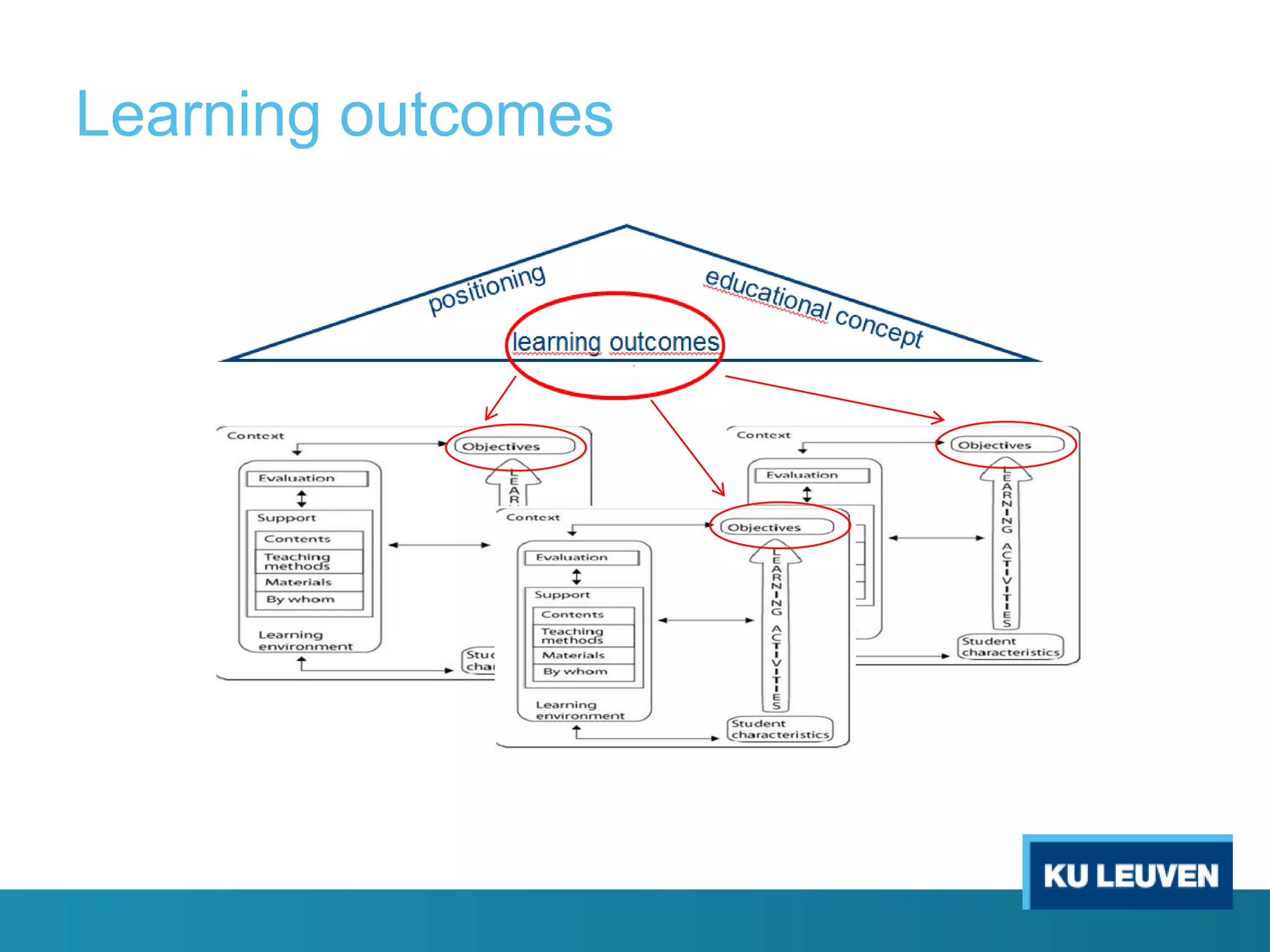
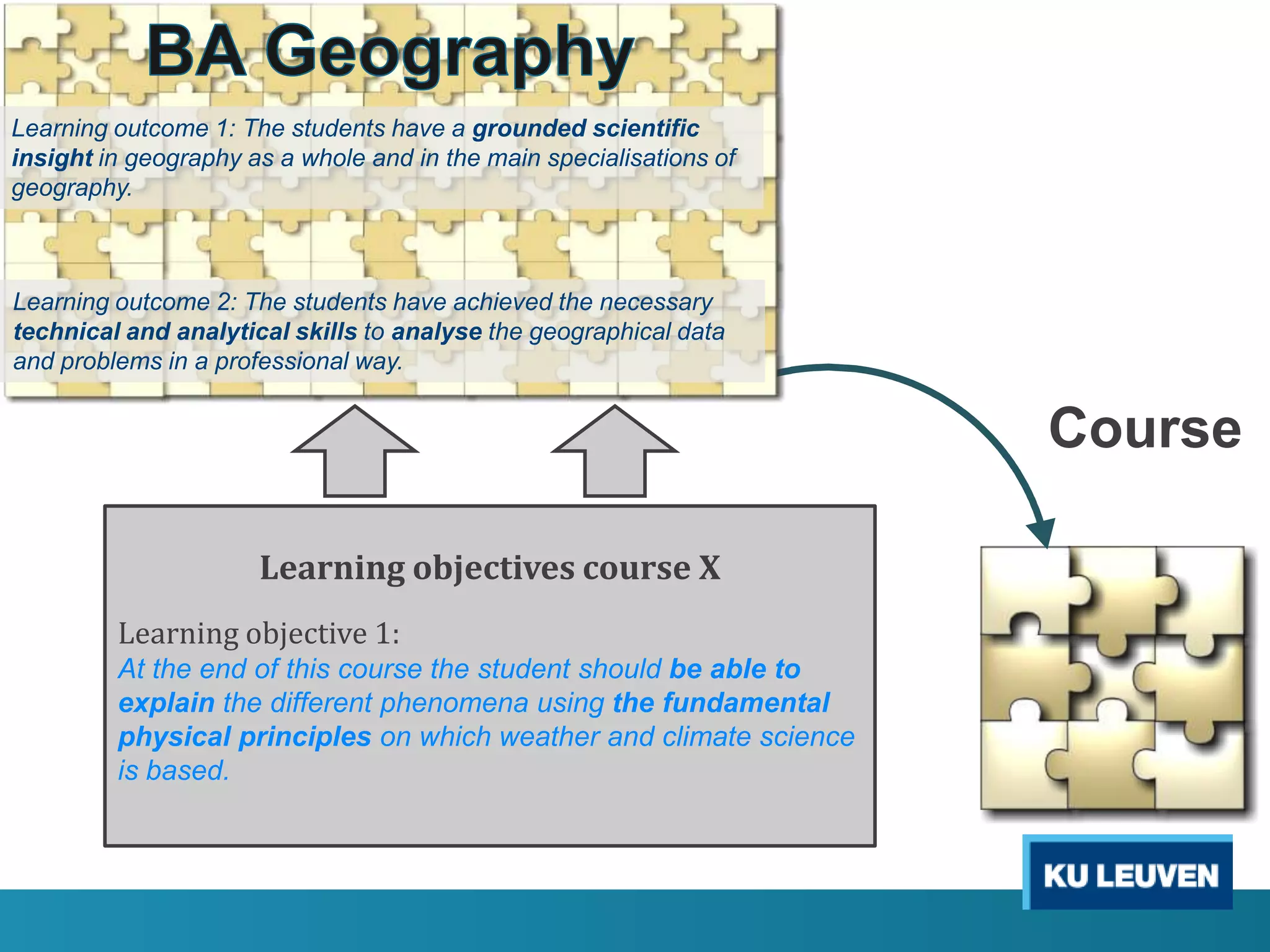
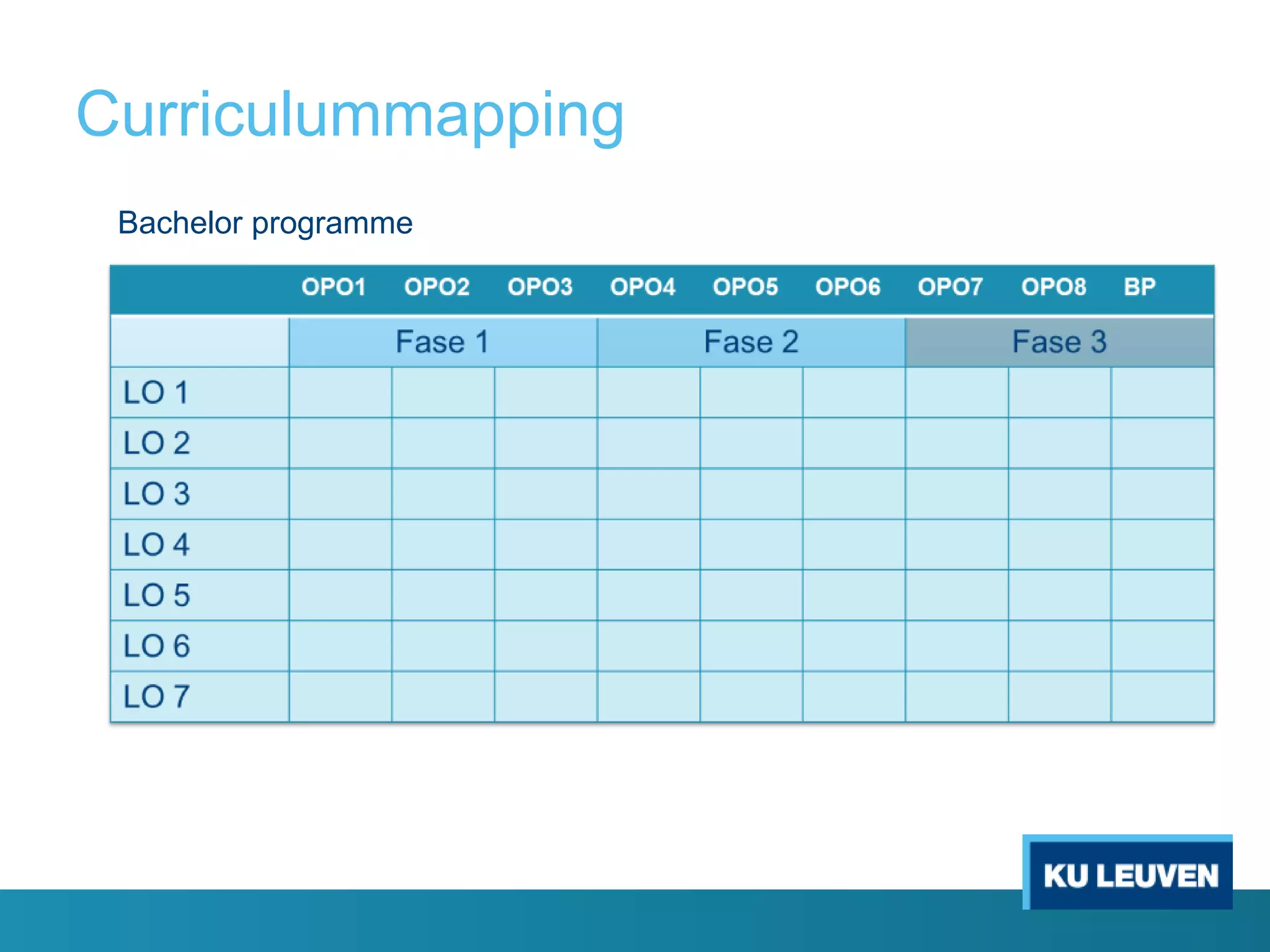
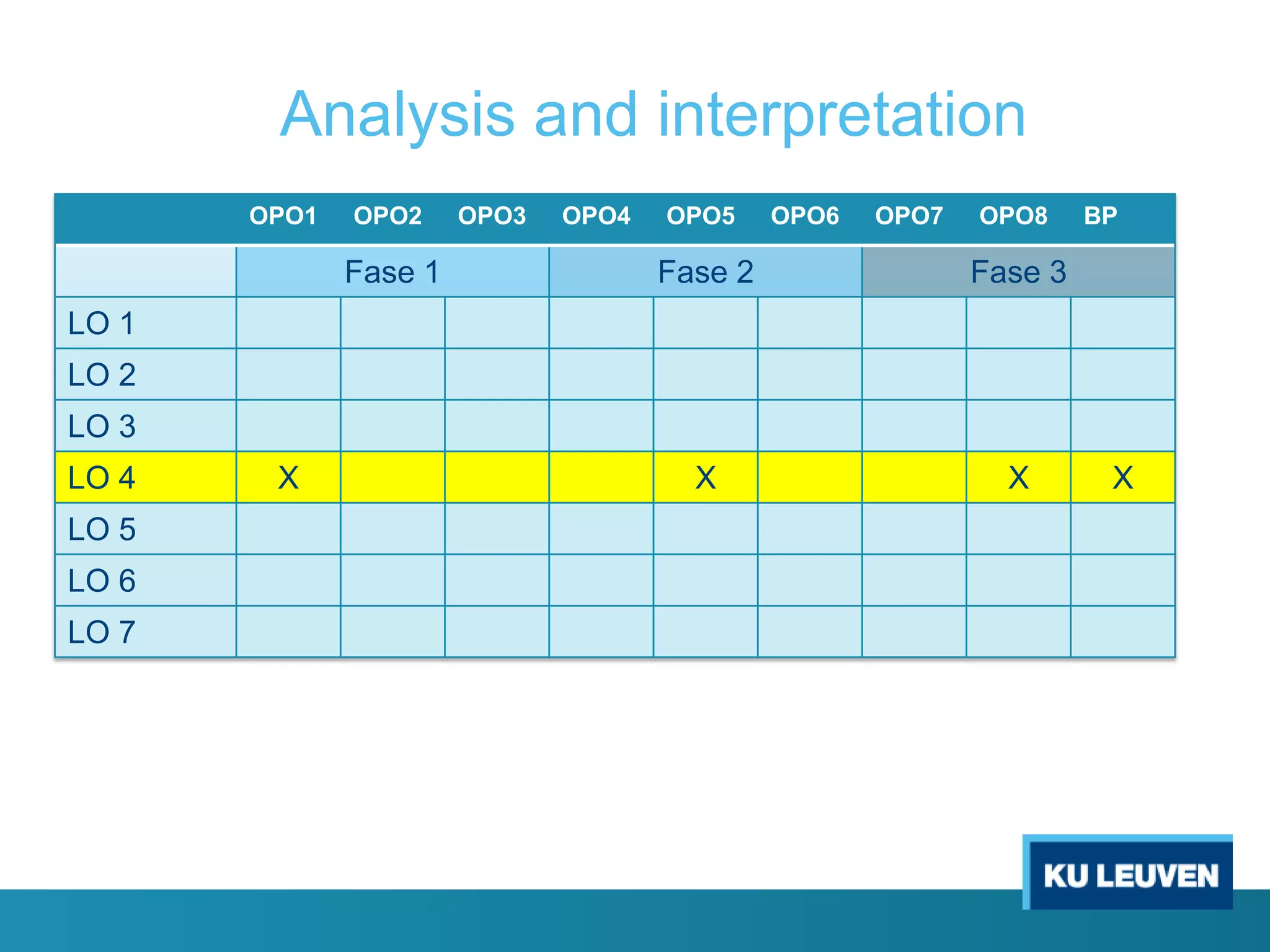
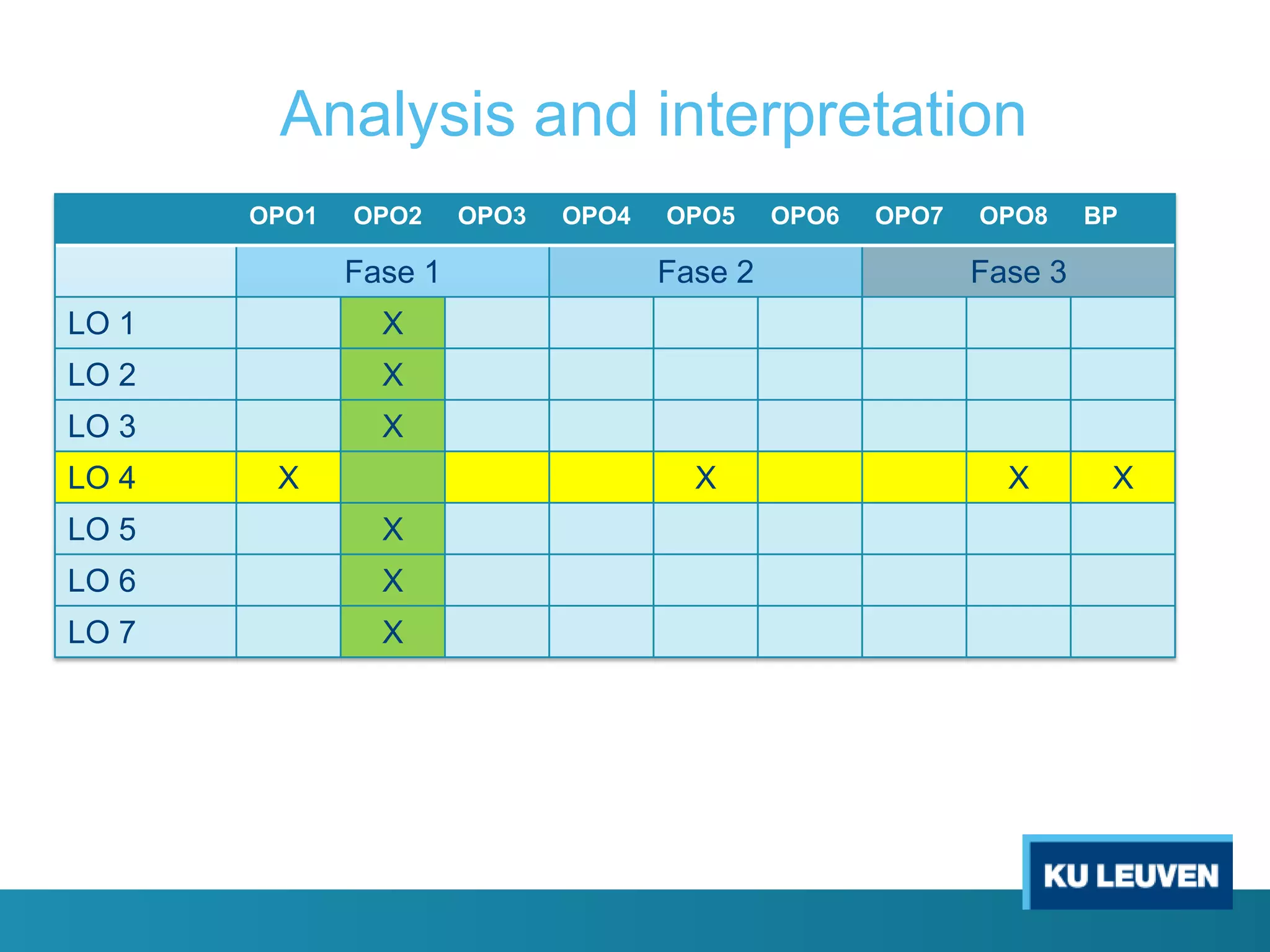
This document discusses curriculum design and alignment. It presents a conceptual scheme for curriculum design with four circles representing quality development: 1) rethinking intentions, 2) translating intentions, 3) implementing the curriculum, and 4) implementing courses. It focuses on learning outcomes, which describe the knowledge, skills, and attitudes students will acquire. Learning outcomes should be aligned across courses and assessed. The document also discusses curriculum mapping to visualize coherence in a program and identify if learning outcomes are realized or if there are gaps.