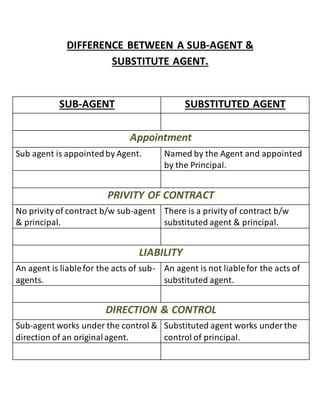
An agent can be held personally liable in certain situations, such as when the agent exceeds their authority or does not disclose the principal. An agency relationship can be terminated either by operation of law, such as the death of a party, or by the acts of the parties, like one party giving notice to the other. A substituted agent works directly for the principal, unlike a sub-agent who works under the control of the original agent, so the principal can hold a substituted agent liable but not a sub-agent.