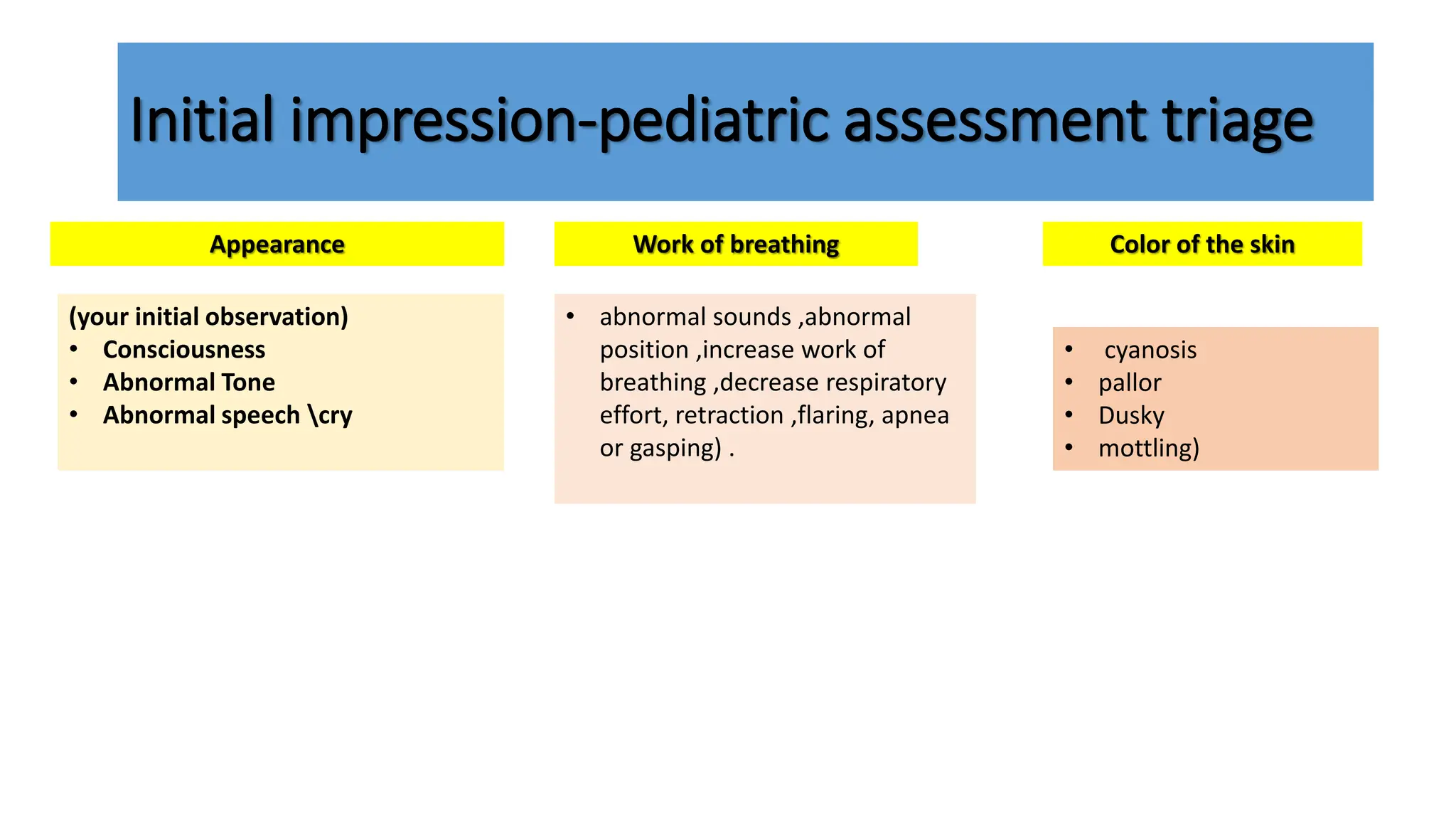
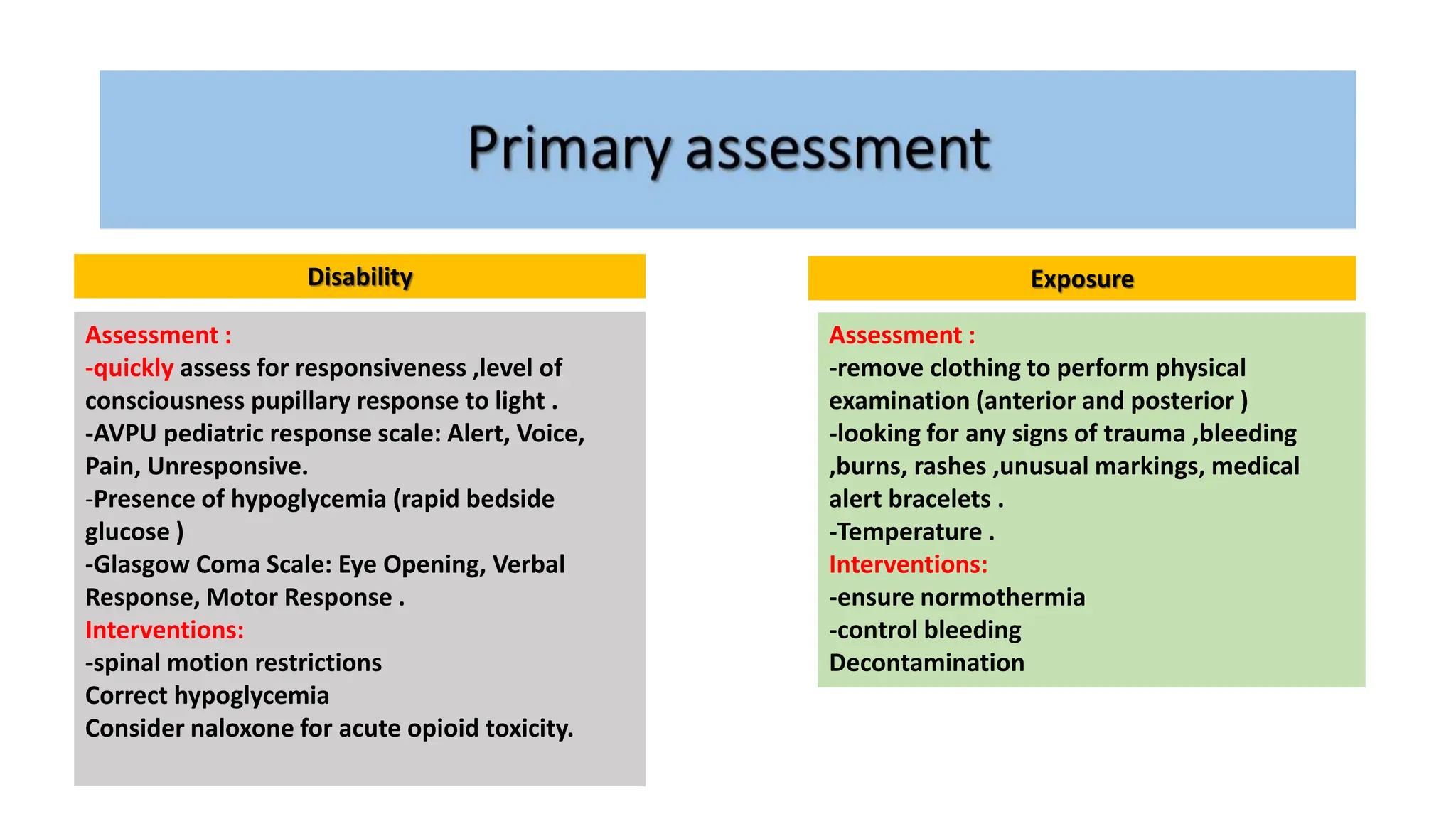
The document outlines a structured assessment and intervention protocol for managing pediatric respiratory and circulatory emergencies. It includes guidelines for primary and secondary assessments, types of respiratory and circulatory issues, and specific interventions such as airway management and medication administration. Emphasis is placed on thorough clinical evaluation, including focused histories and examinations, to guide treatment decisions effectively.