Embed presentation
Download as DOC, PPTX
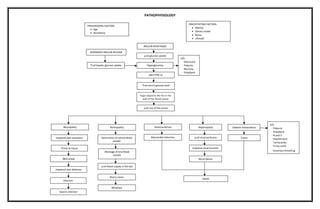

Type 2 diabetes is caused by insulin resistance and deranged insulin release from the pancreas, leading to hyperglycemia. Predisposing factors include age and heredity, while precipitating factors are obesity, diet, stress, and lifestyle. Symptoms of type 2 diabetes include glycosuria, polyuria, nocturia, and polydipsia. Diabetic ketoacidosis can also occur, with symptoms like polyuria, polydipsia, nausea, vomiting, hypotension, tachycardia, and Kussmaul breathing. Long-term complications involve damage to blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of nephropathy, retinopathy, atherosclerosis, neuropathy, infection, and
