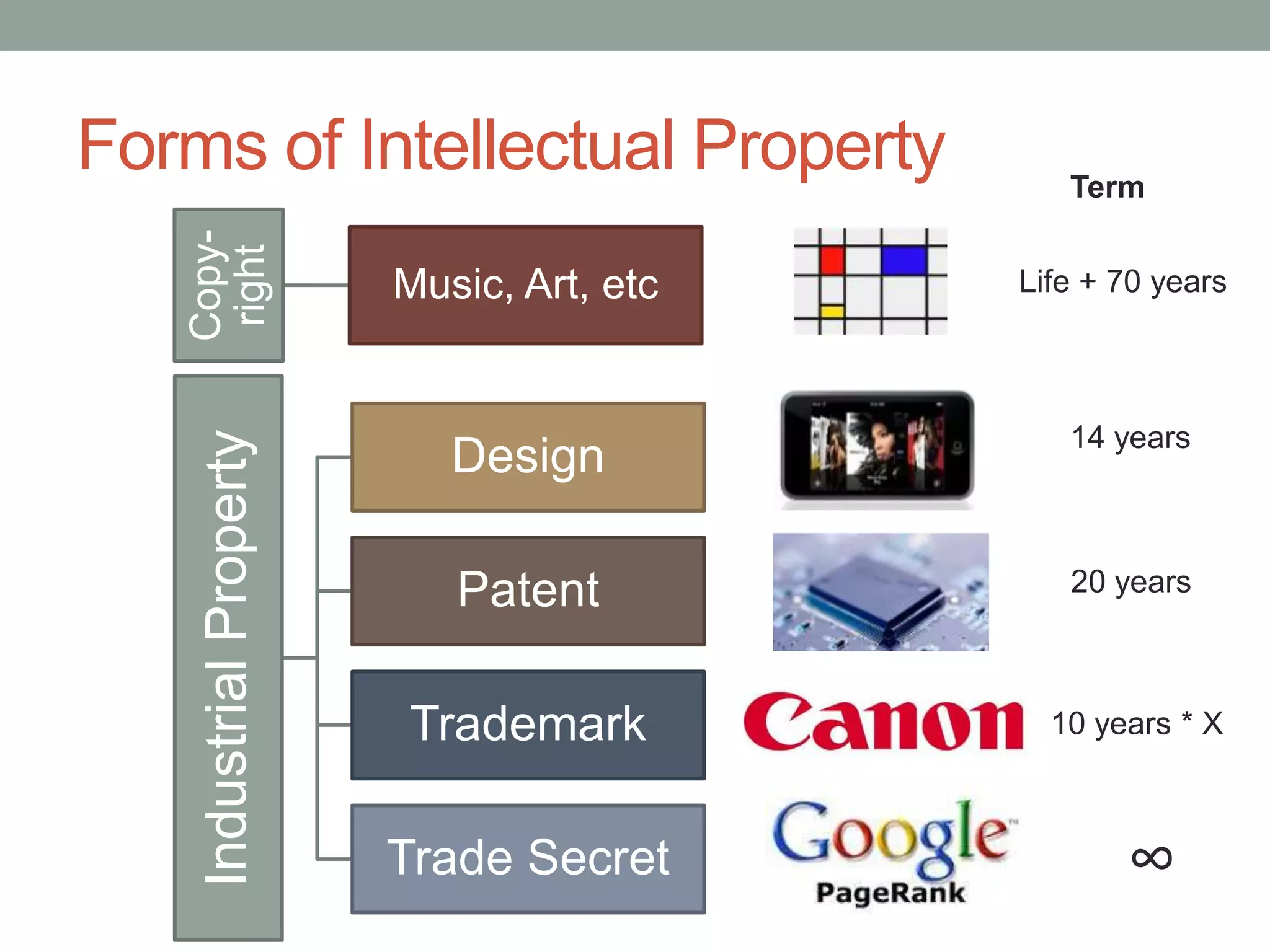
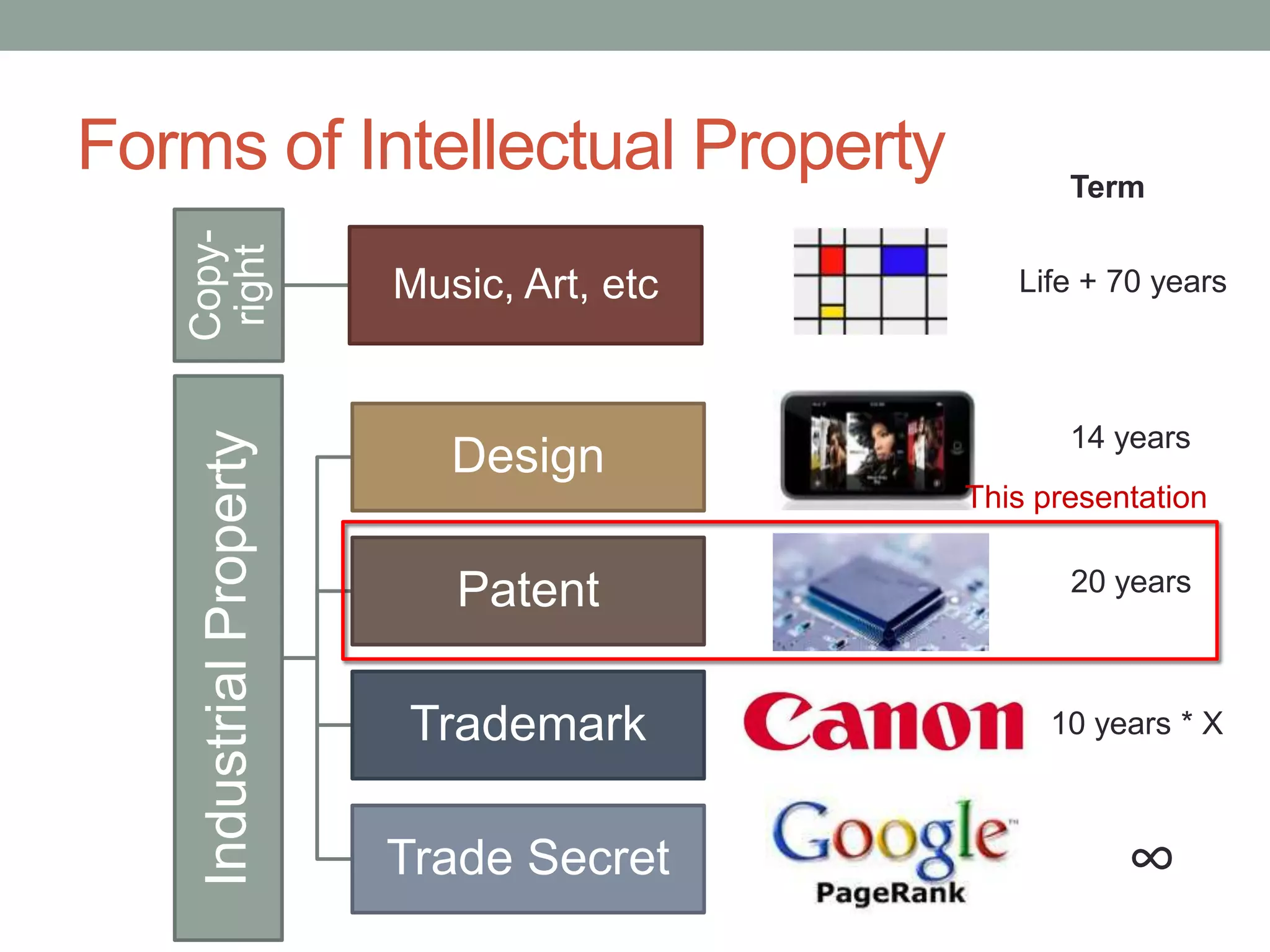
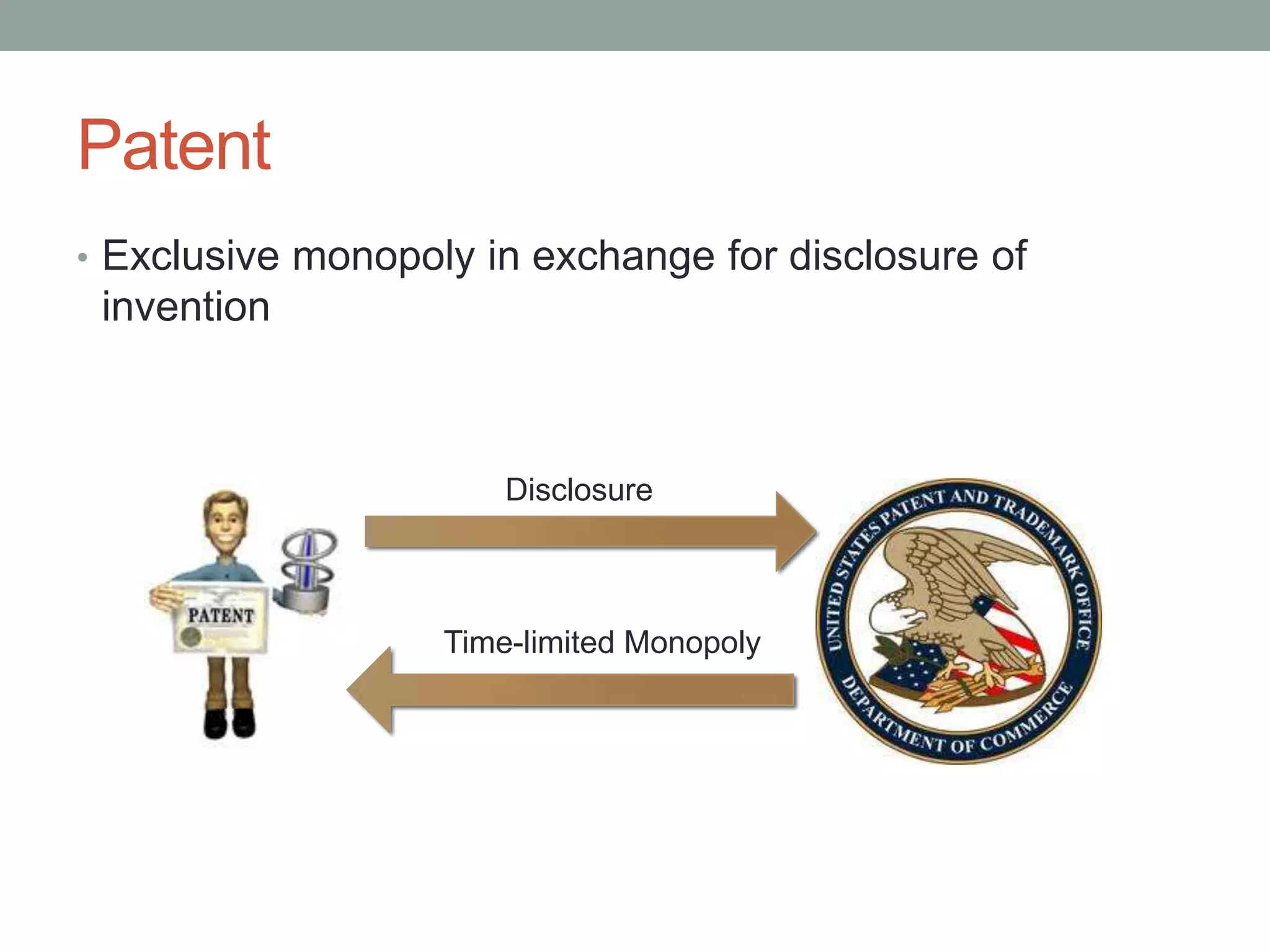
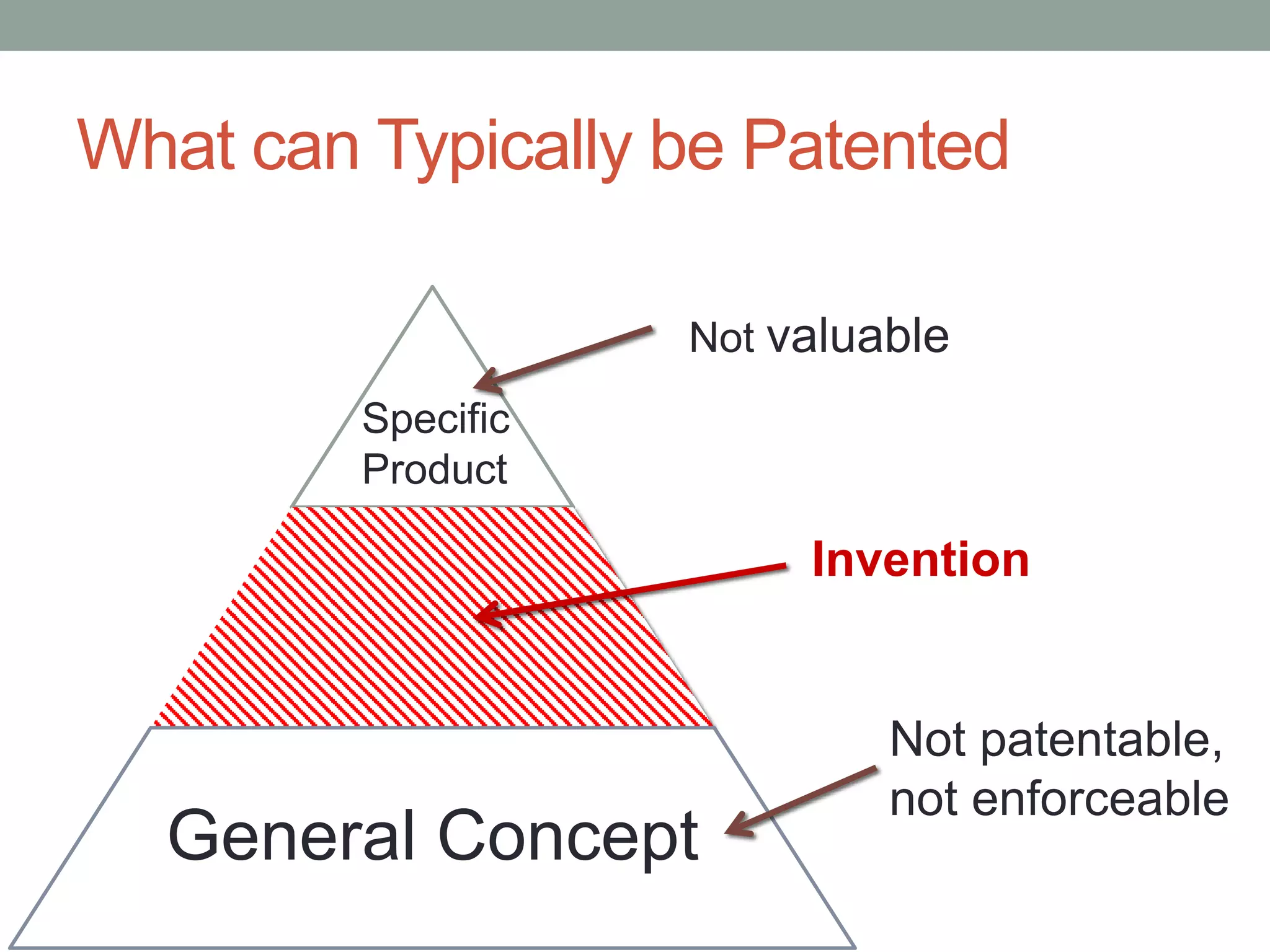
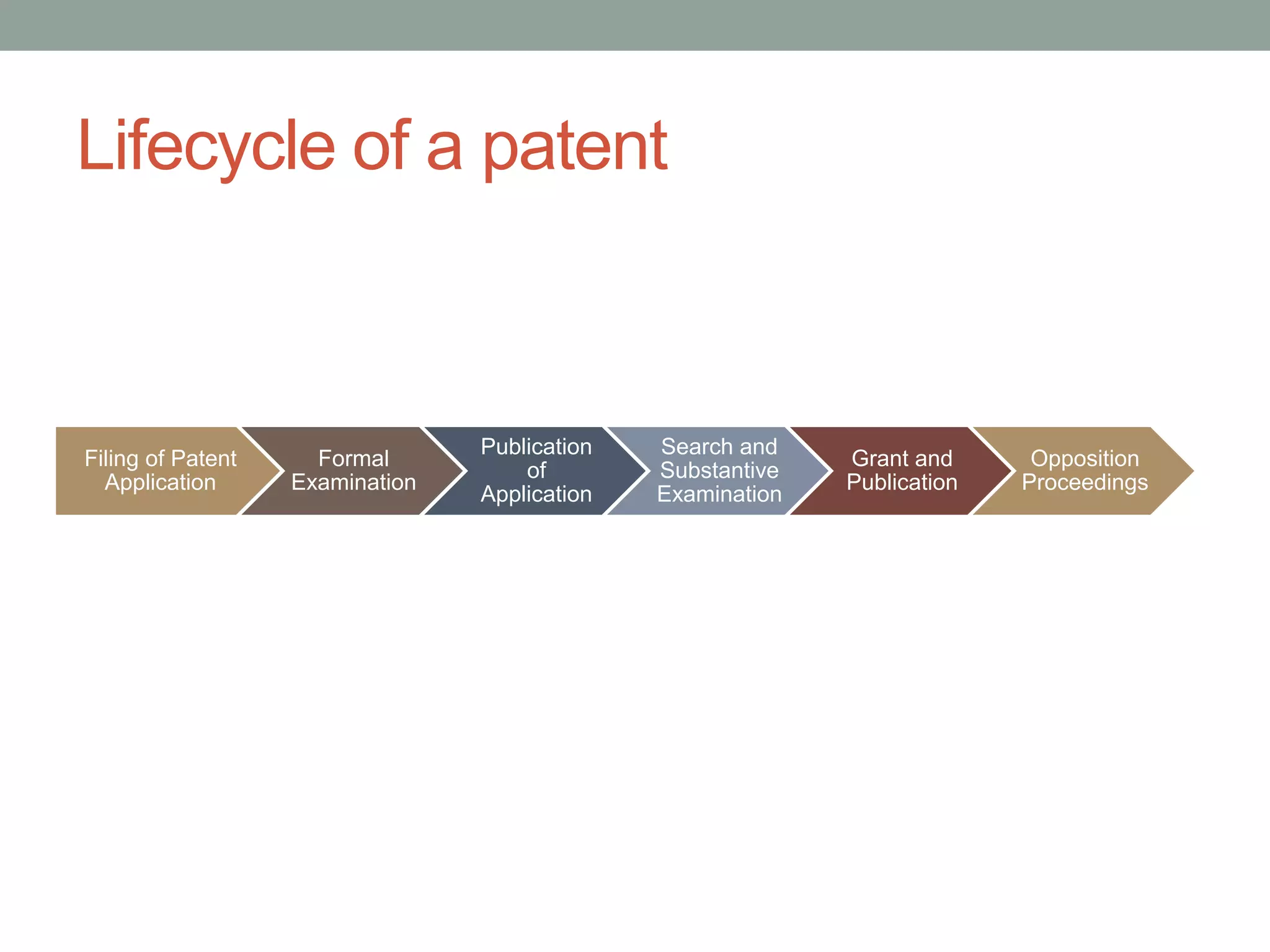
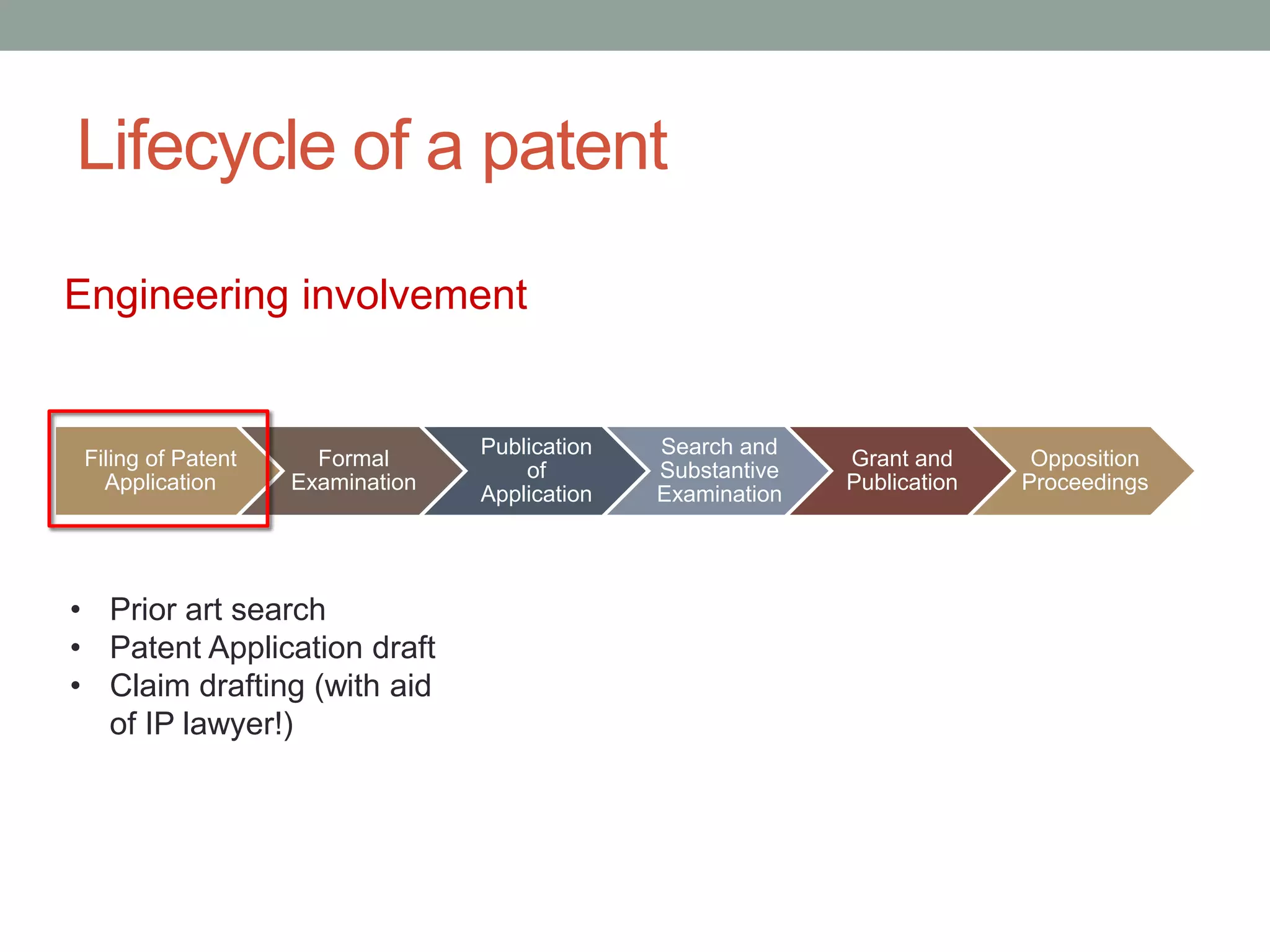
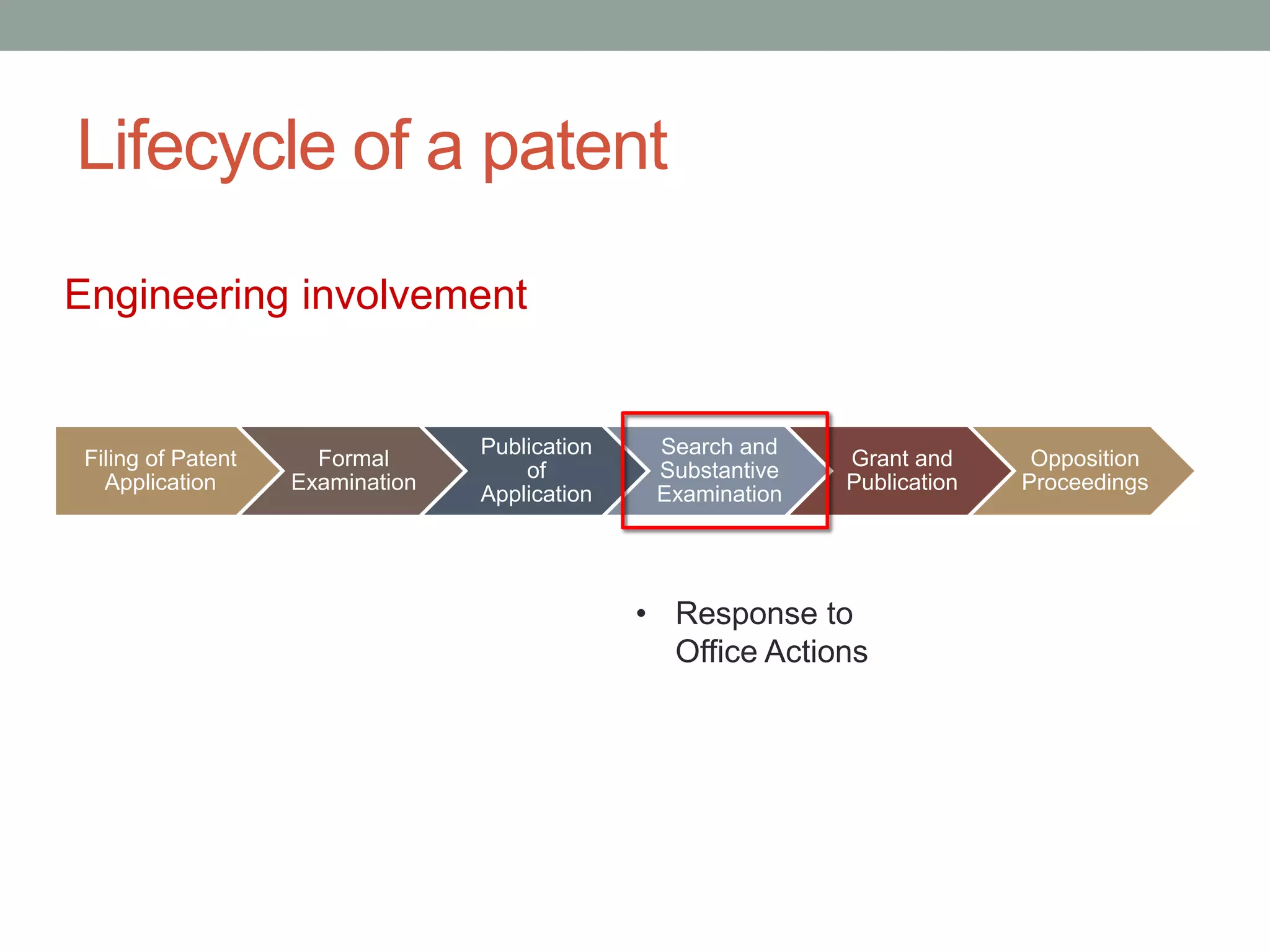
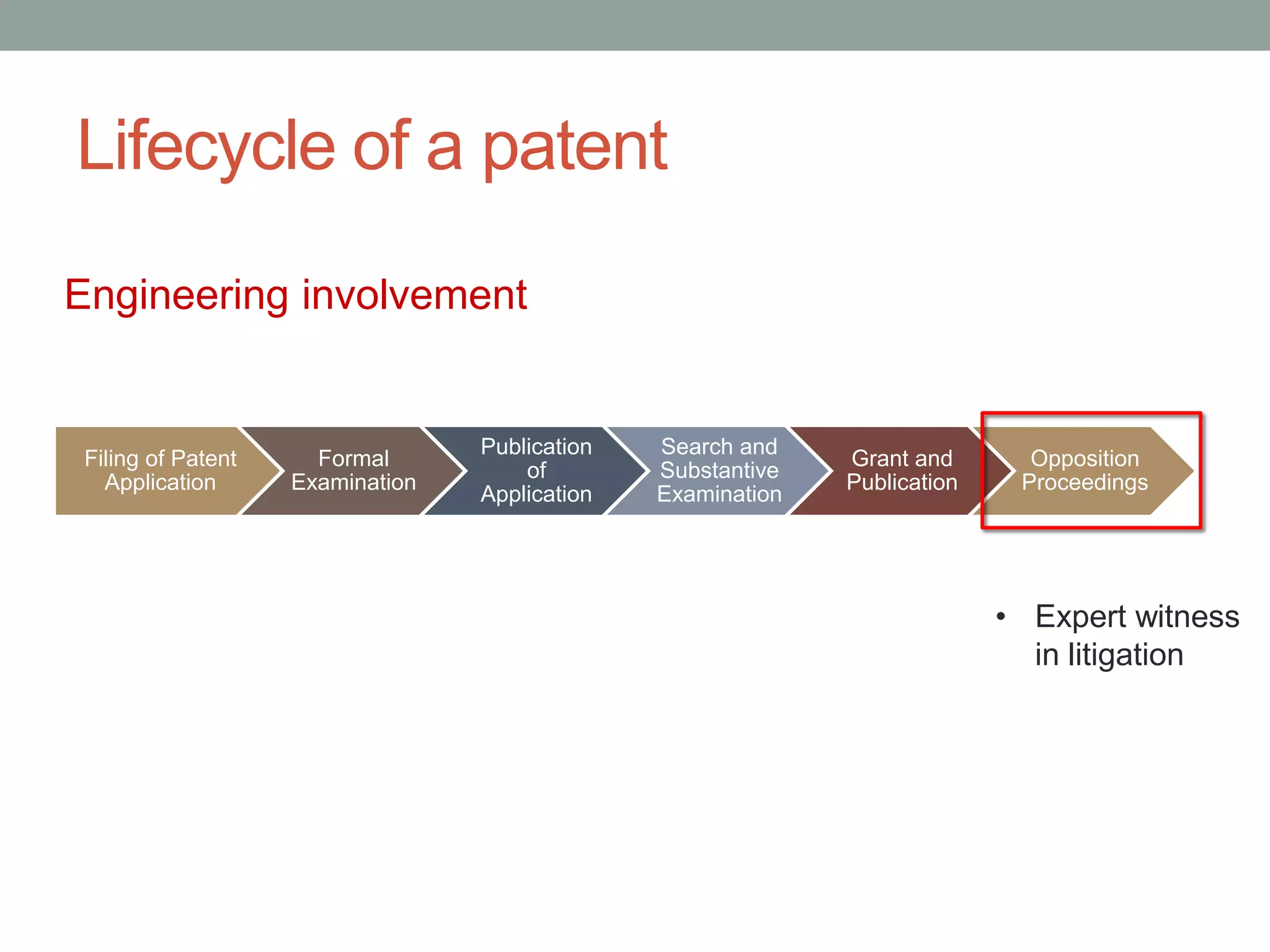
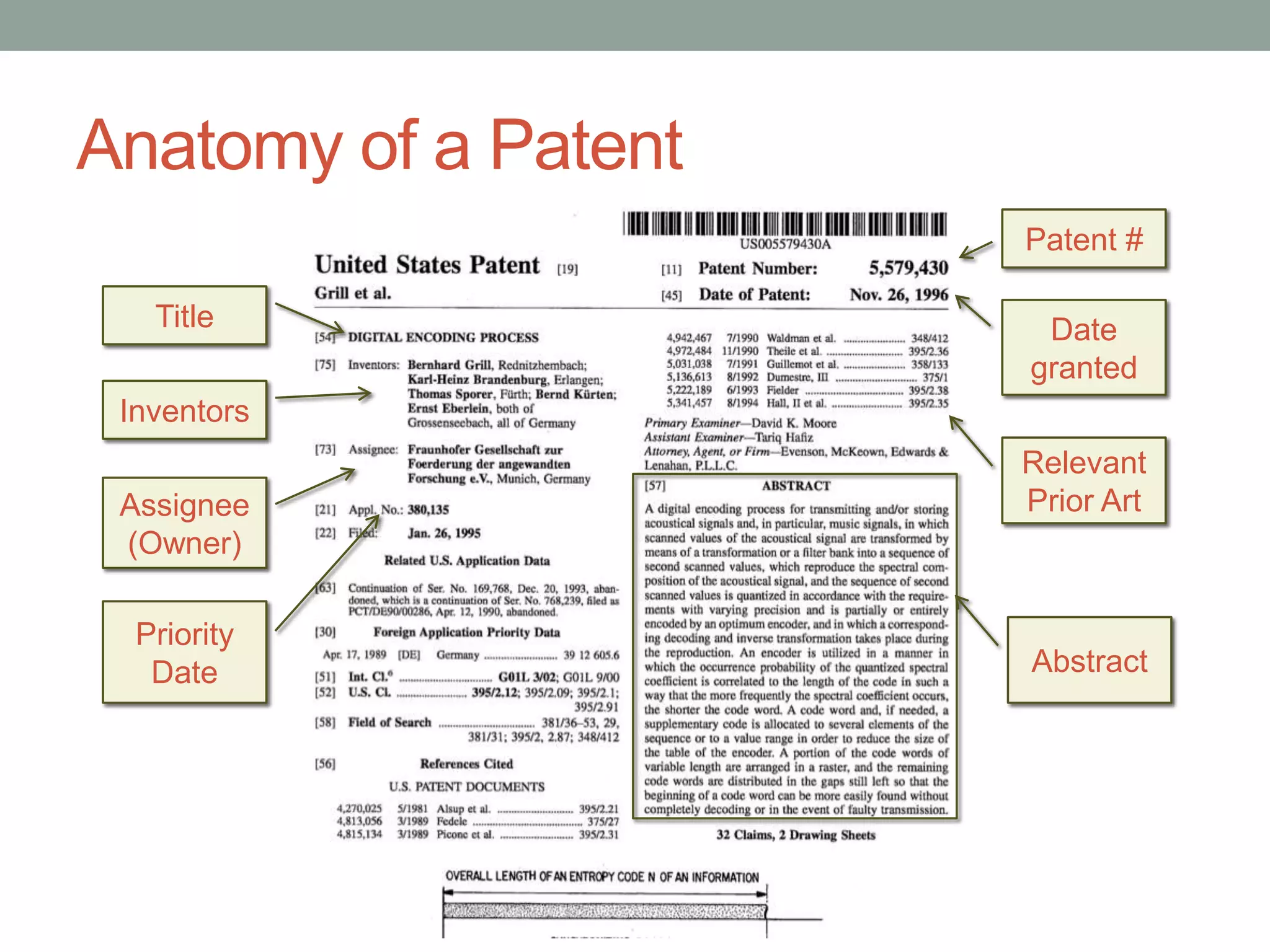
The document provides an overview of patenting and intellectual property (IP) strategy tailored for startups, highlighting various forms of IP, criteria for patentability, and the patent application lifecycle. It discusses the importance of patents in protecting competitive advantages, deterring competitors, and attracting investment, while also noting the challenges and costs involved in the process. Additionally, the document touches on controversies surrounding software patents and the differing views on their patentability in the US and EU.