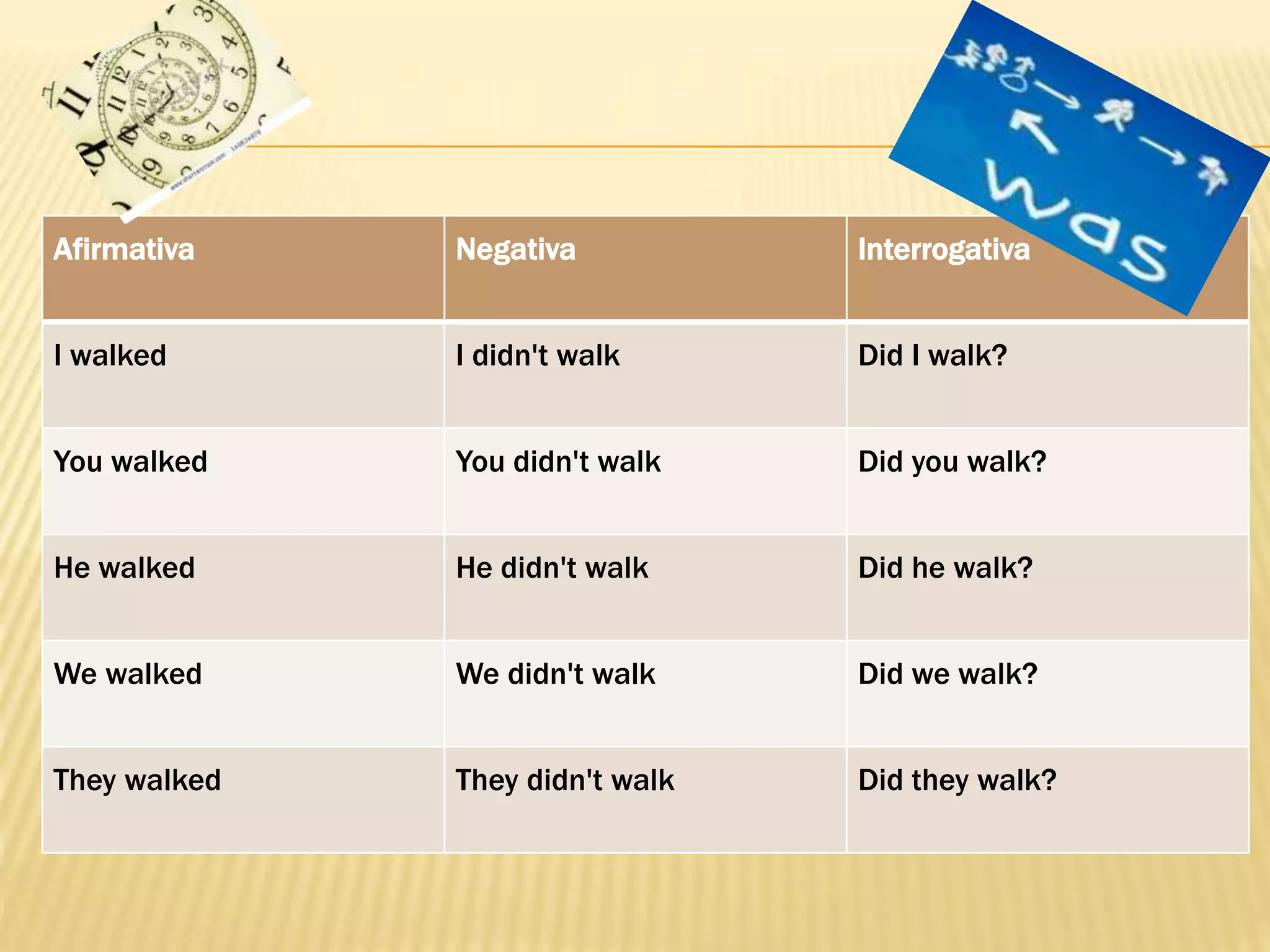
The document discusses the simple past tense in English. It explains that the simple past is used to talk about actions that were completed in the past, regardless of duration. Examples are provided of regular verbs like "walked" and irregular verbs like "gave" in the simple past affirmative, negative, and interrogative forms. Common irregular verbs that form the past tense irregularly, such as "go", "give", and "come" are also demonstrated in simple past sentences.