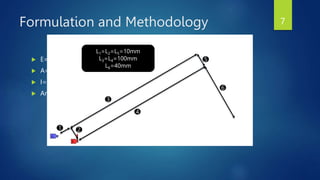
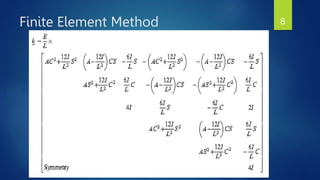
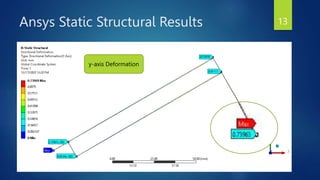
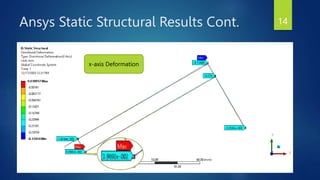
The document presents a semester project on the pantograph mechanism designed by Jawad Zakir, focusing on its low-cost and scalable manipulative capabilities for both micro and macro applications. It includes a literature review on robot manipulator designs, outlines the project's objectives and methodology, and discusses the finite element method and analysis results using ANSYS and MATLAB. The conclusion highlights the effectiveness of the designed mechanism for applications in various industries, showing amplification and displacement comparisons.


![Literature Review
Manipulator design in robots [1]
1 DOF pantograph leg mechanism for the kinematics of machine keeping in
view the idea of low cost and easy operation idea [2]
[2] Operation Analysis of a One-DOF Pantograph Leg Mechanisms (Proceedings of the RAAD 2008 17th International
Workshop on Robotics in Alpe-Adria-Danube Region September 15-17, 2008, Ancona, Italy)
[1]Yang, D. C. H., and Y. Y. Lin. “Pantograph Mechanism as a Non-Traditional Manipulator Structure.” Mechanism and
Machine Theory, vol. 20, no. 2, Jan. 1985, pp. 115–22
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pantographmechanism-230102062619-845bb146/85/Pantograph-Mechanism-pptx-3-320.jpg)
![Literature Review
Manipulator design in robots [1]
1 DOF pantograph leg mechanism for the kinematics of machine keeping in
view the idea of low cost and easy operation idea [2]
Thermal erosion
Complaint mechanism
[2] Operation Analysis of a One-DOF Pantograph Leg Mechanisms (Proceedings of the RAAD 2008 17th International
Workshop on Robotics in Alpe-Adria-Danube Region September 15-17, 2008, Ancona, Italy)
[1]Yang, D. C. H., and Y. Y. Lin. “Pantograph Mechanism as a Non-Traditional Manipulator Structure.” Mechanism and
Machine Theory, vol. 20, no. 2, Jan. 1985, pp. 115–22
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pantographmechanism-230102062619-845bb146/85/Pantograph-Mechanism-pptx-4-320.jpg)