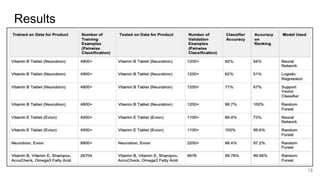
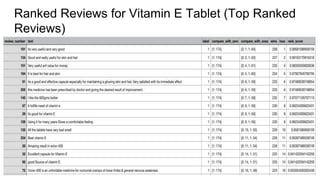
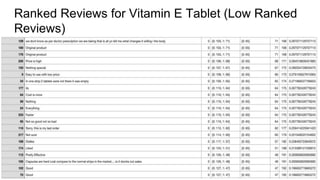
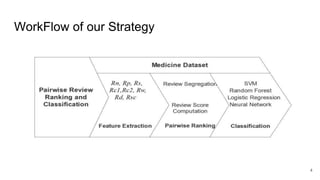
The document discusses a pairwise review ranking method for a medicine e-commerce application, highlighting the importance of reviews in influencing customer decisions. It outlines the process of feature extraction, classification, and performance measures, emphasizing the use of random forest classifiers for achieving optimal results. Future work includes personalizing review rankings based on user preferences and integrating user upvote data.


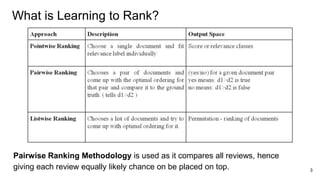


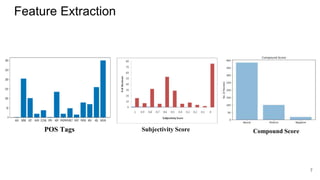


![Classification Model
Classification models Used:
● RandomForest
● Support Vector Classifier
● Logistic Regression
● Neural Network
11
On experimenting with these classifier models, we got the best results with Random
Forest Classifier. [Slide 13]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pairwisereviewsrankingandclassificationformedicinee-commerceapplication-200203053145/85/Pairwise-reviews-ranking-and-classification-11-320.jpg)