This document discusses pregnancy associated breast cancer, including its definition, incidence, challenges, diagnostic workup, treatment strategies, and guidelines. Some key points:
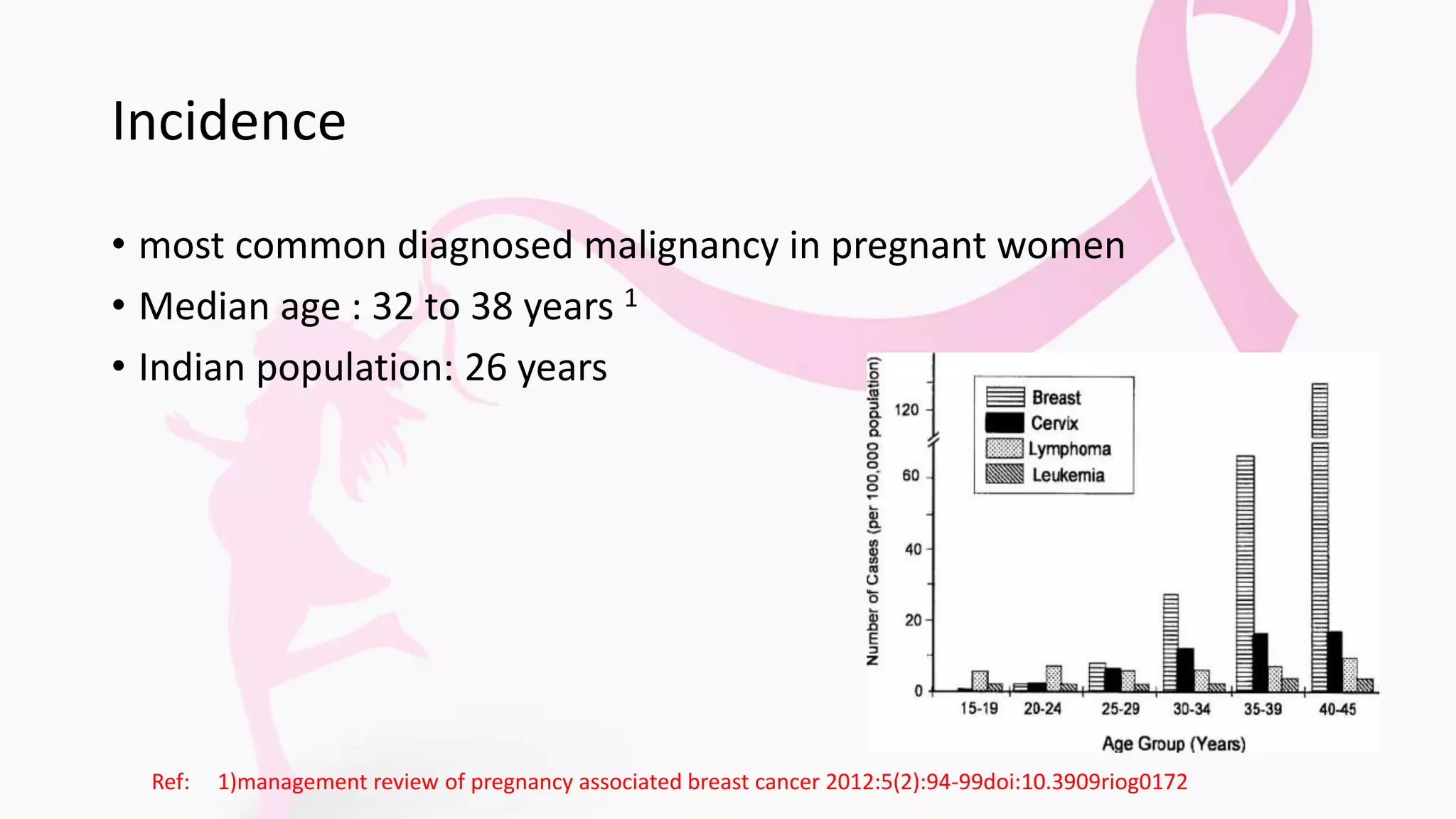
- It is breast cancer diagnosed during pregnancy or within 1 year of delivery, with median age of diagnosis between 32-38 years.
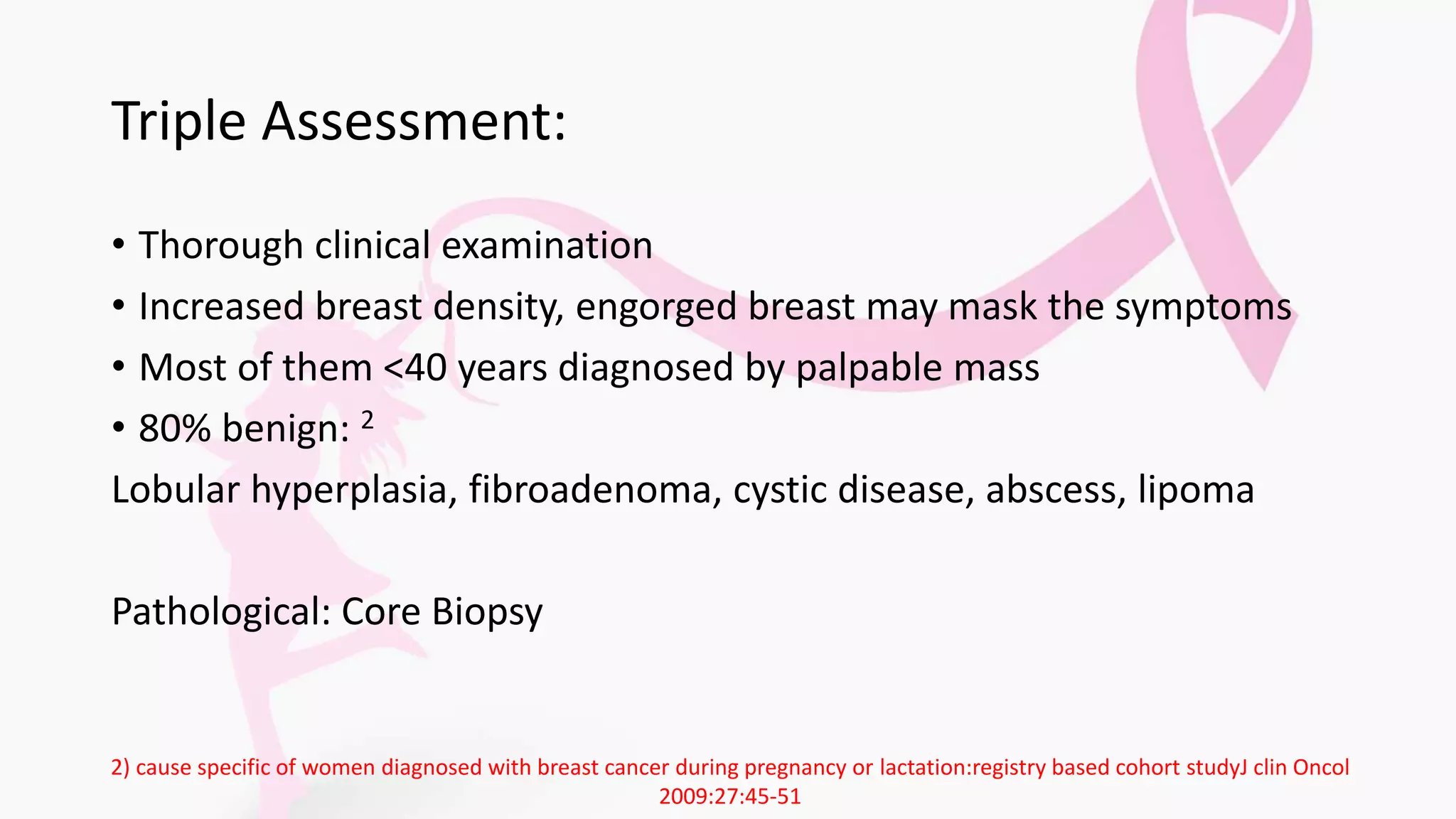
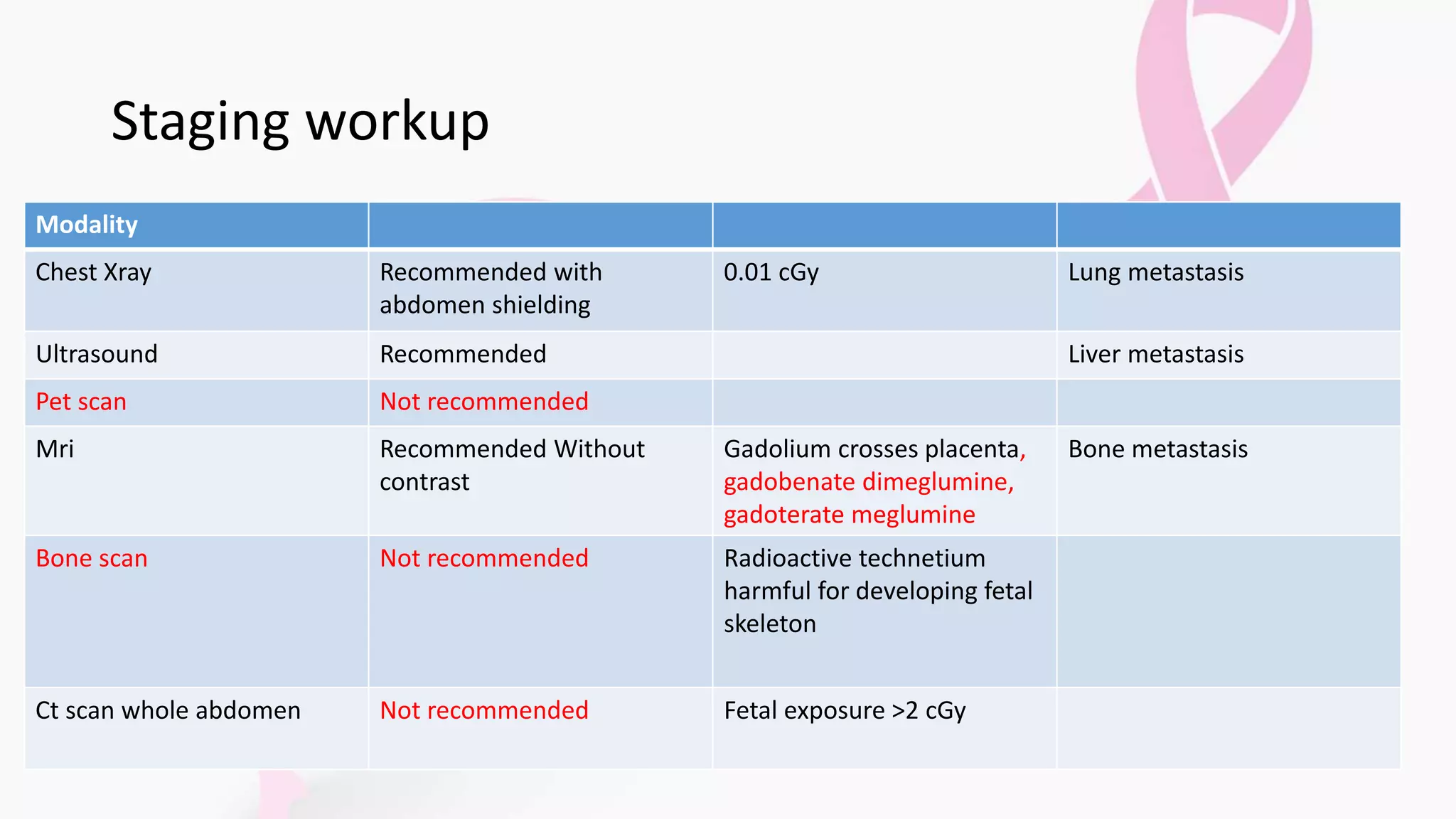
- Triple assessment including clinical exam, imaging like ultrasound and MRI, and biopsy is recommended for diagnosis while limiting radiation exposure to the fetus.
- Treatment depends on trimester but may include surgery, chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, and radiation therapy postpartum. Chemotherapy in the first trimester poses highest risk to the fetus.
- Guidelines from NCCN recommend different treatment strategies based on trimester of diagnosis to