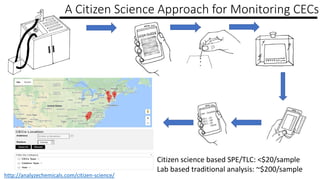
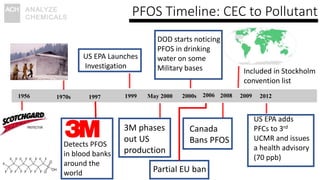
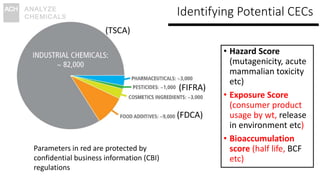
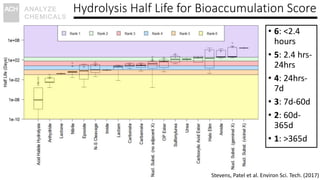
The document discusses the monitoring of contaminants of emerging concern (CECs) in drinking water, emphasizing the relevance of the Safe Water Drinking Act and the classification of CECs. It highlights the historical timeline of PFOS as a CEC transitioning to a pollutant and identifies the need for improved data collection on CECs through citizen science initiatives. The conclusions stress the importance of proactive regulatory changes and the potential for citizen involvement in bridging data gaps at a lower cost.


![Safe Water Drinking Act (SWDA), 1996
• Mandates monitoring of water resources (except private wells used
by less than 25 people) for 114 chemicals such as organics, inorganics
[1] and microorganisms
• Sets enforceable max. contaminant levels (MCLs)
• Mandates that EPA can additionally monitor for no more than 30
unregulated contaminants every five years [2]. This is called
unregulated contaminant monitoring rule (UCMR).
[1] http://scorecard.goodguide.com/chemical-groups/one-list.tcl?short_list_name=mcl
[2] https://www.epa.gov/dwucmr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/owod-05-1-jaypatelnonexistentdata-170605145755/85/Owod-05-1-jay-patel-nonexistent_data-3-320.jpg)
![Contaminants of Emerging Concern (CECs)
European
commission
Funded
Norman
Network [1]
classifies ~900
chemicals as
CECs
[1] http://www.norman-network.net/?q=node/19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/owod-05-1-jaypatelnonexistentdata-170605145755/85/Owod-05-1-jay-patel-nonexistent_data-4-320.jpg)
![Nonexistent Data for CECs in water
[1] https://www2.usgs.gov/envirohealth/geohealth/full_activities_list.html
[2] Hu et al. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett., 2016, 3 (10), pp 344–350
2013-2015 [2]
1999-2009
Public Wells [1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/owod-05-1-jaypatelnonexistentdata-170605145755/85/Owod-05-1-jay-patel-nonexistent_data-8-320.jpg)