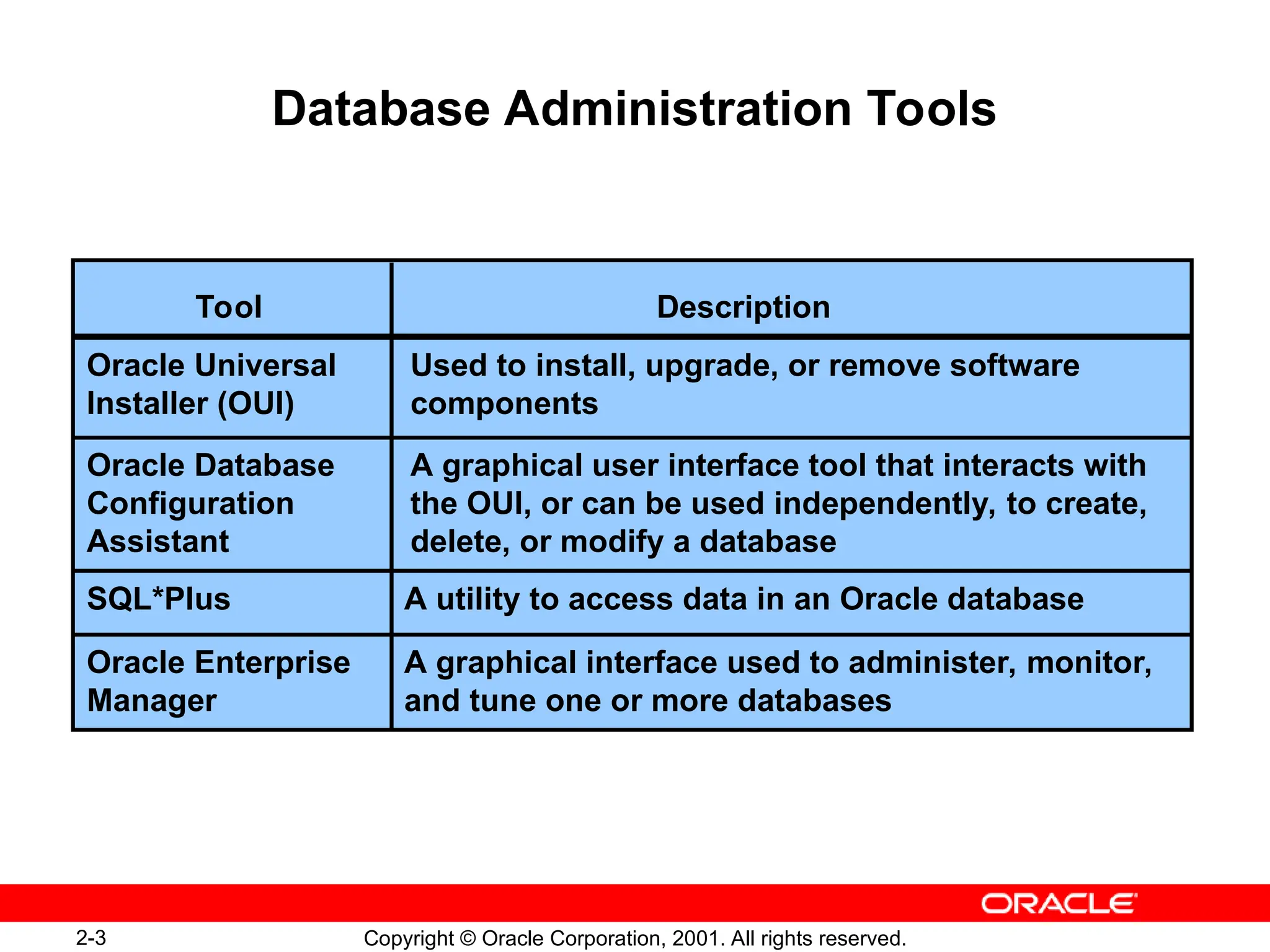
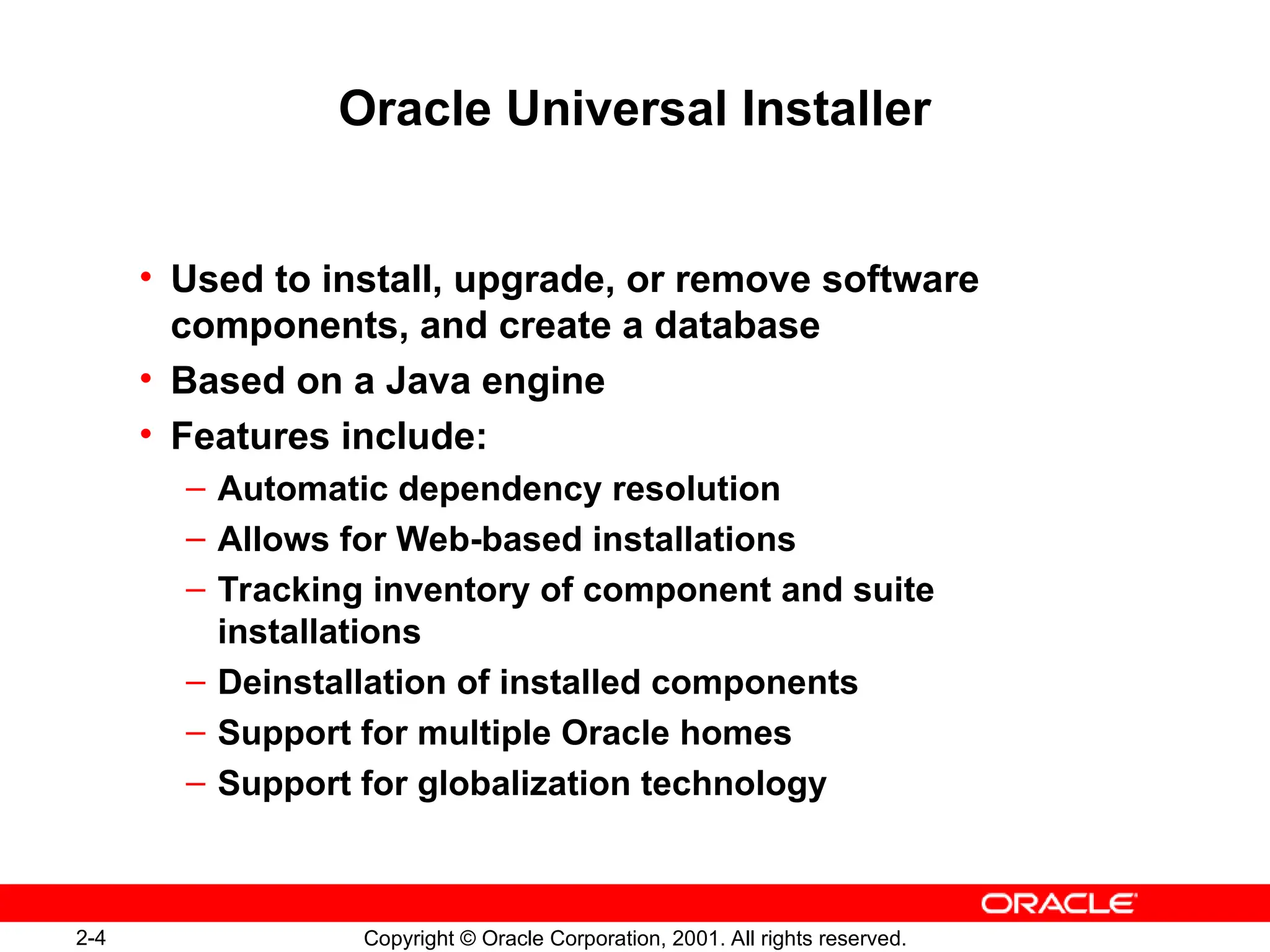
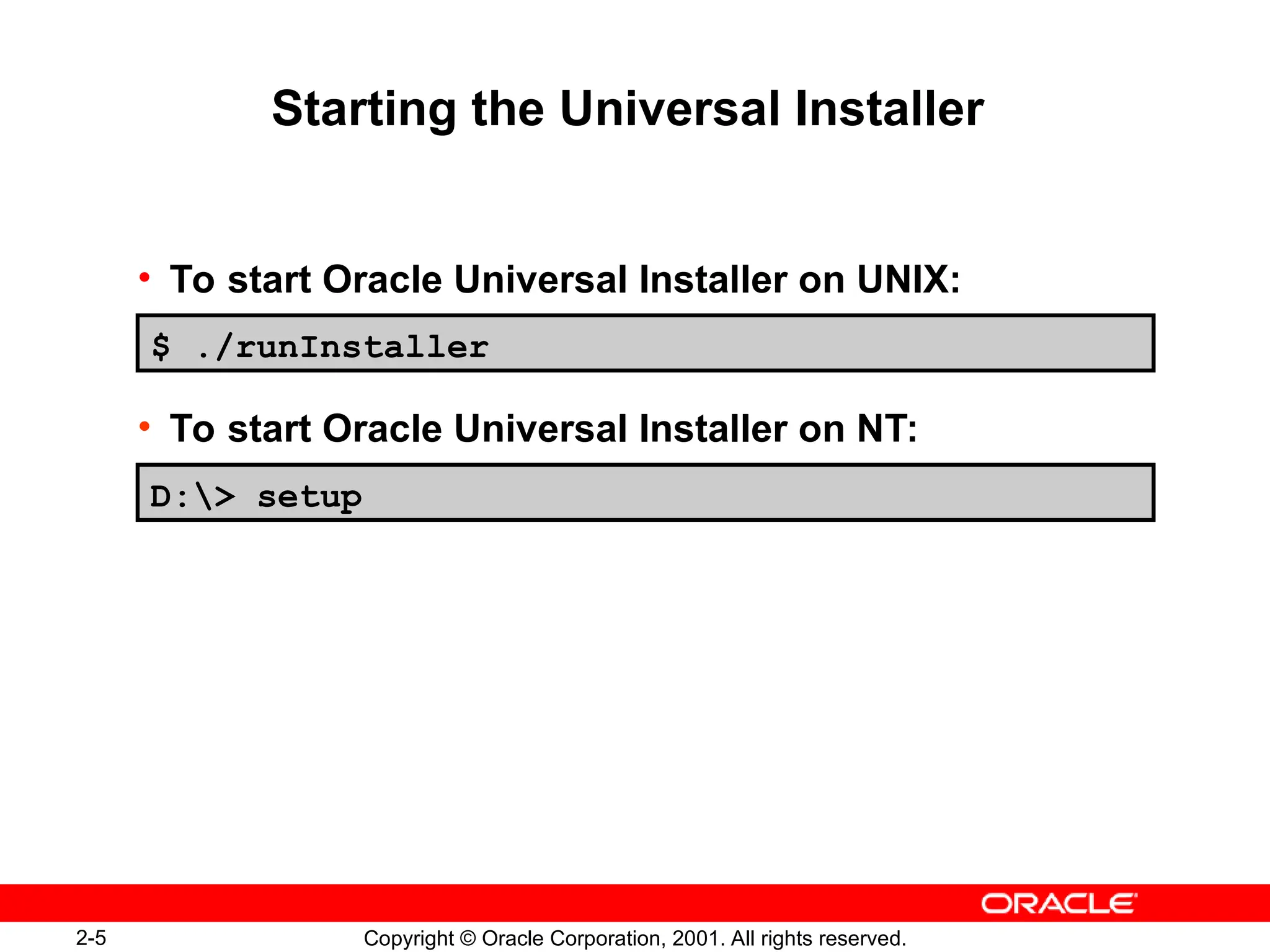
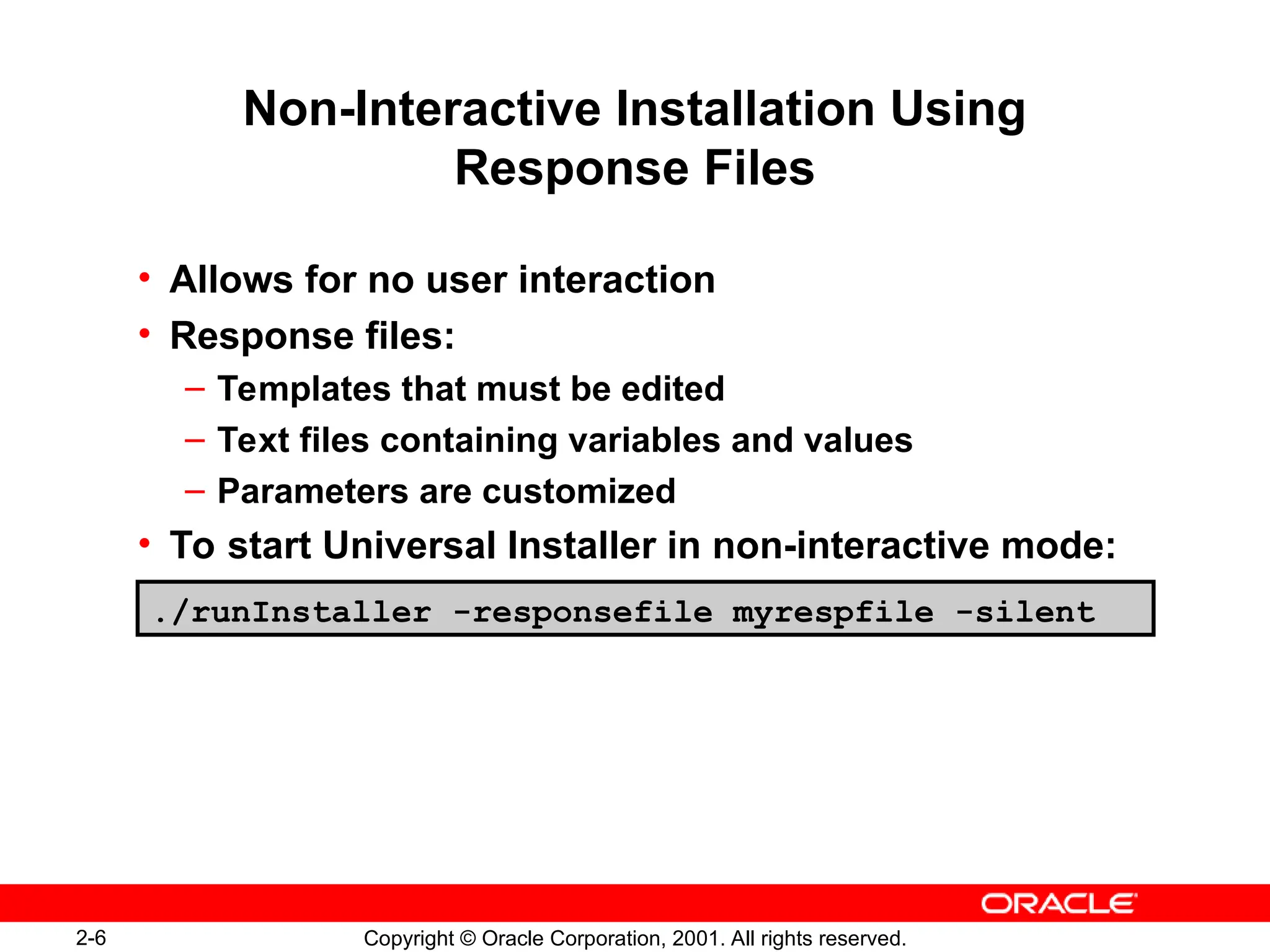
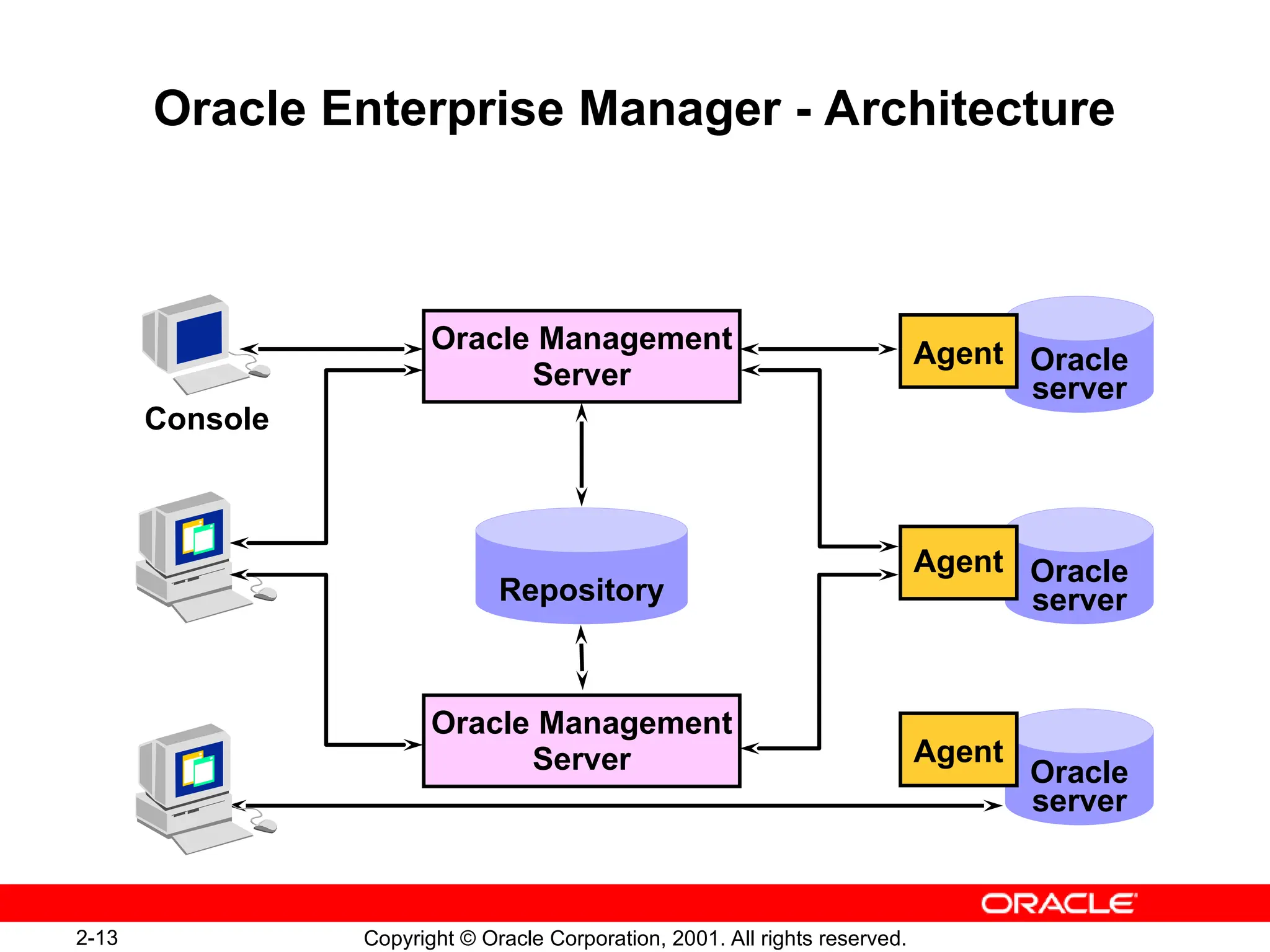
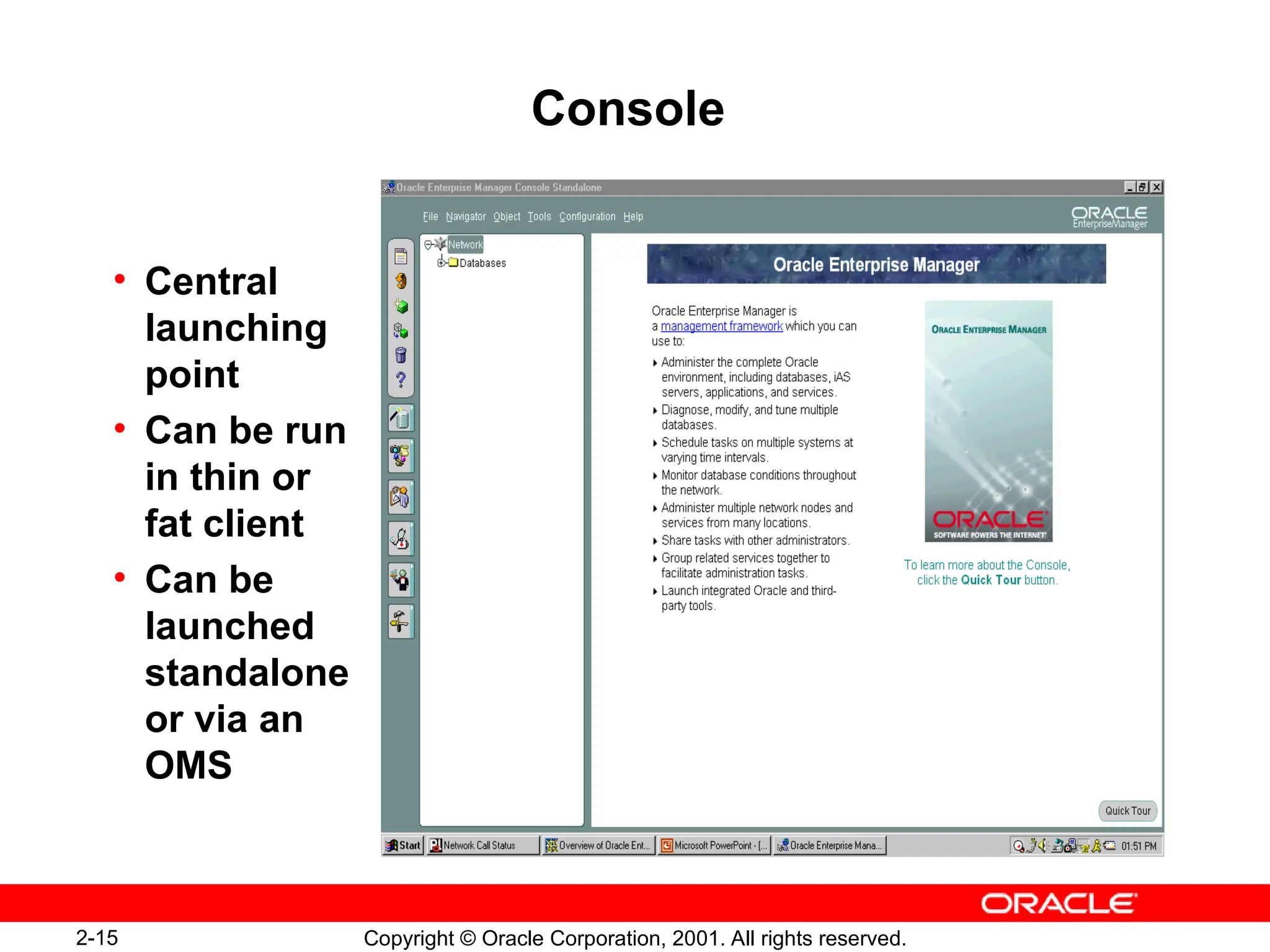
The document outlines essential database administration tools for Oracle, including the Oracle Universal Installer, SQL*Plus, and Oracle Enterprise Manager. It explains their functionalities, such as installing software components, managing databases, and providing centralized system management. The content emphasizes the importance of these tools in database creation, interaction, and administration.